Abstract
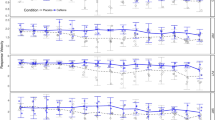
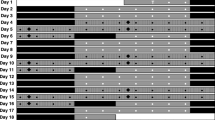
The alerting effects of caffeine were assessed using a standard physiological measure of daytime sleepiness/alertness, the Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT). Healthy young men (n=24) were randomly assigned to receive caffeine 250 mg or placebo administered double blind, at 0900 and 1300 hours on each of 2 days. On the 3rd day both groups received placebo to test for conditioning to the alerting effects of caffeine. Each day sleep latency was measured at 1000, 1200, 1400, and 1600 hours and performance (divided attention at 1030 hours and auditory vigilance at 1430 hours) was assessed. Caffeine increased sleep latency (i.e., improved alertness) and auditory vigilance performance compared to placebo. Tolerance to the effects of caffeine on sleep latency developed over the four administrations. On the conditioning test (day 3) the group receiving caffeine the previous two days was more alert and performed better than the placebo group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr GA, Sharpless NS, Cooper S, Schiff SR, Paredes W, Bridger WH (1983) Classical conditioning, decay and extinction of cocaine-induced hyperactivity and stereotype. Life Sci 33:1341–1351
Carskadon MA, Dement WC (1982) The multiple sleep latency test: what does it measure? Sleep 5:S67-S72
Carskadon MA, Dement WC, Mitler MM, Roth T, Westbrook PR, Keenan S (1986) Guidelines for the Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT). A standard measure of sleepiness. Sleep 9:518–524
Chait LD, Uhlenhuth EH, Johanson CE (1985) The discriminative stimulus and subjective effects ofd-amphetamine in humans. Psychopharmacology 86:307–312
Chait LD, Uhlenhuth EH, Johanson CE (1986) The discriminative stimulus and subjective effects ofd-amphetamine, phenmetrazine and fenfluramine in humans. Psychopharmacology 89:301–306
Clubley W, Bye CE, Henson TA, Peck AW, Riddington CJ (1979) Effects of caffeine and cyuclizine alone and in combination on human performance, subjective effects and EEG activity. Br J Clin Pharmacol 7:157–163
Hinson RE, Poulos CX (1981) Sensitization to the behavioral effects of cocaine: modification by Pavlovian conditioning. Biochem Behav 15:559–562
Karacan I, Thornby JI, Anch M, Booth GH, Williams RL, Salis P (1976) Dose-related sleep disturbances induced by coffee and caffeine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 20:682–689
Levine B, Moyles T, Roehrs T, Fortier J, Roth T (1986) Actigraphic monitoring and polygraphic recording in determination of sleep and wake. Sleep Res 15:247
Levine B, Roehrs T, Zorick F, Roth T (1988) Daytime sleepiness in young adults. Sleep 11:39–46
Lieberman HR, Wurtman RJ, Emde GG, Roberts C, Coviella ILG (1987) The effects of low doses of caffeine on human performance and mood. Psychopharmacology 92:308–312
Lumley M, Roehrs T, Zorick F, Lamphere J, Roth T (1986) The alerting effects of naps in sleep-deprived subjects. Psychophysiology 23:403–408
Lumley M, Roehrs T, Asker D, Zorick F, Roth T (1987) Ethanol and caffeine effects on daytime sleepiness/alertness. Sleep 10:306–312
Mitler MM, Shafor R, Hajdukovich R, Timms RM, Browman CP (1986) Treatment of narcolepsy: objective studies on methylphenidate, pemoline, and protriptyline. Sleep 9:260–264
Nicholson AN, Stone BM (1980) Heterocyclic amphetamine derivatives and caffeine on sleep in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 9:195–203
Pavlov IP (1927) Conditioned reflexes. Oxford University Press, London
Rechtschaffen A, Kales A (1968) A manual of standardized terminology techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects. National Institutes of Health Publications 204, Government Printing Office, Washington DC
Robertson D, Wade D, Workman R, Woosley RL, Oates JA (1981) Tolerance to the humoral and hemodynamic effects of caffeine in man. Clin Invest 67:1111–1117
Tang-Liu DD, Williams RL, Riegelman S (1983) Disposition of caffeine and its metabolites in man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 224:180–185
Zwyghuizen-Doorenbos A, Roehrs T, Schaefer M, Roth T (1988) Test-retest reliability of the MSLT. Sleep 11:562–565
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zwyghuizen-Doorenbos, A., Roehrs, T.A., Lipschutz, L. et al. Effects of caffeine on alertness. Psychopharmacology 100, 36–39 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245786
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245786