Abstract
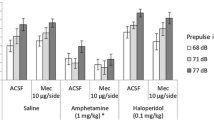
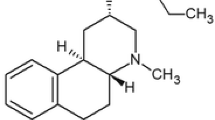
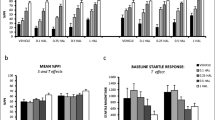
The effect of various typical (haloperidol) and atypical (clozapine, raclopride, remoxipride) antipsychotics on phencyclidine (PCP)-induced disruption of sensorimotor gating was tested in rats using an acoustic startle paradigm. Clozapine (4–40 µmol/kg), haloperidol (1–5 µmol/kg) and raclopride (1–12 µmol/kg) failed to reverse PCP-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response. In contrast, remoxipride (12–60 µmol/kg) caused a dose-dependent block of this effect. PCP-induced disruption of PPI is a widely accepted animal model of a corresponding behavioural deficit observed in schizophrenia although little evidence has been presented that it is in fact sensitive to antipsychotic agents. The present results indicate that remoxipride behaves in a unique way in this model compared to clozapine, haloperidol and raclopride.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E (1991) Clozapine is a potent and selective muscarinic antagonist at the five cloned human muscarinic receptors expressed in CHO-K1 cells, Eur J Pharmacol 192:205–206
Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) Sensorimotor gating and schizophrenia: human and animal model studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:181–188
Braff DL, Grillon C, Geyer MA (1992) Gating and habituation of the startle reflex in schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:206–215
Canton H, Verriele L, Colpaert FC (1990) Binding of typical and atypical antipsychotics to 5-HT1C and 5-HT2 sites: clozapine potently interacts with 5-HT1C sites. Eur J Pharmacol 191:93–96
Deutch AY, Lee MC, Iadarola MJ (1992) Regional specific effects of atypical antipsychotic drugs on striatal fos expression: the nucleus accumbens shell as a locus of antipsychotic action. Mol Cell Neurosci 3:332–341
Erard R, Luisada PV, Peele R (1980) The PCP psychosis: prolonged intoxication or drug precipitated functional illness? J Psychedel Drugs 12:235–245
Garey RA, Heath RG (1976) Effects of phencyclidine on the uptake of3H catecholamines by rat striatal and hypothalamic synaptosomes. Life Sci 18:1105–1110
Hoffman HS, Ison JR (1980) Reflex modification in the domain of startle: I. Some empirical findings and their implications for how the nervous system processes sensory input. Psychol Rev 2:175–189
Jackson DM, Mohell N, Bengtsson A, Malmberg Å (1993) What are atypical neuroleptics and how do they work? In: Brunello N, Mendlewicz J, Racagni G (eds) New generation of antipsychotic drugs: novel mechanisms of action, vol 4. Int Acad Biomed Drug Res, Basel Karger, pp 27–38
Javitt DC, Zukin SR (1991) Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 148:1301–1308
Keith VA, Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1991) Failure of haloperidol to block the effects of phencyclidine and dizocilpine on prepulse inhibition of startle. Biol Psychiatry 30:557–566
Kemp JA, Foster AC, Wong EHF (1987) Non-competitive antagonists of excitatory amino acid receptors. Trends Neurosci 10:294–298
Köhler C, Hall H, Ögren SO, Gawell L (1985) Specific in vitro and in vivo binding of3H raclopride. A potent substituted benzamide drug with high affinity for dopamine D2 receptors in the rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 34:2251–2259
Köhler C, Hall H, Magnusson O, Lewander T, Gustafsson K (1990) Biochemical pharmacology of the atypical neuroleptic remoxipride. Acta Psychiatr Scand 82 [Suppl 358]:27–36
Malmberg Å, Jackson DM, Eriksson A, Mohell N (1993) Unique binding characteristics of antipsychotic agents interacting with human dopamine D2A, D2B, and D3 receptors. Mol Pharmacol 43:749–754
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA (1989) Effects of phencyclidine and phencyclidine biologs on sensorimotor gating in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 2:299–308
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1988) Dopaminergic stimulation disrupts sensorimotor gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology 94:507–514
Miller CL, Bickford PC, Luntz-Leybman V, Adler LE, Gerhardt GA, Freedman R (1992) Phencyclidine and auditory sensory gating in the hippocampus of the rat. Neuropharmacology 31:1041–1048
Mohell N, Sällemark M, Rosqvist S, Malmberg 0A, Högberg T, Jackson DM (1993) Binding characteristics of remoxipride and its metabolites to dopamine D2 and D3 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 238:121–125
Ögren SO, Hall H, Köhler C, Magnusson O, Lindbom L, Ängeby K, Florvall L (1984) Remoxipride, a new potential antipsychotic compound with selective antidopaminergic actions in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 102:459–474
Peng RY, Mansbach RS, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) A D2 dopamine receptor agonist disrupts sensorimotor gating in rats: implications for dopaminergic abnormalities in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 3:211–218
Schwartz JC, Giros B, Martres MP, Sokoloff P (1993) Multiple dopamine receptors as molecular targets for antipsychotics. In: Brunello N, Mendelewicz J, Racagni G (eds) New generation of antipsychotic drugs: novel mechanisms of action, Vol 4. Int Acad Biomed Drug Res, Basel, pp 1–14
Shaikh S, Collier D, Kerwin RW, Pilowsky LS, Gill M, Xu W-M, Thornton A (1993) Dopamine D4 receptor subtypes and response to clozapine. Lancet 341:116
Sibley DR, Monsma FJ (1992) Molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Trends Pharm Sci 13:61–69
Snell LD, Mueller ZL, Gannon RL, Silverman PB, Johnson KM (1984) A comparison between classes of drugs having phencyclidine-like behavioral properties on dopamine efflux in vitro and dopamine metabolism in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 231:261–269
Snell LD, Yi SJ, Johnson KM (1988) Comparison of the effects of MK-801 and phencyclidine on catecholamine uptake and NMDA-induced norepinephrine release. Eur J Pharmacol 145:223–226
Snyder SH (1990) The dopamine connection. Nature 347:121–122
Sokoloff P, Giros B, Martres MP, Bouthenet ML, Schwartz JC (1990) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as target for neuroleptics. Nature 347:146–151
Swerdlow NR, Keith VA, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1991) Effects of spiperone, raclopride, SCH 23390 and clozapine on apomorphine inhibition of sensorimotor gating of the startle response in the rat. J Pharmocol Exp Ther 256:530–536
Tamminga CA, Thaker GK, Buchanan R, Kirkpatrick B, Alphs LD, Chase TN, Carpenter WT (1992) Limbic system abnormalities identified in schizophrenia using positron emission tomography with flourodeoxyglucose and neocortical alterations with deficit syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatary 49:522–530
Tricklebank MD, Bristow LJ, Hutson PH (1992) Alternative approaches to the discovery of novel antipsychotic agents. Prog Drug Res 38:299–366
Van Tol HHM, Bunzow JR, Guan HC, Sunahara RK, Seeman P, Niznik HB, Civelli O (1991) Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature 350:610–614
Venables P (1964) Input dysfunction in schizophrenia. In: Maher BA (ed) Progress in experimental personality research. FL Academic Press, Orlando, pp 1–47
Wong EHF, Knight AR, Woodruff GN (1988) [3H]MK-801 labels a site on theN-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel complex in rat brain membranes. J Neurochem 50:274–281
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johansson, C., Jackson, D.M. & Svensson, L. The atypical antipsychotic, remoxipride, blocks phencyclidine-induced disruption of prepulse inhibition in the rat. Psychopharmacology 116, 437–442 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247475
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247475