Abstract
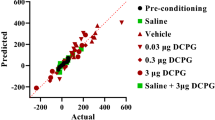
An unbiased place preference conditioning procedure was used to examine the secondary reinforcing effects of selective D-1 dopamine (DA) receptor antagonists and the neuroanatomical substrates mediating these effects. Systemic administration of SCH-23390 or the non-benzazepine D-1 receptor antagonist A-69024 produced dose-related conditioned aversions for the drug-associated place. In contrast, the D-2 antagonists spiperone and (−)sulpiride were without effect. SCH-23390-induced place aversions were also observed after intracerebroventricular administration. The minimum dose producing this effect was significantly lower than that after systemic injection. Aversive effects were also observed after microinjection of SCH-23390 into the n. accumbens. In contrast, microinjections of this antagonist into the ventral tegmental area, caudate putamen or medial prefrontal cortex were without effect. These data confirm that the blockade of D-1 but not D-2 DA receptors induces aversive states. Furthermore, they suggest that D-1 receptors in the n. accumbens may play an important role in the regulation of non-drug induced affective states.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnt J, Hyttel J (1985) Differential involvement of dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptors in the circling behavior induced by apomorphine, SKF 38393, pergolide and LY 171555 in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats. Psychopharmacology 85:346–352
Bijak M, Smialowski A (1989) Serotonin receptor blocking effect of SCH-23390. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 32:585–587
Billiard W, Ruperto G, Grosby L, Iorio L, Barnett A (1984) Characterization of the binding of3H-SCH-23390, a selective D-1 receptor antagonist ligand, in rat striatum. Life Sci 35:1885–1893
Bozarth MA, Wise RA (1981) Heroin reward is dependent on a dopaminergic substrate. Life Sci 29:1881–1886
Chipkin RE, Iorio LC, Coffin LC, McQuade RD, Berger JG, Barnett A (1988) Pharmacological profile of SCH-39166: a dopamine D1-1 selective benzonaphthazepine with potential antipsychotic activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247:1093–1102
Clark D, White FJ (1987) D-1 dopamine receptor — the search for a function: a critical evaluation of the D-1/D-2 dopamine receptor classification and its functional implications. Synapse 1:347–350
Hyttel J, Arnt J (1983) Characterization of binding of3H SCH-23390 to dopamine D-1 receptors. Correlation to other D-1 and D-2 measures and effect of selective lesions. J Neural Transm 68:171–189
Iorio L, Barnett A, Leitz F, Houser V, Korduba C (1983) SCH-23390: a potential benzazepine antipsychotic with unique interactions on dopaminergic systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226:462–468
Kerkman DJ, Ackerman M, Artman LD, Mackenzien RG, Johnson MC, Bednanz L, Montana W, Asin KE, Stampfli H, Kebabian JW (1989) A-69024: a non-benzazepine antagonist with selectivity for the dopamine D-1 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 166:481–491
Koob GF, Le HT, Creese I (1987) The D-1 dopamine receptor antagonist SCH-23390 increases cocaine self-administration in the rat. Neurosci Lett 79:315–320
Kurumiya S, Nakajima S (1988) Dopamine D1 receptors in the nucleus accumbens: involvement in the reinforcing effects of tegmental stimulation. Brain Res 448:1–6
Leone P, DiChiara GD (1987) Blockade of D-1 receptors by SCH-23390 antagonizes morphine and amphetamine-induced place preference conditioning. Eur J Pharmacol 134:251–254
Morency MA, Beninger RJ (1986) Dopaminergic substrates of cocaine-induced place conditioning. Brain Res 399:33–41
Mucha RF, Herz A (1985) Motivational properties of μ- and κ-opioid receptor agonists, studied with place and taste preference conditioning procedures. Psychopharmacology 86:274–280
Myers RD, Hoch DB (1978)14C-Dopamine microinjected into the brain-stem of the rat: dispersion, kinetics, site content and functional dose. Brain Res Bull 3:601–609
Nakajima S, McKenzie GM (1986) Reduction of the rewarding effect of brain stimulation by a blockade of dopamine D1 receptor with SCH-23390. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:919–923
Nakajima S, Wise RA (1987) Heroin self-administration in the rat suppressed by SCH-23390. Proc 17th Ann Soc Neurosci 13:1545
Nomiko G, Spyraki C (1988) Effects of ritanserin on the rewarding properties ofd-amphetamine, morphine and diazepam revealed by conditioned place preference in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:853–858
Ott T, Schmitt M, Krug M, Matthies H (1974) Intrahippocampal injections of chemicals: analysis of spread. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2:715–718
Paxinos G, Watson C (1982) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, Sydney
Pellegrino LJ, Pellegrino AS, Cushman AJ (1981) A stereotaxic atlas of the rat brain. Plenum Press, New York
Routtenberg A (1972) Intracranial chemical injections and behavior: a critical review. Behav Biol 7:601–641
Schubert P, Teschemacher H, Kreutzberg GW, Herz A (1970) Intracerebral distribution pattern of radioactive morphine and morphine-like drugs after intraventricular and intrathecal injection. Histochemie 22:277–288
Shippenberg TS, Herz A (1987) Place preference conditioning reveals the involvement of D-1 dopamine receptors in the motivational properties of μ- and κ-opioid agonists. Brain Res 436:169–172
Shippenberg TS, Herz A (1988) Motivational effects of opioids: influence of D-1 versus D-2 receptor antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 151:233–242
Shippenberg TS, Bals-Kubik R, Herz A (1987) Motivational properties of opioids: evidence that an activation of δ-receptors mediates reinforcement processes. Brain Res 436:234–239
Spyraki C, Fibiger HC, Phillips AG (1982) Dopaminergic substrates of amphetamine-induced place preference conditioning. Brain Res 253:185–193
Waddington JL (1986) Behavioral correlates of the action of selective D-1 dopamine receptor antagonists. Impact of SCH-23390 and SKF-83566 and functionally interactive D-1:D-2 receptor systems. Biochem Pharmacol 35:3661–3667
Wise RA, Bozarth MA (1982) Actions of drugs of abuse on brain reward systems: an update with specific attention to opiates. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:239–243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shippenberg, T.S., Bals-Kubik, R., Huber, A. et al. Neuroanatomical substrates mediating the aversive effects of D-1 dopamine receptor antagonists. Psychopharmacology 103, 209–214 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244205
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244205