Summary
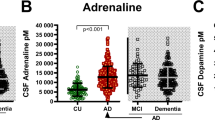
We measured the concentrations of total (conjugated and unconjugated) monoamines (dopamine, DA; norepinephrine, NE) and monoamine metabolites (homovanillic acid, HVA; 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenyleneglycol, MHPG; 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, 5-HIAA) in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), using HPLC-ECD in 11 patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) or senile dementia of the Alzheimer type (SDAT), 17 patients with vascular dementia of the Binswanger type (VDBT), and 15 controls. In AD/SDAT, there was a significant decrease in the DA concentration and a significant increase in the MHPG concentration. The average NE concentration was not altered, but significantly increased with the progression of intellectual disability. There were no significant changes in HVA and 5-HIAA concentrations. Patients with VDBT showed a significant increase in the DA concentration and a significant decrease in HVA and 5-HIAA concentrations. The DA concentrations increased significantly with the progression of dementia and ventricular enlargement. These results indicate that the noradrenergic and dopaminergic system in particular are altered in AD/SDAT, while the dopaminergic and serotonergic systems are mainly involved in VDBT.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolfsson R, Gottfries CG, Ross BE, Winblad B (1979) Changes in the brain catecholamines in patients with dementia of Alzheimer type. Br J Psychiatry 135: 216–223
American Psychiatric Association (1987) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 3rd ed (revised). APA, Washington DC, pp 21–23
Argentiero V, Tavolato B (1980) Dopamine (DA) and serotonin metabolic levels in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in Alzheimer's presenile dementia under basic conditions and after stimulation with cerebral cortex phospholipids (BC-PL). J Neurol 224: 53–58
Bareggi SR, Franceschi M, Bonini L, Zecca L, Smirne S (1982) Decreased CSF concentrations of homovanillic acid and α-aminobutyric acid in Alzheimer's disease. Age- or disease-related modification?. Arch Neurol 39:709–712
Bartholini G, Pletscher A, Tissot R (1966) On the origin of homovanillic acid in the cerebrospinal fluid. Experientia 22: 609–610
Björklund A, Divac I, Lindvall O (1978) Regional distribution of catecholamines in monkey cerebral cortex, evidence for a dopaminergic innervation of the primate prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Lett 7: 115–119
Bowen DD, Sims NR, Benton JS, Curzon G, Davison AN (1981) Treatment of Alzheimer's disease: a cautionary note. N Engl J Med 305: 1016
Bråne G, Gottfries CG, Blennow K, Karlsson I, Lekman A, Parnetti L, Svennerholm L, Wallin A (1989) Monoamine metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid and behavioral ratings in patients with early and late onset Alzheimer dementia. Alzheimer Disease and Associated Disorders 3: 148–156
Brun A, Gustafson L (1976) Distribution of cerebral degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. A clinicopathological study. Arch Psychiat Nervenkr 223:15–33
Carlsson A (1983) Changes in neurotransmitter systems in the aging brain and in Alzheimer's disease. In: Reisberg B (ed) Alzheimer's disease. Macmillan, New York, pp 100–106
Christensen A-L (1990) Neuropsychological approach to Alzheimer's dementia. In: Hasegawa K, Homma A (eds) Psychogeriatrics. Biomedical and social advances. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam Princetom Hong Kong Tokyo Sydney, pp 169–174
Cross AJ, Grow TJ, Perry EK, Perry RH, Blessed G, Tomlinson BE (1981) Reduced dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity in Alzheimer's disease. Br Med J 282: 93–94
Cross AJ, Grow TJ, Johnson JA, Joseph MH, Perry EK, Perry RH, Blessed G, Tomlinson BE (1983) Monoamine metabolism in senile dementia of Alzheimer type. J Neurol Sci 60:383–392
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-Mental State”. A practical method of grading. The cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Gottfries CG, Gottfries I, Roos BE (1969) Homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleactic acid in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with senile dementia, presenile dementia and parkinsonism. J Neurochem 16: 1341–1345
Gottfries CG, Gottfries I, Roos BE (1970) Homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid cerebrospinal fluid related to rated mental and motor impairment in senile and presenile dementia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 46: 99–105
Guard O, Renaud B, Chazot G (1976) Métabolisme cérébral de la dopamine et de la sérotonine au cours des maladies d'Alzheimer et de Pick. Etude dynamique par le test au probénécide. Encephale 2: 293–303
Hachinski VC, Iliff LD, Zilhka E, Du Boulay GH, McAllister VL, Marshall J, Ross Russell RW, Symon L (1975) Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol 32: 632–637
