Abstract
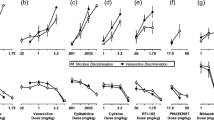
This study evaluated the effects of two central nicotinic-cholinergic receptor agonists and an antagonist on performance accuracy of a rat, delayed stimulus discrimination task (DSDT). Rats were trained to discriminate between an auditory and visual stimulus by pressing a right or left lever. To diminish the rat's ability to use mediating spatial strategies to solve the task, computer automated, retractable doors separated the animal from the levers during delay intervals, thus reducing positioning at the lever. After stable baselines were achieved, rats were grouped and administered placebo (saline) and nicotine, lobeline or mecamylamine in a randomized dose series. Each group received two complete series of the selected compound on different occasions. Mecamylamine impaired DSDT accuracy in a dose-dependent manner while optimal doses of nicotine and lobeline significantly improved accuracy. Nicotine differed from lobeline in regard to its interaction with a dose of mecamylamine (1.0 mg/kg) that had not impaired DSDT accuracy. Combined administration of lobeline and mecamylamine was followed by a significantly increased level of DSDT accuracy that was similar to the improvement following administration of lobeline alone. In contrast, combined administration of nicotine and mecamylamine did not result in increased DSDT accuracy. Furthermore, lobeline administration similarly improved accuracy of trials associated with both the light and the tone, while nicotine improved accuracy of trials associated with the light to a much greater degree. These data suggest that the increases in DSDT accuracy associated with lobeline may be expressed through non-nicotinic mechanisms or a nicotinic receptor which is not blocked by mecamylamine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abood LG, Salles KS, Maiti A (1988) Structure-activity studies of carbamate and other esters: agonists and antagonists to nicotine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30: 403–408
Acri JB, Grunberg NE, Morse DE (1991) Effects of nicotine on the acoustic startle reflex amplitude in rats. Psychopharmacology 104: 244–248
Acri, JB, Morse DE Popke JE, Grunberg NE (1994) Nicotine increasing sensory gating, measured as inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology 114: 369–374
Adler LE, Hoffer LJ, Griffith J, Waldo MC, Freedman R (1992) Normalization by nicotine of deficient auditory sensory gating in the relatives of schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 32: 607–616
Barlow RB, Johnson O (1989) Relations between structure and nicotine-like activity: X-ray crystal structure and analysis of (-)-cytisine and (-)-lobeline hydrochloride and a comparison with (-)-nicotine and other nicotine-like compounds. Br J Pharmacol 98: 799–808
Brioni JD, Linville DG, Cadman ED, Williams S, Buckley M, Anderson DJ, Arneric SP (1991) Classical nicotinic agonists differentially affect cognition, cortical cerebral blood flow (DBF) and dopamine (DA) release. Soc Neurosci Abstr 17: 1236
Buccafusco JJ, Jackson WJ (1991) Beneficial effects of nicotine administered prior to a delayed matching-to-sample task in young and aged monkeys. Neurobiol Aging 2: 233–238
Bushnell PJ, Padilla SS, Ward T, Carey NP, Olszyk VB (1991) Behavioral and neurochemical changes in rats dosed repeatedly with diisopropylfluorophosphate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256 [2]: 741–750
Clarke PBS, Pert CB, Pert A (1984) Autoradiographic distribution of nicotine receptors in rat brain. Brain Res 323: 390–395
Clarke PBS, Schwartz RD, Paul SM, Pert CB, Pert A (1985) Nicotinic binding in rat brain: autoradiographic comparison of [3H]acetylcholine, [3H]nicotine, and [125I]-α-bungarotoxin. J Neurosci 5: 1307–1315
Collins AC, Bhat RV, Pauly JR, Marks MJ (1990) Modulation of nicotine receptors by chronic exposure to nicotinic agonists and antagonists. In: Book G, Marsh J (eds) The biology of nicotine dependence. Ciba Foundation Symposia, West Sussex, England, John Wiley & Sons, pp 68–86
Decker MW, Majchrazak MJ, Anderson DJ (1992) Effects of nicotine on spatial memory deficits in rats with septal lesions. Brain Res 572: 281–285
Decker MW, Buckley MJ, Brioni JD (1994) Differential effects of pretreatment with nicotine and lobeline on nicotine-induced changes in body temperature and locomotor activity in mice. Drug Dev Res 31: 52–58
Dunne MP, MacDonald D, Hartley LR (1986) The effects of nicotine upon memory and problem solving performance. Physiol Behav 37: 849–854
Dunnett SB (1985) Comparative effects of cholinergic drugs and lesions of nucleus basalis of fimbria-fornix on delayed matching in rats. Psychopharmacology 87: 357–363
Dunnett SB, Martel FL (1990) Proactive interference effects on short-term memory in rats: I. Basic parameters and drug effects. Behav Neurosci 104[5]: 655–665
Elrod K, Buccafusco JJ (1991) Correlation of the amnestic effects of nicotinic antagonists with inhibition of regional brain acetylcholine synthesis in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 258: 403–409
Elrod K, Buccafusco JJ, Jackson WJ (1988) Nicotine enhances delayed matching-to-sample performance by primates. Life Sci 43: 277–287
Flynn DA, Mash DC (1986) Characterization ofl-[3H]nicotine binding in human cerebral cortex: comparison between Alzheimer's disease and the normal. J Neurochem 47: 1948–1954
Geller I, Hartmann R, Blum K (1971) Effects of nicotine, nicotine monomethiodide, lobeline, chlordiazepoxide, meprobamate and caffeine on a discrimination task in laboratory rats. Psychopharmacologia 20: 355–365
Gellerman LW (1933) Chance order of alternating stimuli in visual discrimination experiments. J Genet Psychol 42: 207–208
