Abstract
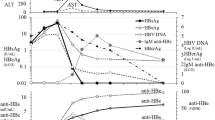
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infections are frequently associated with exacerbations of hepatitis of which the majority are due to reactivation of viral activity. Variation in a viral genome during persistent infection has been shown to be a possible cause for reactivation. In this study, we have found another possible mechanism. HBV in a patient with repeated exacerbations was isolated at six different times during follow-up and was characterized by polymerase chain reaction and DNA sequencing. The first episode of exacerbation was accompanied with increased replication of an HBV strain. The second episode, however, was associated with the sudden appearance of an HBV strain that displayed enough sequence variations to warrant the designation as a separate strain. The results suggested a reinfection event by another independent HBV. Subsequent exacerbations were then related to coactivation of both viral stains. These observations provide significant information toward understanding the acute exacerbations of chronic type B hepatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carmen WF, Thomas HC. Genetic variation in hepatitis B virus. Gastroenterology 102:711–719;1992.
Chen DS, Lai MY, Sung JL. Anti-HBs reactivity in hepatitis B surface antigen positive serum samples: With special emphasis on heterotypic antibody. J Formosan Med Assoc 81:1357–1364;1982.
Chen DS. Acute viral hepatitis in a hyperendemic area of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: The experience from Taiwan. In: Oda T, Okuda K, eds. New Trends in Hepatology. Tokyo, Medical Tosho, 60–66;1986.
Chen DS. Hepatitis B virus infection, its sequelae, and prevention in Taiwan. In: Okuda K, Ishak KG, eds. Neoplasms of the Liver. Tokyo, Springer, 71–80;1987.
Chen JY, Harrison TJ, Lee SC, Chen DS, Zukerman AJ. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis by hybridization with subgenomic DNA fragments. Hepatology 8:518–523;1988.
Davis GL, Hoofnagle JH, Waggoner JG. Spontaneous reactivation of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology 86:230–235;1984.
Foutch PG, Carey WD, Tabor E, et al. Concomitant hepatitis B surface antigen and antibody in thirteen patients. Ann Intern Med 99:460–463;1983.
Girones R, Miller RH. Mutation rate of the hepadnavirus genome. Virology 170:595–597;1989.
Hahn BH, Shaw GM, Taylor ME, et al. Genetic variation in HTLV-III LAV over time in patients with AIDS or at risk for AIDS. Science 232:1548–1553;1986.
Hoofnagle JH, Gerety RJ, Smallwood LA, Barker LF. Subtyping of hepatitis B surface antigen and antibody by radioimmunoassay. Gastroenterology 72:290–296;1977.
Hoofnagle JH, Dusheiko GM, Seeff LB, Jones EA, Waggoner JG, Bales ZB. Seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to antibody in chronic type B hepatitis. Ann Intern Med 94:744–748;1981.
Kaneko S, Miller RH, Feinstone SM, Unoura M, Kobayashi K, Hattori N, Purcell RH. Detection of serum hepatitis B virus DNA in patients with chronic hepatitis using the polymerase chain reaction assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:312–316;1989.
Koike K, Iino S, Kurai K, Mitamura K, Endo Y, Oka H. IgM anti-HBc in anti-HBe-positive chronic type B hepatitis with acute exacerbations. Hepatology 7:573–576;1987.
Koziol DE, Alter HJ, Holland PV. The development of HBsAg-positive hepatitis despite the previous existence of antibody to HBsAg. J Immunol 117:2260–2262;1976.
Kurai K, Iino S, Koike K, Mitamura K, Endo Y, Oka H. Pre-S2 antigen in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A new marker for HBV replication. In: Zuckerman AJ, ed. Viral Hepatitis and Liver Disease. New York, Liss, 284–286;1988.
Lai MY, Chen DS, Lee SC, Su IJ, Yang PM, Hsu HC, Sung JL. Reactivation of hepatitis B virus in anti-HBe-positive chronic active type B hepatitis: Molecular and immunohistochemical studies. Hepatogastroenterology 35:17–21;1988.
