Abstract
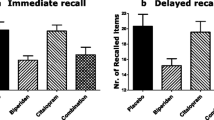
The mixedα 1/α 2 adrenoceptor agonist clonidine has been shown by us previously to impair certain attentional and executive functions in healthy volunteers. The present investigation examines the effects of theα 2 adrenoceptor antagonist idazoxan (IDZ) on cognitive function in patients with dementia of frontal type (DFT). Using a placebo-controlled ABBA design, three DFT patients were given two doses of IDZ and tested on a range of computerised tests of attention, memory and executive function. Idazoxan was found to produce dose-dependent improvements in performance, particularly on tests of planning, sustained attention, verbal fluency and episodic memory. In contrast, IDZ produced deficits in performance on a test of spatial working memory. These results suggest that IDZ may be useful as a putative cognitive enhancer, particularly in patients showing a specific pattern of frontal lobe dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham WC, Delanoy RL, Dunn AJ, Zornetzer SF (1979) Locus coeruleus stimulation decreases deoxyglucose uptake in ipsilateral cerebral cortex. Brain Res 172:387–392
Arnsten AFT, Cai JX (1994) Postsynaptic alpha-2 receptor stimulation improves memory in aged monkeys: indirect effects of yohimbine versus direct effects of clonidine. Neurobiol Aging 14:597–603
Arnsten AFT, Goldman-Rakic PS (1985) Alpha-2 adrenergic mechanisms in prefrontal cortex associated with cognitive decline in aged nonhuman primates. Science 230:1273–1276
Aston-Jones G, Chiang C, Alexinsky T (1991) Discharge of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats and monkeys suggest a role in vigilance. In: Barnes CD, Pompeiano O (eds) Progress in brain research, vol. 88. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp 501–520
Baddeley A (1986) Working memory. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Beckett PJ, Finch L (1982) Theα 1 andα 2-adrenoceptor involvement in the central cardiovascular action of clonidine in the conscious renal hypertensive cat. Eur J Pharmacol 82:155–160
Benton AL (1968) Differential effects of frontal lobe disease. Neuropsychologia 6:53–60
Bricca G, Dontenwill M, Molines A, Feldman J, Belcourt A, Bousquet P (1989) The imidazoline preferring receptor: binding studies in bovine, rat and human brainstem. Eur J Pharmacol 162:1–9
Cohen RM, Semple WE, Gross M, Holcomb HJ, Dowling S, Nordahl TE (1988) Functional localization of sustained attention. Neuropsychiat Neuropsychol Behav Neurol 1:3–20
Coull JT, Middleton HC, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (1995a) Contrasting effects of clonidine and diazepam on tests of working memory and planning. Psychopharmacology 120:311–321
Coull JT, Middleton HC, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (1995b) Clonidine and diazepam have differential effects on tests of attention and learning. Psychopharmacology 120:322–332
Davies DR, Parasuraman R (1982) The Psychology of vigilance. Academic Press, London
Dennis T, L'Heureux R, Carter C, Scatton B (1987) Pre-synapticα 2-adrenoceptors play a major role in the effects of idazoxan on cortical noradrenaline (as measured by in vivo dialysis) in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 241:642–649
De Vos H, Bricca G, De Keyser J, De Backer JP, Bousquet P, Vauquelin G (1994) Imidazoline receptors, non-adrenergic idazoxan binding sites and alpha-2 adrenoceptors in the human central nevous system. Neuroscience 59:589–598
Downes JJ, Roberts AC, Sahakian BJ, Evenden JL, Morris RG, Robbins TW (1989) Impaired extradimensional shift performance in medicated and unmedicated Parkinson's disease: evidence for a specific attentional dysfunction. Neuropsychologia 27:1329–1344
Doxey JC, Roach AG, Smith CFC (1983) Studies on RX781094. A selective and specific antagonist ofα 2 adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol 78:489–505
Elfgren C, Passant U, Risberg J (1993) Neuropsychological findings in frontal lobe dementia. Dementia 4:214–219
Fields RB, van Kammen DP, Peters JL, Rosen J, Van Kammen WB, Nugent A, Stipetic M, Linnoila M (1988) Clonidine improves memory function in schizophrenia independently from change in psychosis: preliminary findings. Schizophr Res 1:417–423