Giacobini E, DeSarno P, Clark B, McIlhany M (1989) The cholinergic receptor system of the human brain. Neurochemical and pharmacological aspects of aging and Alzheimer's. In: Nordberg A (ed) Progress in brain research. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 335–343
Grady S, Marks MJ, Wonnacott S, Collins AC (1992) Characterization of nicotinic receptor mediated [3H]dopamine release from synaptosomes prepared from mouse striatum. J Neurochem 59: 848–856
Gray JA (1983) The neuropsychology of anxiety. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK
Haroutunian V, Barnes E, Davis KL (1985) Cholinergic modulation of memory in rat. Psychopharmacology 87: 266–271
Heyser CJ, Hampson RE, Deadwyler SA (1993) Effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol on delayed match to sample performance in rats: alterations in short-term memory associated with changes in task specific firing of hippocampal cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264[1]: 294–307
Khan IM, Taylor P, Yaksh TL (1994) Cardiovascular and behavioral responses to nicotinic agents administered intrathecally. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270: 150–158
Kirk RC, White KG, McNaughton N (1988) Low dose scopolamine affects discriminability but not rate of forgetting in delayed conditional discrimination. Psychopharmacology 96: 541–546
Levin ED (1992) Nicotinic systems and cognitive function. Psychopharmacology 108: 417–531
Levin ED, Rose JE (1990) Anticholinergic sensitivity following chronic nicotine administration as measured by radial-arm maze performance in rats. Behav Pharmacol 1: 511–520
Levin ED, Lee C, Rose JE, Reyes A, Ellison G, Jaravik M, Gritz E (1990) Chronic nicotine and withdrawal effects on radial-arm maze performance in rats. Behav Neural Biol 53: 269–276
London ED, Connolly RJ, Szikszay M, Wamsley JK (1985a) Distribution of cerebral metabolic effects of nicotine in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 110: 391–392
London ED, Waller SB, Wamsley JK (1986b) Autoradiographic localization of [3H]nicotine binding sites in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 53: 179–184
Mundy WR, Iwamoto ET (1988a) Actions of nicotine on the acquisition of an autoshaped lever-touch response in rats. Psychopharmacology 94: 267–274
Mundy WR, Iwamoto ET (1988b) Nicotine impairs acquisition of radial-arm maze performance in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40: 119–122
Newhouse P, Sunderland T, Narang P, Mellow AM, Fertig JB, Lawlor BA, Murphy DL (1990) Neuroendocrine, physiological and behavioral responses following intravenous nicotine in non-smoking healthy volunteers and patients with Alzheimer's disease. Psychoneuroendocrinology 15: 471–484
Perry EK, Perry RH, Smith CJ, Dick DJ, Candy JM, Edwardson JA, Fairbairn A, Blessed G (1987) Nicotinic receptor abnormalities in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 50: 806–809
Pontecorvo MJ (1983) Effects of proactive interference on rats' continuous nonmatching-to-sample performance. Animal Learning Behaviour 11: 356–366
Reavill C, Walther B, Stolerman IP, Testa B (1990) Behavioral and pharmacokinetic studies on nicotine, cytisine and lobeline. Neuropharmacology 29: 619–624
Rupniak NMJ, Steventon MJ, Field MJ, Jennings CA, Iversen SD (1989) Comparison of the effects of four cholinomimetic agents on cognition in primates following disruption by scopolamine or by lists of objects. Psychopharmacology 99: 189–195
Schechter MD, Rosecrans JA (1972) Nicotine as a discriminative cue in rats: Inability of related drugs to produce a nicotine-like cueing effect. Psychopharmacologia 27: 379–387
Spencer DG Jr, Pontecorvo MJ, Heise GA (1985) Central cholinergic involvement in working memory: effects of scopolamine on continuous nonmatching and discrimination performance in the rat. Behav Neurosci 99[6]: 1049–1065
Squire LR, Zola-Morgan S, Chen SK (1988) Human amnesia and animal models of amnesia: performance of amnesic patients on tests designed for the monkey. Behav Neurosci 102: 210–221
Stolerman IP, Goldfarb T, Fink R, Jarvik ME (1973) Influence of cigarette smoking with nicotine antagonists. Psychopharmacology 28: 247–259
Tan S, Kirk RC, Abraham WC, McNaughton N (1990) Chlordiazepoxide reduces discriminability, but not rate of forgetting in delayed conditional discrimination. Psychopharmacology 101: 550–554
Taylor P (1990) Agents acting at the neuromuscular junction and autonomic ganglia. In: Gilman AG, Rall TW, Nies AS, Taylor P (eds) Goodman and Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 8th edn. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 166–186
Terry AV, Jr, Buccafusco JJ, Jackson WJ (1993) Scopolamine reversal of nicotine enhanced delayed matching-to-sample performance in monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45: 925–929
Thomas JR, Ahlers ST, Schrot J (1991) Cold-induced impairment of delayed matching in rats. Behav Neural Biol 55: 19–30
Warburton DM (1992) Nicotine as a cognitive enhancer. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 16: 181–919
West R, Hack S (1991) Effect of cigarettes on memory search and subjective ratings. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 38: 281–286
Whitehouse PJ, Martino AM, Antuono PG, Lowenstein P, Coyle JT, Price DL, Kellar KJ (1986) Nicotinic acetylcholine binding sites in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 371: 146–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Terry, A.V., Buccafusco, J.J., Zagrodnik, S. et al. Effects of stimulation or blockade of central nicotinic-cholinergic receptors on performance of a novel version of the rat stimulus discrimination task. Psychopharmacology 123, 172–181 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246174
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246174