Abstract
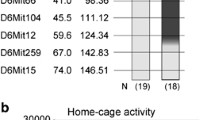
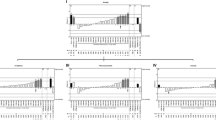
To elucidate genes associated with cocaine's locomotor stimulant effects, we used recombinant inbred-quantitative trait loci (RI-QTL) analyses to identify chromosomal loci associated with locomotor activity before (baseline) and after cocaine treatment. RI-QTL analyses seek to identify associations between a quantitative measure of a phenotype and one or more previously mapped marker loci across a panel of RI strains. In the present study, 11 BXD RI strains were used to identify several putative QTLs for each phenotype. Both baseline locomotor activity and cocaine's locomotor stimulant effects are polygenic, with both unique and overlapping genetic influences. The largest associations for baseline activity were observed on chromosomes 5 and 9 and the largest associations for cocaine's psychomotor stimulant effects on chromosomes 3 and 17.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carroll ME, Lac ST, Asenio M, Kragh R (1990) Fluoxetine reduces intravenous cocaine self-administration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35: 237–244
Cohen P (1990) Desires for cocaine. In: Warburton DM (ed) Addiction controversies. Chur: Harwood 212–222
Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Gilbert DJ, Eppig JT, Maltais LJ, Miller JC, Dietrich WF, Weaver A, Lincoln SE, Steen RG, Stein LD, Nadeau JH, Lander ES (1993) A genetic linkage map of the mouse: current applications and future prospects. Science 262: 57–66
Costall B, Naylor RJ (1992) Serotonin and psychiatric disorders: a key to new therapeutic approaches. Arzneimittelforschung 42: 246–249
Crabbe, JC, Belknap JK, Buck KJ (1994) Genetic animal models of alcohol and drug abuse. Science 264: 1715–1723
De Wit J, Uhlenhuth EH, Johanson CE (1986) Individual differences in the reinforcing and subjective effects of amphetamine and diazepam. Drug Alcohol Depend 16: 341–360
George FR, Porrino LJ, Ritz MC, Goldberg SR (1991) Inbred rat strain comparisons indicate different sites of action for cocaine and amphetamine locomotor stimulant effects. Psychopharmacology 104: 457–462
Gora-Maslak G, McClearn GE, Crabbe JC, Phillips TJ, Belknap JK, Plomin R (1991) Use of recombinant inbred strains to identify quantitative trait loci in psychopharmacology. Psychopharmacology 104: 413–424
Guitart X, Beitner-Johnson D, Marby DW, Kosten TA, Nestler EJ (1992) Fisher and Lewis rat strains differ in basal levels of neurofilament proteins and their regulation by chronic morphine in the mesolimbic dopamine system. Synapse 12: 242–253
Le Moal M, Simon H (1991) Mesocortical dopaminergic network: functional and regulator roles. Physiol Rev 71: 155–234
Lossie AC, Vandenbergh DJ, Camper SA (1994) Localization of the dopamine transporter gene, Dat1, on mouse chromosome 13. Mammalian Genome 5: 117–118
Maltais LJ, Doolittle DP, Roderick TH, Hillyard AL, Davisson MT (1994) Locus map of mouse. Mouse Genome 92: 62–85
Marley RJ, Witkin JM, Goldberg SR (1991a) Genetic factors influence changes in sensitivity to the convulsant properties of cocaine following chronic treatment. Brain Res 542: 1–7
Marley RJ, Witkin JM, Goldberg SR (1991b) A pharmacogenetic evaluation of the role of local anesthetic actions in the cocaine kindling process. Brain Res 562: 251–257
Miner LL, Marley RJ (1995) Chromosomal mapping of loci influencing sensitivity to cocaine-induced seizures in BXD recombinant inbred strains of mice. Psychopharmacology 117: 62–66
Porrino LJ, Ritz MC, Goodman NL, Sharpe LG, Kuhar MJ, Goldberg SR (1988) Differential effects of the pharmacological manipulation of serotonin systems on cocaine and amphetamine self-administration in rats. Life Sci 45: 1529–1535
Ritz MC, Lamb RJ, Goldberg SR, Kuhar MJ (1987) Cocaine receptors on dopamine transporters are related to self-administration of cocaine. Science 237: 1219–1223
Ruth JA, Ullman EA, Collins AC (1988) An analysis of cocaine effects on locomotor activities and heart rate in four inbred mouse strains. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 29: 157–162
Schechter MD (1992) Rats bred for differences in preference to cocaine: other behavioral measurements. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43: 1015–1021
Shuster L, Yu G, Bates A (1977) Sensitization to cocaine stimulation in mice. Psychopharmacology 52: 185–190
Silverman BW (1986) Density estimates for statistics and data analysis. Chapman and Hall, London
Tolliver BK, Belknap JK, Woods WE, Carney JM (1994) Genetic analysis of sensitization and tolerance to cocaine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270: 1230–1238
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miner, L.L., Marley, R.J. Chromosomal mapping of the psychomotor stimulant effects of cocaine in BXD recombinant inbred mice. Psychopharmacology 122, 209–214 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246541
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246541