Hasegawa K, Inoue K, Moriya K (1974) An investigation of dementia rating scale for the elderly. Clin Psychiatry 16: 965–969 (in Japanese)
Jagust WJ, Budinger TF, Reed BR (1987) The diagnosis of dementia with single photon emission computed tomography. Arch Neurol 44:258–262
Kopin IJ, Gordon EK, Jimerson DC, Polinsky RJ (1983) Relation between plasma and cerebrospinal fluid levels of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol. Science 219: 73–75
Lotz PR, Ballinger WE Jr, Quisling RG (1986) Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy: CT spectrum and pathologic correlation. AJNR 7:817–822
Mann DMA, Lincoln J, Yates PO, Stamp JE, Toper S (1980) Changes in the monoamine containing neurons of the human CNS in senile dementia. Br J Psychiatry 136: 533–541
Mann DMA, Yates PO, Hawkes J (1982) The noradrenergic system in Alzheimer and multi-infarct dementias. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45: 113–119
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 34: 939–944
Meese W, Lanksch W, Wende S (1976) Cerebral atrophy and computerized tomography-Aspects of a qualitative and quantitative analysis. In: Lanksch W, Kazner E (eds) Cranial computerized tomography. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 222–232
Molliver ME, Grzanna R, Lidov HGW, Morrison JH, Olschowka JA (1982) Monoamine systems in the cerebral cortex. In: Chan-Palay V, Palay B (eds) Cytochemical methods in neuroanatomy. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 255–277
Palmer AM, Sims NR, Bowen DM, Neary D, Palo J, Wikstrom J, Davison AN (1984) Monoamine metabolite concentrations in lumbar cerebrospinal fluid of patients with histologically verified Alzheimer's dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47:481–484
Parnetti L, Gottfries J, Karlsson I, Långström G, Gottfries C-G, Svennerholm L (1987) Monoamines and their metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with senile dementia of Alzheimer type using high performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Acta Psychiatr Scand 75: 542–548
Pastuszko A, Wilson DF, Ercińska M (1982) Neurotransmitter metabolism in rat brain synaptosomes: effect of anoxia and pH. J Neurochem 38: 1657–1667
Raskind MA, Peskind ER, Halter JB, Jimerson DC (1984) Norepinephrine and MHPG levels in CSF and plasma in Alzheimer's disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 41: 343–346
Román GC (1987) Senile dementia of the Binswanger type. A vascular form of dementia in the elderly. JAMA 258: 1782–1788
Siesjö BK (1978) Brain energy metabolism and catecholaminergic activity in hypoxia, hypercapnia and ischemia J Neural Transm 14[Suppl]: 17–22
Slivka A, Brannan TS, Weinberger J, Knott PJ, Cohen G (1988) Increase in extracellular dopamine in the striatum during cerebral ischemia: a study utilizing cerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem 50:1714–1718
Smirne S, Franceschi M, Truci G, Camerlingo M, Pirola R, Ferini-Strambi L, Bareggi SR (1985) Homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid modifications in CSF of patients with stroke and multi-infarct dementia. Stroke 16: 1003–1005
Soininen H, MacDonald E, Rekonen M, Riekkinen PJ (1981) Homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with senile dementia of Alzheimer type. Acta Neurol Scand 64: 101–107
Tomlinson BE, Irving D, Blessed G (1981) Cell loss in the locus coeruleus in senile dementia of Alzheimer type. J Neurol Sci 49: 419–428
Tyce GM, Rorie DK, Byer DE, Danielson DR (1985) Free and conjugated amines in human lumbar cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurochem 49: 322–324
Weinberger J, Cohen G (1982) The differential effect of ischemia on the active uptake of dopamine, γ-aminobutyric acid, and glutamate by brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem 38: 963–968
Wester P, Bergström U, Eriksson A, Gezelius C, Hardy J, Winblad B (1990) Ventricular cerebrospinal fluid monoamine transmitter and metabolite concentrations reflect human brain neurochemistry in autopsy cases. J Neurochem 54: 1148–1156
Winblad B, Adolfsson R, Carlsson A, Gottfries CG (1982) Biogenic amines in brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. In: Corkin, S, Davis KL, Growdon JH, Usolin E, Wurtman RJ (eds) Alzheimer's disease: a report of progress in research. Raven Press, New York, pp 25–33
Wolfe N, Linn R, Babikian VL, Knoefel JE, Albert ML (1990) Frontal systems impairment following multiple lacunar infarcts. Arch Neurol 47: 129–132
Wood PL, Etienne P, Lal S, Gauthier S, Cajal S, Nair NPV (1982) Reduced lumbar CSF somatostantin levels in Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci 31: 2073–2079
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tohgi, H., Ueno, M., Abe, T. et al. Concentration of monoamines and their metabolites in the cerebrospinal fluid from patients with senile dementia of the Alzheimer type and vascular dementia of the Binswanger type. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 4, 69–77 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02257623
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02257623