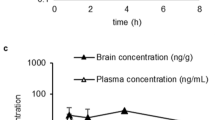
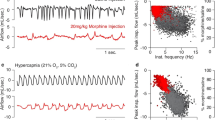
Abstract
The twoβ-adrenoceptor agonists salbutamol and clenbuterol have been shown to be effective antidepressant drugs. Flerobuterol, a newβ-adrenoceptor agonist, exhibits antidepressant activity in animal models. Given the long-standing notion that the serotonergic (5-HT) system might be involved in the etiology and/or the therapeutics of affective disorders and that this class of adrenergic agents can alter factors regulating 5-HT transmission, the effects of acute and repeated administrations of flerobuterol on the 5-HT system were studied. Acute administration of flerobuterol (up to 2 mg/kg, IV) did not modify the firing rate of dorsal raphe 5-HT neurons. However, the sustained administration of flerobuterol for two days (0.5 mg/kg/day, SC, delivered by an osmotic minipump) produced a marked decrease of the firing rate of 5-HT neurons. The reversal of this effect of flerobuterol by the somatodendritic 5-HT autoreceptor antagonist spiperone suggests that this decrease in the firing activity of 5-HT neurons in rats treated for 2 days with flerobuterol resulted from an enhanced synaptic availability of 5-HT. This initial decrease in firing activity of 5-HT neurons was followed by a progressive recovery to normal after 14 days of treatment with flerobuterol. At this point in time, the effect of intravenous lysergic acid diethylamide on the firing of 5-HT neurons was attenuated, indicating that the somatodendritic 5-HT autoreceptors had desensitized. The effectiveness of the electrical stimulation of the ascending 5-HT pathway in suppressing the firing activity of dorsal hippocampus pyramidal neurons was markedly enhanced in rats treated with flerobuterol for 14 days. This enhanced efficacy of the stimulation could not be ascribed to an increased sensitivity of the postsynaptic neurons to 5-HT, since their responsiveness to microiontophoretic applications of 5-HT was unaltered. Neither could this enhanced 5-HT signal transfer be attributed to a modification of the function of terminal 5-HT autoreceptors in controlling 5-HT release, since the decremental effect of increasing the frequency of stimulation (from 1–5 Hz) was similar in control and in flerobuterol-treated rats. In keeping with available data, it is most likely that the enhancement of 5-HT neurotransmission by long-term administration of flerobuterol is due to an increased availability of the neurotransmitter. It is concluded that the enhancement of 5-HT neurotransmission might underlie the therapeutic action ofβ-adrenoceptor agonists in major depression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK (1978) Feedback regulation of central monoaminergic neurons: evidence from single-cell recording studies. In: Youdim MBH, Lovenberg W, Sharman DF, Lagnado JR (eds) Essays in neurochemistry and neuropharmacology. Wiley, New York, pp 1–32
Avorn J, Everitt DE, Weiss S (1986) Increased antidepressant use in patients prescribedβ-blockers. JAMA 255:357–360
Bille J, Masse JL, Gairaud M, Rodossio M (1979) Note préliminaire sur les effets antidépresseurs d'un béta-stimulant. Ann Méd Psychol 137:9
Blier P, de Montigny C (1983) Electrophysiological studies on the effect of repeated zimelidine administration on serotonergic neurotransmission in the rat. J Neurosci 3:1270–1278
Blier P, de Montigny C (1985) Serotonergic but not noradrenergic neurons in rat central nervous system adapt to long-term treatment with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Neuroscience 16:949–955
Blier P, de Montigny C (1987) Modification of 5-HT neuron properties by sustained administration of the 5-HT1A agonist gepirone: electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Synapse 1:470–480
Blier P, de Montigny C, Chaput Y (1987) Modifications of the serotonin system by antidepressant treatments: implications for the therapeutic response in major depression. J Clin Psychopharmacol 7S:24–35
Blier P, Chaput Y, de Montigny C (1988) Long-term 5-HT reuptake blockade, but not monoamine oxidase inhibition, decreases the function of terminal 5-HT autoreceptors: an electrophysiological study in the rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:246–254
Blier P, Steinberg S, Chaput Y, de Montigny C (1989) Electrophysiological assessment of putative antagonists of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors: a single-cell study in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 67:98–105
