Abstract
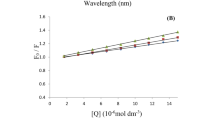
Ethanol effects on warfarin binding to human serum albumin (HSA) have been studied by equilibrium dialysis and fluorescence methods at pH 7.4 in phosphate-buffered saline at 37°C. In the presence of various amounts of ethanol fluorescence intensity of bound warfarin decreased significantly but this intensity reduction was not solely from displacement of bound warfarin from HSA. By comparing fluorescence and equilibrium dialysis data we concluded that fluorescence intensity reduction of warfarin was mainly the result of changes in the surrounding environment of the warfarin binding site by ethanol interaction with HSA and that displacement of bound warfarin was not significant compared to the fluorescence intensity changes. The dissociation constant of warfarin binding to HSA decreased with an increasing amount of ethanol. From the changes in fluorescence intensity upon warfarin binding to HSA with the presence of ethanol ranging from 0 to 5.0% the following dissociation constants (Kd) were determined: 0% ethanol 5.39 ± 0.2 µM, 0.1% ethanol 5.86 ± 0.1 µM, 0.3% ethanol 5.83 ± 0.2 µM, 0.5% ethanol 6.76 ± 0.1 µM, 1% ethanol 7.01 ± 0.1 µM, 3% ethanol 9.9 ± 0.7 µM, 5% ethanol 13.01 ± 0.1 µM. From the equilibrium dialysis with the same ranges of ethanol presence the following Kd values were obtained: 0% ethanol 6.62 ± 1.6 µM, 0.1% ethanol 6.81 ± 1.1 µM, 0.3% ethanol 8.26 ± 2.5 µM, 0.5% ethanol 8.86 ± 1.9 µM, 1% ethanol 11.01 ± 4.2 µM, 3% ethanol 20.75 ± 2.4 µM, 5% ethanol 21.67 ± 2.2 µM. The results suggest that warfarin bound to HSA was displaced by ethanol. These data indicate that ethanol influence on warfarin binding to HSA may alter the pharmacokinetics of warfarin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams WL. Potential for adverse drug-alcohol interactions among retirement community residents. J Am Geriatr Soc 43:1021–1025;1995.
Avdulov NA, Chochina SV, Daragan VA, Schroeder F, Mayo KH, Wood WG. Direct binding of ethanol to bovine serum albumin a fluorescent and 13C NMR multiplet relaxation study. Biochemistry 35:340–347;1996.
Avdulov NA, Wood WG, Harris RA. Effects of ethanol on structural parameters of rat brain membranes: Relationship to genetic differences in ethanol sensitivity. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 18:53–59;1994.
Chakrabarti SK. Cooperativity of warfarin binding with human serum albumin induced by free acid anion. Biochem Pharmacol 27:739–743;1978.
Deitrich RA, Dunwiddie TV, Harris RA, Erwin VG. Mechanism of action of ethanol: Initial central nervous system actions. Pharmacol Rev 41:489–537;1989.
Garten S, Wosilait WD. Comparative study of the binding of coumarin anticoagulants and serum albumins. Biochem Pharmacol 20:1661–1668;1971.
Harder S, Thurman P, Clinically important drug interactions with anticoagulants. An update. Clin Pharmacokinet 30:416–444;1996.
He XM, Carter DC. Atomic structure and chemistry of human serum albumin. Nature 358;209–215;1992.
Jones AW. The drunkest drinking driver in Sweden: Blood alcohol concentration 0.545%, w/v. J Stud Alcohol 60:400–406;1999.
Larsen FG, Larsen CG, Jakobsen P, Brodersen R. Interaction of warfarin with human serum albumin. Mol Pharmacol 27:263–270;1984.
Li C, Peoples RW, Weight FF. Alcohol action on a neuronal membrane receptor: Evidence for a direct interaction with the receptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8200–8204;1994.
Lubas B, Soltysik-Rasek M, Lesniewska I. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance study of the association of monovalent and divalent alcohols with bovine serum albumin. Biochemistry 18:4943–4951;1979.
Maclaren R, Wachsman BA, Swift DK, Kuhl DA. Warfarin resistance associated with intravenous lipid administration: Discussion of propofol and review of the literature. Pharmacotherapy 17:1331–1337;1997.
Maes V, Engelborghs Y, Hoebeke J, Maras Y, Vercruysse A. Fluorimetric analysis of the binding of warfarin to human serum albumin. Equilibrium and kinetic study. Mol Pharmacol 21:100–107;1982.
Ogiso T, Iwaki M, Konishi Y. Effect of furosemide on plasma clearance, anticoagulant effect and protein binding of warfarin in rats. J Pharmacobiodyn 5:829–840;1982.
O'Reilly RA, Kowitz PE. Studies on the coumarin anticoagulant drugs: Interaction of human plasma albumin and warfarin sodium. J Clin Invest 46:829–837;1967.
Orr A, Ivanova VS, Bonner WM. ‘Water-bug’ dialysis technique. Biotechniques 19/2:204;1995.
Pinkerton TC, Koeplinger KA. Determination of warfarin-human serum albumin protein binding parameters by an improved Hummel-Dreyer high-performance liquid chromatographic method using internal surface reversed-phase columns. Anal Chem 62:2114–2122;1990.
Sioris LJ, Weibert RT, Pentel PR. Potentiation of warfarin anticoagulation by sulfisoixazole. Arch Intern Med 140:546–547;1980.
Slater SJ, Cox KJA, Lombardi JV, Ho C, Kelly MB, Rubin E, Stubbs CD. Inhibition of protein kinase C by alcohols and anaesthetics. Nature 364:82–84;1993.
Sudlow G, Birkett DJ, Wade DN. The characterization of two specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol Pharmacol 11:824–832;1975.
Sudlow G, Birkett DJ, Wade DN. Further characterization of specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol Pharmacol 12:1052–1061;1976.
Taira Z, Terada H. Specific and non-specific ligand binding to serum albumin. Biochem Pharmacol 34:1995–2005;1985.
Wilting J, van der Giesen F, Janssen LHM, Weiderman MM, Otagiri M. The effect of albumin conformation on the binding of warfarin to human serum albumin. J Biol Chem 255:3032–3037;1980.
Yacobi A, Udall JA, Levy G. Serum protein binding as a determinant of warfarin body clearance and anticoagulant effect. Clin Pharmacol Ther 19:552–558;1976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ha, CE., Petersen, C.E., Park, D.S. et al. Investigations of the effects of ethanol on warfarin binding to human serum albumin. J Biomed Sci 7, 114–121 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256617
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02256617