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-Mental State”: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Francis PT, Holmes C, Webster MT, Stratmann GC, Procter AW, Bowen DM (1993) Preliminary neurochemical findings in non-Alzheimer dementia due to lobar atrophy. Dementia 4:172–177
Friedland RP, Koss E, Lerner A, Hedera P, Ellis W, Dronkers N, Ober BA, Jagust WJ (1993) Functional imaging, the frontal lobes and dementia. Dementia 4:192–203
Frith CD (1987) The positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia reflect impairments in the perception and initiation of action. Psychol Med 17:631–648
Gallagher M, Kapp BS, Musty RE, Driscoll PA (1977) Memory formation: evidence for a specific neurochemical system in the amygdala. Science 198:423–425
Glue P, Wilson S, Lawson C, Campling GM, Franklin M, Cowen PJ, Nutt DJ (1991) Acute and chronic idazoxan in normal volunteers: biochemical, physiological and psychological effects. J Psychopharmacol 5:396–403
Gregory CA, Hodges JR (1993) Dementia of frontal type and the focal lobar atrophies. Int Rev Psychiatry 5:397–406
Gustafson L (1993) Clinical picture of frontal lobe degeneration of non-Alzheimer type. Dementia 4:143–148
Jones GMM, Sahakian BJ, Levy R, Warburton DM, Gray JA (1992) Effects of acute subcutaneous nicotine on attention, information processing and short-term memory in Alzheimer's disease. Psychopharmacology 108:485–494
Krystal JH, McDougle CJ, Woods SW, Price LH, Heninger GR, Charney DS (1992) Dose-response relationships for oral idazoxan effects in healthy human subjects: comparison with oral yohimbine. Psychopharmacology 108:313–319
Langer SZ, Cavero I, Massinham R (1980) Recent developments in noradrenergic neurotransmission and its relevance to the mechanism of action of certain antihypertensive agents. Hypertension 2:372–382
Liddle PF (1987) Schizophrenic syndromes, cognitive performance and neurological dysfunction. Psychol Med 17:49–57
Litman RE, Hong WW, Weissman EM, Su T-P, Potter WZ, Pickar D (1993) Idazoxan, anα 2 antagonist, augments fluphenazine in schizophrenic patients: a pilot study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 13:264–267
McNicol D (1972) A primer of signal detection theory. George Allen and Unwin, London
Mair RG, McEntee WJ (1986) Cognitive enhancement in Korsakoff's pyschosis by clonidine: a comparison withl-dopa and ephedrine.Psychopharmacology 88:374–380
Middleton HC, Coull JT, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (1994) Clonidine-induced changes in the spectral distribution of heart-rate variability correlate with performance on a test of sustained attention. J Psychopharmacol 8:1–7
Milner B (1964) Some effects of frontal lobectomy in man. In: Warren JM, Akert K (eds) The frontal granular crotex and behaviour. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 313–331
Neary D (1989) Non-Alzheimer dementia. Curr Opin Neurol Neurosurg 2:457–459
Neary D, Snowden JS, Northern B, Goulding PJ (1988) Dementia of frontal lobe type. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:353–361
Nelson HE (1982) National adult reading test manual. NFER-Nelson, Windsor, Berks
Orrell MW, Sahakian BJ (1991) Dementia of frontal lobe type. Psychol Med 21:553–556
Owen AM, Downes JJ, Sahakian BJ, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1990) Planning and spatial working memory following frontal lobe lesions in man. Neuropsychologia 29:993–1006
Owen AM, Morris RG, Sahakian BJ, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1995a) Double dissociations of memory and executive functions in working memory tasks following frontal lobe excisions, temporal lobe excisions or amygdalo-hippocampectomy in man. Brain (in press)
Owen AM, Sahakian BJ, Semple J, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1995b) Visuo-spatial short-term recognition memory and learning after temporal lobe excisions, frontal lobe excisions or amygdalo-hippocampectomy in man. Neuropsychologia 33:1–24
Robbins TW (1984) Cortical noradrenaline, attention and arousal. Psychol Med 14:13–21