Chaput Y, de Montigny C (1988) Effects of the 5-hydroxytryptamine1 receptor antagonist, BMY 7378, on 5-hydroxytryptamine neurotransmission: electrophysiological studies in the rat central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:359–370
Chaput Y, Blier P, de Montigny C (1986) In vivo electrophysiological evidence for the regulatory role of autoreceptors on serotonergic terminals. J Neurosci 6:2796–2801
Chaput Y, Blier P, de Montigny C (1988) Acute and long-term effects of antidepressant serotonin (5-HT) reuptake blockers on the efficacy of 5-HT neurotransmission: electrophysiological studies in the rat central nervous system. Adv Biol Psychiatry 17:1–17
Coppen A (1967) The biochemistry of affective disorders. Br J Psychiatry 113:1237–1264
Cowen PJ, Grahame-Smith DG, Green AR, Heal DJ (1982)β-Adrenoceptors agonists enhance 5-hydroxytryptamine-mediated behavioural responses. Br J Pharmacol 76:265–270
Cullum VA, Farmer JB, Jack D, Levy GP (1969) Salbutamol a new selectiveβ-adrenoceptive receptor stimulant. Br J Pharmacol 35:141–151
de Montigny C, Aghaganian GK (1977) Preferential action of 5-methoxytryptamine and 5-methoxydimethyltryptamine on presynaptic serotonin receptors: a comparative iontophoretic study with LSD and serotonin. Neuropharmacology 16:811–818
de Montigny C, Chaput Y, Blier P (1989) Long-term tricyclic and electroconvulsive treatment increase the responsiveness of dorsal hippocampus 5-HT1A receptors: an electrophysiological study in the rat. Soc Neurosci Abstr 15:342.21
de Montigny C, Lista A, Blier P (1990) Pre- and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors exhibit different electrophysiological properties: I. Effects of spiperone. Soc Neurosci Abst 16:462–464
Duteil J, Rambert FR, Pointeau AM, Mangiameli P, Assous E (1988) Flerobuterol: a new antidepressant drug related to beta adrenergic agonists. Experimental profile in mice. Psychopharmacology [Suppl] 96:276
Erdö SL, Kiss B, Rossdy B (1982) Effect of salbutamol on the cerebral levels, uptake and turnover of serotonin. Eur J Pharmacol 78:357–361
Frances H, Simon P (1986) The effect of a beta agonist on behaviour mediated by 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors. Biol Psychiatry 21:1072–1075
Frances H, Puech AJ, Simon P (1978) Profil psychopharmacologique de l'isoprénaline et du salbutamol. J Pharmacol (Paris) 9:25–34
Frances H, Martin P, Simon P (1985) Modulation par les agonistes bêta-adrénergiques des effets d'une stimulation sérotoninergique chez la souris. Communication présentée à l'Association française des Pharmacologistes. Grenoble, 25–26 Avril, p 34 (abstract)
Frances H, Bulach C, Simon P, Fillion M, Fillion G (1986) Chronic beta-adrenergic stimulation increases in mice the sensitivity to methysergide and the number of cerebral high affinity serotonin binding sites (5-HT1). J Neural Transm 67:215–224
Goudemand M, Dubois F, Roeland P, Fontan M, Parquet PJ (1980) Médication bêta-sympathomimétique et dépression. Lille Médical 25:522–525
Göthert M (1980) Serotonin-receptor-mediated modulation of Ca2+-dependent 5-hydroxytryptamine release from neurones of the rat brain cortex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 314:223–230
Green AR, Goodwin GM, De Souza RJ, Heal DJ (1986) Theβ 2-adrenoceptor agonists clenbuterol and salbutamol enhance the hypothermic action of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamine) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) in mice by a central mechanism. Neuropharmacology 25:21–24
Haigler HJ, Aghajanian GK (1974a) Lysergic acid diethylamide and serotonin: a comparison of effects on serotonergic neurons and neurons receiving a serotonergic input. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 188:688–699
Haigler HJ, Aghajanian GK (1974b) Peripheral serotonin antagonists: failure to antagonize serotonin in brain areas receiving a prominent serotonergic input. J Neural Transm 35:257–273
Hallberg H, Almgren O, Svensson TH (1981) Increased brain serotonergic and noradrenergic activity after repeated systemic administration of the beta-2 adrenoceptor agonist salbutamol, a putative antidepressant drug. Psychopharmacology 73:201–207
Hallberg H, Almgren O, Svensson TH (1982) Reduced brain serotonergic activity after repeated treatment withβ-adrenoceptor antagonists. Psychopharmacology 76:114–117
Handley SL, Singh L (1984) The effects ofβ 2-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on the head-twitch in male mice. Br J Pharmacol 61:128
Hicks TP (1984) The history and development of microiontophoresis in experimental neurobiology. Prog Neurobiol 22:185–240
