Abstract
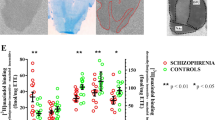
The specific binding of the D2-dopamine receptor antagonist radioligand [3H] raclopride was quantitated in the postmortem caudate and frontal cortex from schizophrenic suicide victims and control subjects. In schizophrenic suicides the density of binding sites (Bmax) was higher (40%,P<0.05) in the caudate, whereas it did not change in the cortex as compared to those in controls. The apparent dissociation constants (K d ) were also found increased both in caudate (24%) and cortex (75%) from schizophrenics, but these apparent decreases in receptor affinity did not reach statistical significance. The mean Bmax value in drug-free schizophrenic suicides (n=3) did not differ from the Bmax value in neuroleptic drug-treated schizophrenics (n=7) but it was found increased in respect to control subjects (n=9). No differences in [3H] raclopride binding were observed between non-schizophrenic suicide victims (n=4) and matched controls (n=4), suggesting that the modifications of D2-dopamine receptors in schizophrenia are not related to suicide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker GB, Greenshaw AJ (1989) Effects of long-term administration of antidepressants and neuroleptics on receptors in the central nervous system. Cell Mol Nerobiol 9:1–44
Breier A, Astrachan BM (1984) Characterization of schizophrenic patients who commit suicide. Am J Psychiatry 141:206–209
Caldwell CB, Gottesman II (1990) Schizophrenics kill themselves too: a review of risk factors for suicide. Schizophr Bull 16:571–589
Carlsson A (1988) The current status of the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 1:179–186
Cross AJ, Crow TJ, Owen F (1981) [3H]flupenthixol binding in postmortem brains of schizophrenics: evidence for a selective increase in dopamine D2 receptors. Psychopharmacology 74:122–124
Cross AJ, Crow TJ, Ferrier IN, Johnstone EC, McCreadie RM, Owen F, Owens DGC, Poulter M (1983) Dopamine receptor changes in schizophrenia in relation to the disease process and movement disorder. J Neural Transm Suppl 18:265–272
De Lean A, Munson P J, Rodbard D (1978) Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol 235:E97-E102
Farde L, Wiesel FA, Stone-Elander S, Halldin C, Nordström AL, Hall H, Sedvall G (1990) D2 dopamine receptors in neurolepticnaive schizophrenic patients. A positron emission tomography study with [11C]raclopride. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:213–219
Hall H, Wedel I, Halldin C, Kopp J, Farde L (1990) Comparison of the in vitro receptor binding properties of N- [3H]methylspiperone and [3H]raclopride to rat and human brain membranes. J Neurochem 55:2048–2057
Joyce JN, Lexow N, Bird E, Winokur A (1988) Organization of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in human striatum: receptor autoradiographic studies in Huntington's disease and schizophrenia. Synapse 2:546–557
Kornhuber J, Riederer P, Reynolds GP, Beckmann H, Jellinger K, Gabriel E (1989) [3H]Spiperone binding sites in post-mortem brains from schizophrenic patients: relationship to neuroleptic drug treatment, abnormal movements, and positive symptoms. J Neural Transm 75:1–10
Köhler C, Hall H, Ögren SO, Gawell L (1985) Specific in vitro and in vivo binding of [3H]raclopride. A potent substituted benzamide drug with high affinity for dopamine D2 receptors in the rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 34:2251–2259
Lee T, Seeman P (1980) Elevation of brain neuroleptic/dopamine receptors in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 137:191–197
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin Phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mackay AVP, Bird ED, Spokes EG, Rossor M, Iversen LL, Creese I, Snyder SH (1980) Dopamine receptors and schizophrenia: drug effect or illness?. Lancet ii:915–916
Martinot JL, Peron-Magnan P, Huret JD, Mazoyer B, Baron JC, Boulenger JP, Loc'h C, Maziere B, Caillard V, Loo H, Syrota A (1990) Striatal D2 dopaminergic receptors assessed with positron emission tomography and [76Br] bromospiperone in untreated schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 147:44–50
Martinot JL, Paillere-Martinot ML, Loc'h C, Hardy P, Poirier MF, Mazoyer B, Beaufils B, Maziere B, Allilaire JF, Syrota A (1991) The estimated density of D2 striatal receptors in schizophrenia. A study with positron emission tomography and76Br-Bromolisuride. Br J Psychiatry 158:346–350
Meana JJ, Barturen F, Garcia-Sevilla JA (1992) α2-Adrenoceptors in the brain of suicide victims: increased receptor density associated with major depression. Biol Psychiatry 31:471–490
Mita T, Hanada S, Nishino N, Kuno T, Nakai H, Yamadori T, Mizoi Y, Tanaka C (1986) Decreased serotonin S2 and increased dopamine D2 receptors in chronic schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 21:1407–1414
Motulsky HJ, Ransnas LA (1987) Fitting curves to data using nonlinear regression: a practical and nonmathematical review. FASEB J 1:365–374
Munson PJ, Rodbard D (1980) LIGAND: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem 107:220–239
Roy A (1982) suicide in chronic schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 141:171–177
Sedvall G (1990) PET imaging of dopamine receptors in human basal ganglia: relevance to mental illness. TINS 13:302–308
Seeman P (1987) Dopamine receptors and the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Synapse 1:133–152
Seeman P, Niznik HB (1990) Dopamine receptors and transporters in Parkinson's disease and schizophrenia. FASEB J 4:2737–2444
Toru M, Watanabe S, Shibuya H, Nishikawa T, Noda K, Mitsushio H, Ichikawa H, Kurumaji A, Takashima M, Mataga N, Ogawa A (1988) Neurotransmitters, receptors and neuropeptides in post-mortem brains of chronic schizophrenic patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand 78:121–137
Winokur G, Tsuang M (1975) The Iowa 500:Suicide in mania, depression, and schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 132:650–651
Wong DF, Wagner Jr HN, Tune LE, Dannals RF, Pearlson GD, Links JM, Tamminga CA, Broussolle EP, Ravert HT, Wilson AA, Toung JKT, Malat J, Williams JA, O'Tuama LA, Snyder SH, Kuhar MJ, Gjedde A (1986) Positron emission tomography reveals elevated D2 dopamine receptors in drug-naive schizophrenics. Science 234:1558–1563
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruiz, J., Gabilondo, A.M., Javier Meana, J. et al. Increased [3H] raclopride binding sites in postmortem brains from schizophrenic violent suicide victims. Psychopharmacology 109, 410–414 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247716
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247716