Sahakian BJ, Joyce E, Lishman WA (1987) Cholinergic effects on constructional abilities and on mnemonic processes: a case report. Psychol Med 17:329–333
Sahakian BJ, Morris RGM, Evenden JL, Heald A, Levy R, Philpot M, Robbins TW (1988) A comparative study of visuospatial memory and learning in Alzheimer type dementia and Parkinson's disease. Brain 111:695–718
Sahakian BJ, Jones GMM, Levy R, Gray JA, Warburton DM (1989) The effects of nicotine on attention, information processing, and short-term memory in patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type Br J Psychiatry 154:797–800
Sahakian BJ, Owen AM, Morant NJ, Eagger SA, Boddington S, Crayton L, Crockford HA, Crooks M, Levy R (1993) Further analysis of the cognitive effects of tetrahydroaminoacradine (THA) in Alzheimer's disease: assessment of attentional and mnemonic function using CANTAB. Psychopharmacology: 110:395–401
Sahgal A (1987) Some limitations of indices derived from signal detection theory: evaluation of an alternative index for measuring bias in memory tasks. Psychopharmacology 91:517–520
Sahgal A, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW, Wray CJ, Lloyd S, Cook JH, McKeith IG, Disley JCA, Eagger S, Boddington S, Edwardson JA (1991) Detection of visual memory and learning deficits in Alzheimer's disease using the Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery. Dementia 2:150–158
Schmidt M, Matochik J, Risinger R, Zametkin A, Schouten J, Cohen R, Potter W (1994) Effects of idazoxan on regional brain metabolism. Abstract for American Society for Clinical Pharma-cology and Therapeutics, Spring meeting
Shallice T (1982) Specific impairments in planning. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B298:199–209
Smith AP, Wilson SJ, Glue P, Nutt DJ (1992) The effects and after effects of theα 2-adrenoceptor antagonist idazoxan on mood, memory and attention in normal volunteers. J Psychopharmacol 6:376–381
Stein L, Belluzzi JD, Wise CD (1975) Memory enhancement by central administration of norepinephrine. Brain Res 84:329–335
Sunderland T, Tariot PN, Mueller EA, Murphy DL, Weingartner H, Cohen RM (1985) Cognitive and behavioural sensitivity to scopolamine in Alzheimer patients and controls. Psychopharmacol Bull 21:676–679
Sunderland T, Tario PN, Weingartner H, Murphy DL, Newhouse PA, Mueller EA, Cohen RM (1986) Pharmacological modelling of Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 10:599–619
Trenerry MR, Jack CR, Ivnik RJ, Sharbrough FW, Cascino GD, Hirschorn KA, Marsh WR, Kelly PJ, Meyer FB (1993) MRI hippocampal volumes and memory function before and after temporal lobectomy. Neurology 43:1800–1805
Troster AI, Butters N, Salmon DP, Cullum CM, Jacobs D, Brandt J, White RF (1993) The diagnostic utility of savings scores: differentiating Alzheimer's and Huntington's disease with the logical memory and visual reproduction tests. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 15:773–788
Wechsler D (1955) Wechsler adult intelligence scale. The Psychological Corporation, New York
Wechsler D (1987) Wechsler memory scale—revised. The Psychological Corporation, Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, New York
Wesnes K, Warburton DM (1984) Effects of scopolamine and nicotine on human rapid information processing performance. Psychopharmacology 82:147–150
Wilkins AJ, Shallice T, McCarthy R (1987) Frontal lesions and sustained attention. Neuropsychologia 25:359–365
Wilson B, Cockburn J, Baddeley AD (1985) Rivermead behavioural memory test. Thames Valley Test, Titchfield, Fareham
Woods DL, Knight RT (1986) Electrophysiologic evidence of increased distractability after dorsolateral prefrontal lesions. Neurology 36:212–216
Woods SW, Hoffer PB, McDougle CJ, Krystal JH, Heninger GR, Charney DS (1991) Effects of yohimbine on regional cerebral blood flow in panic disorder. Soc Neurosci Abstr 17:293.8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coull, J.T., Sahakian, B.J. & Hodges, J.R. Theα 2 antagonist idazoxan remediates certain attentional and executive dysfunction in patients with dementia of frontal type. Psychopharmacology 123, 239–249 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246578
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246578