Hoyer D, Engel D, Kalkman MO (1985) Molecular pharmacology of 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 sites in rat and pig brain membranes: radioligand binding studies with [3H]5-HT, [3H]8-OH-DPAT, (−) [125I]iodocyanopindolol, [3H]mesulergine and [3H]ketanserin. Eur J Pharmacol 118:13–23
Kandel ER, Spencer WA (1961) Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. II. After potentials and repetitive firing. J Neurophysiol 24:243–259
Lakoski J, Aghajanian GK (1985) Effects of ketanserin on neuronal responses to serotonin in the prefrontal cortex, lateral geniculate and dorsal raphe nucleus. Neuropharmacology 24:265–273
Lanfumey L, Adrien J (1988) Adaptive changes ofβ-adrenergic receptors after neonatal locus coeruleus lesion: regulation of serotoninergic unit activity. Synapse 2:644–649
Lanfumey L, Gallisson MC, Daval G, Hamon M (1986) Beta-adrenergic receptor autoradiography in rats treated neonatally with 6-OH-DA. Soc Neurosci Abstr 12:11.11
Lapin JP, Oxenkrug GF (1969) Intensification of the central serotonergic processes as a possible determinant of the thymoleptic effect. Lancet II:132–136
Lecrubier Y, Puech AJ, Jouvent R, Simon P, Widlocher D (1980) A beta-adrenergic stimulant (salbutamol) versus clomipramine in depression: a controlled study. Br J Psychiatry 136:354–358
Lerer B, Ebstein RP, Belmaker RH (1981) Subsensitivity of human beta-adrenergic adenylate cyclase after salbutamol treatment of depression. Psychopharmacology 75:169–172
Lum IT, Piercey MF (1988) Electrophysiological evidence that spiperone is an antagonist of 5-HT1A receptors in the dorsal raphe nucleus. Eur J Pharmacol 149:9–15
Nimgaonkar VL, Green AR, Cowen PJ, Heal DJ, Grahame-Smith DG, Deakin JFW (1983) Studies on the mechanisms by which clenbuterol, aβ-adrenoceptor agonist, enhances 5-HT-mediated behaviour and increases metabolism of 5-HT in the brain of the rat. Neuropharmacology 22:739–749
Ortmann R, Martin S, Radeke E, Delini-Stula A (1981) Interaction ofβ-adrenoceptor agonists with the serotonergic system in rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 316:225–230
Paxinos G, Watson C (1982) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Petrie WM, Maffucci RJ, Woosley RL (1982) Propranolol and depression. Am J Psychiatry 139:92–94
Puech AJ, Henry M, Martin P, Thévenet G, Rambert FA, Duteil J (1988) Preferential central versus peripheral effect of the beta agonist flerobuterol in rats: comparison with salbutamol. Psychopharmacology [Suppl] 96:276
Simon P, Lecrubier Y, Jouvent R, Puech A, Widlöcher D (1984) Beta-receptor stimulation in the treatment of depression. Adv Biochem Pharmacol 39:293–300
Sleight AJ, Smith RJ, Marsden CA, Palfreyman MG (1989) The effects of chronic treatment with amitriptyline and MDL 72394 on the control of 5-HT release in vivo. Neuropharmacology 28:477–480
Sprouse JS, Aghajanian GK (1987) Electrophysiological responses of serotoninergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists. Synapse 1:3–9
von Engelhardt G (1976) Pharmakologisches wirkungs Profil von NAB 365 (clenbuterol) einen neuen bronkolytikum mit einer selektiven Wirkung auf die adrenergenβ 2-Rezeptoren. Arzneimittelforsch 26:1404–1420
Waal HJ (1967) Propranolol-induced depression. Br Med J 2:50
Waldmeier PC (1981) Stimulation of central serotonin turnover byβ-adrenoceptor agonists. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 317:115–119
Welner SA, de Montigny C, Desroches J, Desjardins P, Suranyi-Cadotte BE (1989) Autoradiographic quantification of serotonin1A receptors in rat brain following antidepressant drug treatment. Synapse 4:347–352
Wheatley D (1975) An adrenergic drug in depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 32:653–655
Widlöcher D, Lecrubrier Y, Jouvent R, Puech AJ, Simon P (1977) Antidepressant effect of salbutamol. Lancet II:767–768
Willner P (1985) Antidepressants and serotonergic neurotransmission: an integrative review. Psychopharmacology 85:387–404
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Zini R, Morin D, Tillement JP (1988) Interactions of flerobuterol, a new antidepressant drug, with beta adrenoceptors in rat CNS. Psychopharmacology [Suppl] 96:276
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouthillier, A., Blier, P. & de Montigny, C. Flerobuterol, aβ-adrenoceptor agonist, enhances serotonergic neurotransmission: an electrophysiological study in the rat brain. Psychopharmacology 103, 357–365 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244290
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244290