Abstract
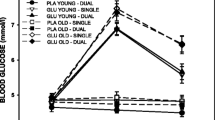
As it has been suggested that blood glucose might play a role in the action of some cognitive enhancing drugs, the influence of glucose containing drinks on human memory was examined. In a double-blind study the influence was examined of a drink containing 50 g glucose, or a placebo, on the ability to recall a word list. There was a significant correlation between blood glucose values and the number of words recalled. Those whose blood glucose levels were increasing remembered significantly more words than those whose blood glucose levels were falling. No relationship was found between blood glucose and performance on a test of spatial memory. In a second study blood glucose levels were raised for 2 h by taking a series of glucose-containing drinks. The number of words recalled from a word list correlated significantly with blood glucose levels but not with recall of a Wechsler story. The glucose-induced improvement in memory did not occur only in those whose blood glucose levels were initially low; rather it occurred irrespective of initial blood glucose level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azari NP (1991) Effects of glucose on memory processes in young adults. Psychopharmacology 105:521–524
Benton D (1989) Dietary sugar hyperactivity and cognitive functioning. J Appl Nutr 41:13–22
Benton D (1990) The impact of increasing blood glucose on psychological functioning. Biol Psychol 30:13–19
Benton D, Sargent J (1992) Breakfast blood glucose and memory. Biol Psychol 33:207–210
Benton D, Kumari N, Brain PF (1982) Mild hypoglycaemia and questionnaire measures of aggression. Biol Psychol 14:129–135
Benton D, Brett V, Brain PF (1987) Glucose improves attention and reaction to frustration in children. Biol Psychol 24:95–100
Durkin TP, Messier C, de Boer P, Westerink BHC (1992) Raised blood glucose levels enhance scopolamine-induced acetylcholine overflow from the hippocampus: an in vivo microdialysis study in the rat. Behav Brain Res 49:181–188
Gold PE (1986) Glucose modulation of memory storage processing. Behav Neural Biol 45:342–349
Gonder-Frederick L, Hall JL, Vogt J, Cox DJ, Green J, Gold PE (1987) Memory enhancement in elderly humans: effects of glucose ingestion. Physiol Behav 41:503–504
Hall JL, Gold PE (1990) Adrenalectomy-induced memory deficits: role of plasma glucose levels. Physiol Behav 47:27–33
Hall JL, Gonder-Frederick LA, Chewning WW, Silveira J, Gold PE (1989) Glucose enhancement of performance on memory tests in young and aged humans. Neuropsychologia 27:1129–1138
Jaffard R, Galey D, Micheau J, Durkin T (1985) The cholinergic septo-hippocampal pathway and learning and memory. In: Will BE, Schmitt P, Dalrymple-Alford JC (eds) Brain plasticity, learning and memory. Plenum Press, New York, pp 167–181
Kent S (1976) Is diabetes a form of accelerated aging? Geriatrics 31:140–151
Lapp JE (1981) Effects of glycemic alterations and noun imagery on the learning of paired associates. J Learn Disabil 14:35–38
Manning CA, Hall JL, Gold PE (1990) Glucose effects on memory and other neuropsychological tests in elderly humans. Psychol Sci 1:307–311
Marks V, Rose FG (1981) Hypoglycaemia (2nd edn). Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Matthews DR, Holman RR, Bown E, Steenson J, Watson A, Hughes S, Scott D (1987) Pen-sized digital 30-second blood glucose meter. Lancet 1:778–779
Matthies H, Rauca C, Liebmann H (1974) Changes in acetylcholine content of different brain regions of the rat during a learning experiment. J Neurochem 23:1109–1113
Messier C, White NM (1987) Memory improvement by glucose, fructose, and two glucose analogs: a possible effect on peripheral glucose transport. Behav Neural Biol 48:104–127
Messier C, Durkin T, Mrabet O, Destrade C (1990) Memory-improving action of glucose: indirect evidence for a facilitation of hippocampal acetylcholine synthesis. Behav Brain Res 39:135–143
Paivio A, Yuille JC, Madigan SA (1968) Concreteness imagery and meaningfulness values for 925 nouns. J Exp Psychol 76:1–25
Rauca C, Kammerer E, Matthies H (1980) Choline uptake and permanent memory storage. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13:21–25
Ricny J, Tucek S, Novakova J (1992) Acetylcarnitine, carnitine and glucose diminish the effect of muscarinic antagonist quinuclidinyl benzilate on striatal acetylcholine content. Brain Res 576:215–219
Stone WS, Croul CE, Gold PE (1988) Attenuation of scopolamine-induced amnesia in mice. Psychopharmacology 96:417–420
Stone WS, Rudd RJ, Gold PE (1990a) Amphetamine, epinephrine, and glucose enhancement of memory retrieval. Psychobiology 18:227–230
Stone WS, Wenk GL, Olton DS, Gold PE (1990b) Poor blood glucose regulation predicts sleep and memory deficits in normal aged rats. J Gerontol 45:B169-B173
Toumane A, Durkin T, Marighetto A, Galey D, Jaffard R (1988) Differential hippocampal and cortical cholinergic activation during the aquisition, retention, reversal and extinction of a spatial discrimination in an 8-arm radial maze by mice. Behav Brain Res 30:225–234
Tucek S, Ricny J, Dolezal V (1982) Acetylcoenzyme-A and the control of the synthesis of acetylcholine in the brain. Acta Neurobiol 39:1704–1709
Wenk GL (1989) An hypothesis on the role of glucose in the mechanism of action of cognitive enhancers. Psychopharmacology 99:431–438
Wechsler D (1987) Wechsler memory scale — revised. The Psychological Corporation, Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benton, D., Owens, D.S. Blood glucose and human memory. Psychopharmacology 113, 83–88 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244338
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244338