Lemon SM, Gates NL, Simms TE, Bancroft WH. IgM antibody to hepatitis B core antigen as a diagnostic parameter of acute infection with hepatitis B virus. J Infect Dis 143:803–809;1981.
Liaw YF, Tai DL, Chu CM, Pao CC, Chen TJ. Acute exacerbations in chronic type B hepatitis: Comparison between HBeAg and antibody-positive patients. Hepatology 7:20–23;1987.
Liaw YF, Pao CC, Chu CM, Sheen IS, Huang MJ. Changes of serum hepatitis B virus DNA in two types of clinical events preceding spontaneous hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion in chronic type B hepatitis. Hepatology 7:1–3;1987.
Lutley R, Petursson G, Pallisson PA, Gerogsson G, Klein J, Nathanson N. Antigenic drift in visna: Virus variation during long-term infection of Iceland sheep. J Gen Virol 64:1433–1440;1983.
Maeland A, Skaug K, Storvold G, Kittelsen P. Reactivation of hepatitis B (letter). Lancet i:1083;1989.
Milich DR, Thornton GB, Neurath AR, Kent SB, Michel ML, Tiollais P, Chisari FV. Enhanced immunogenicity of the pre-S region of hepatitis B surface antigen. Science 228:1195–1199;1985.
Nishioka K, Levin AG, Simons MJ. Hepatitis B antigen, antigen subtypes, and hepatitis B antibody in normal subjects and patients with liver diseases. Bull WHO 52:293–300;1975.
Okamoto H, Yotsumoto S, Akahane Y, Yamanaka T, Miyazaki Y, Sugai Y, Tsuda F, Tanaka T, Miyakawa Y, Mayumi M. Hepatitis B viruses with pre-core regions defect prevail in persistently infected hosts along with seroconversion to antibody against e antigen. J Virol 64:1298–1303;1990.
Ono Y, Onda H, Sasada R, Igarashi K, Sugime Y, Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res 11:1747–1757;1983.
Pasek M, Goto T, Gilbert W, Zink B, Schaller H, Mackay P, Leadbetter G, Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression inE. coli. Nature 282:575–580;1979.
Rizzetto M, Hoyer B, Canese MG, Shih JWK, Purcell RH, Gerin JL. Delta agent: Association of delta agent with hepatitis B surface antigen and RNA in serum of delta-infected chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:6124–6128;1980.
Saiki RK, Gelfand DH, Stoffel S, Scharf SJ, Higuchi R, Horn GT, Mullis KB, Ehrlich HA. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 239:487–491;1988.
Salinovich O, Payne SL, Montelaro RC, Hussan KA, Issel CJ, Schnorr KL. Rapid emergence of novel antigenic and genetic variants of equine infectious anemia virus during persistent infection. J Virol 57:71–80;1986.
Sjogren M, Hoofnagle JH. Immunoglobulin M antibody to hepatitis B core antigen in patients with chronic type B hepatitis. Gastroenterology 89:252–258;1985.
Smedile A, Dentico P, Zanetti A, Sagnelli E, Nordenfelt E, Actis GC, Rizzetto M. Infection with delta agent in chronic HBsAg carriers. Gastroenterology 81:992–997;1981.
Sung JL, Chen DS. Geographic distribution of the subtype of hepatitis B surface antigen in Chinese. Gastroenterol Jpn 12:58–63;1977.
Tsai SL, Chen PJ, Lai MY, Yang PM, Sung JL, Huang JH, Hwang LH, Chang TH, Chen DS. Acute exacerbations of chronic type B hepatitis are accompanied by increased T cell response to hepatitis B core and e antigen. J Clin Invest 89:87–96;1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P.J., Chen, M.L. & Chen, D.S. A viral mechanism in acute exacerbations of chronic type B hepatitis: Hepatitis B virus reinfection and subsequent reactivation of two viral strains. J Biomed Sci 1, 7–12 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02258334
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02258334