Abstract
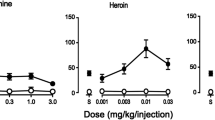
The present study examined the cross-tolerance profiles of associatively and nonassociatively morphine-tolerant rats with analgesia produced by morphine and fentanyl (mu-receptor agonists) and U50,488H (a kappa-receptor agonist). Subjects were given a series of eight morphine injections either paired or unpaired with a distinctive environment and then tested for tolerance using the tail-flick method. Evidence was found that nonassociative morphine tolerance, which was produced using a 6-h interdose interval (IDI), was receptor-specific, i.e. cross-tolerant with analgesia produced by mu-specific, but not kappa-specific drugs. Nonassociative tolerance was characterized by a shift to the right in dose-response curves of 0.32 log units in morphine-tested animals and 0.28 log units in fentanyl-tested animals. Conversely, associative morphine tolerance, which was produced using a 96-h IDI, evidenced a lack of receptor specificity by showing cross-tolerance to the analgesic effects of U50,488H. Associative tolerance was characterized by shifts of 0.42 log units in morphine-tested animals, 0.34 log units in fentanyl-tested animals, and 0.39 log units in U50,488H-tested animals. These results were interpreted as suggesting the mechanisms responsible for associative tolerance differ from those producing nonassociative tolerance. This conclusion is problematic for theories of learned tolerance that assume a unitary set of mechanisms subserving associative and nonassociative tolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker TB, Tiffany ST (1985) Morphine tolerance as habituation. Psychol Rev 92:78–108
Bhargava HN, Ramarao P, Gulati A (1989) Effect of chronic administration of U50488H on tolerance to its pharmacological actions and on multiple opioid receptors in rat brain regions and spinal cord. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251:21–26
Borchard RE, Barnes CD, Eltherington LG (1990) Drug dosage in laboratory animals: a handbook, 3rd edn. Telford Press, New Jersey
Cepeda-Benito A, Tiffany ST (1992) Effect of number of conditioning trials on the development of associative tolerance to morphine. Psychopharmacology 109:172–176
Cepeda-Benito A, Tiffany ST (1995) Role of drug-administration cues in the associative control of morphine tolerance in the rat. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Chang K, Cuatrecasas P (1979) Multiple opiate receptors: enkephalins and morphine bind to receptors of different specificity. J Biol Chem 254:2610–2618
Cohen J, Cohen P (1975) Applied multiple regression/correlational analysis for the behavioral sciences. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillside, New Jersey
Collier HOJ (1984) Cellular aspects of opioid tolerance and dependence. In: Hughes J, Collier HOJ, Rance MJ, Tyers MB (eds) Opioids past, present and future. Taylor and Francis, London, pp 109–125
Cowan A (1981) Simple in vivo tests that differentiate prototype agonsists at opiate receptors. Life Sci 28:1559–1570
Craft RM, Picker MJ, Dykstra LA (1989) Differential cross-tolerance to opioid agonists in morphine-tolerant pigeons responding under a schedule of food presentation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 249:386–393
Domjan M (1993) The principles of learning and behavior, 3rd edn. Brooks/Cole, Pacific Grove, Calif.
Fernandes M, Kluwe S, Coper H (1977) The development of tolerance to morphine in the rat. Psychopharmacology 54:197–201
Fernandes M, Kluwe S, Coper H (1982) Development and loss of tolerance to morphine in the rat. Psychopharmacology 78:234–238
Goudie AJ, Demellweek C (1986) Conditioning factors in drug tolerance. In: Goldberg SR, Stolerman IP (eds), Behavioral analysis of drug dependence. Academic Press, New York, pp 225–285
Johnson SM, Fleming WW (1989) Mechanisms of cellular adaptive sensitivity changes: applications to opioid tolerance and dependence. Pharmacol Rev 41:435–483
Martin WR, Eades CG, Thomson JA, Huppler RE, Gilbert PE (1976) The effects of morphine and nalorphine-like drugs in the nondependent and morphine dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 197:517–532
Maude-Griffin PM, Tiffany ST (1989) Associative morphine tolerance in the rat: examinations of compensatory responding and cross-tolerance with stress-induced analgesia. Behav Neural Biol 51:11–33
Poulos CX, Cappell H (1991) Homeostatic theory of drug tolerance: a general model of physiological adaption. Psychol Rev 98:390–408
Siegel S (1975) Evidence from rats that morphine tolerance is a learned response. J Comp Physiol Psychol 89:498–506
Tiffany ST, Maude-Griffin PM (1988) Tolerance to morphine in the rat: associative and nonassociative effects. Behav Neurosci 102:534–543
Tiffany ST, Maude-Griffin PM, Drobes DJ (1991) The effect of interdose interval on the development of associative and nonassociative tolerance. Behav Neurosci 105:49–61
Tiffany ST, Drobes DJ, Cepeda-Benito A (1992) Contribution of associative and nonassociative processes to the development of morphine tolerance. Psychopharmacology 109:185–190
Trujillo KA, Akil H (1994) Inhibition of opiate tolerance by noncompetitiveN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor agonists. Brain Res 663:178–188
VonVoigtlander PF, Lahti RA, Ludens JH (1983) U50488H: a selective and structurally novel non-mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:7–12
Wood PL (1982) Multiple opiate receptors: support for unique mu, delta and kappa sites. Neuropharmacology 21:487–497
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carter, B.L., Tiffany, S.T. Cross-tolerance of associative and nonassociative morphine tolerance in the rat with mu- and kappa-specific opioids. Psychopharmacology 123, 289–296 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246583
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246583