Abstract
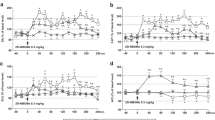
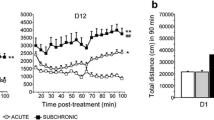
Clonazepam administration may lead to tolerance and “withdrawal” syndromes in clinical use. To assess the effects of this drug in a mouse model, we administered clonazepam (1.5 mg/kg/day) for 1–14 days and evaluated open-field activity, cortical clonazepam concentrations, and binding and function at the GABAA receptor. We also evaluated the same parameters at 1, 2, 4 and 7 days after discontinuation of 7 days of clonazepam administration. During chronic treatment, tolerance developed to the effects of clonazepam on motor activity at 7 days and persisted to 14 days. Cortical clonazepam concentrations did not change significantly during this period. Benzodiazepine receptor binding in vivo was decreased in cortex at days 7 and 14 of clonazepam, but was unchanged in other regions. Binding determined in vitro was also decreased at these points. TBPS (t-butylbicyclophosphorothionate) binding in cortex was slightly, but not significantly, decreased. Muscimol-stimulated chloride uptake was also decreased at days 7 and 14. After clonazepam discontinuation, open-field activity returned to control values at 1 day but was increased above baseline at 4 days. Benzodiazepine binding in vivo and in vitro, as well as TBPS binding, were increased at 4 days. Muscimol-stimulated chloride uptake was also increased at this point. These results indicate that chronic clonazepam administration is associated with tolerance to motoric effects, with discontinuation effects, and with receptor alterations in a mouse model. Clonazepam is similar to other benzodiazepines in this regard.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bang F, Birket-Smith E, Mikkelsen B (1976) Clonazepam in the treatment of epilepsy. Epilepsia 17:321–324
Browne TR (1983) Benzodiazepines. In: Browne TR, Feldman RG (eds) Epilepsy, diagnosis and management. Little Brown, Boston, pp 233–245
Davies MF, Sasaki SE, Carlen PL (1988) Hyperexcitability of hippocampal CA1 neurons in brain slices of rats chronically administered clonazepam. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247:737–744
Gent JP, Feely MP, Haigh JRM (1985) Differences between the tolerance characteristics of two anticonvulsant benzodiazepines. Life Sci 37:849–856
Greenblatt DJ, Shader RI (1978) Dependence, tolerance, and addiction to benzodiazepines. Drug Metab Dispos 8:13–28
Greenblatt DJ, Miller LG, Shader RI (1987) Clonazepam pharmacokinetics, brain uptake, and receptor interactions. J Clin Psychiatry 48 [Oct. Suppl.]:4–9
Haefely W (1988) Partial agonists of the benzodiazepine receptor: from animal data to results in patients. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 45:275–292
Haigh RM, Feely M, Gent JP (1986) Tolerance to the anticonvulsant effect of clonazepam in mice: no concurrent change in plasma concentration. J Pharm Pharmacol 38:931–934
Kang I, Miller LG (1991) Chronic lorazepan administration is associated with decreased GABAA receptor subunit nRNA concentrations. Brit J Pharmacol (in press)
Lopez F, Miller LG, Greenblatt DJ, Chesley S, Schatzki A, Shader RI (1990) Chronic administration of benzodiazepines. V. Rapid onset of behavioral and neurochemical alterations after alprazolam discontinuation. Neuropharmacology 29:237–241
Löscher W, Honack D, Hashem A (1987) Anticonvulsant efficacy of clonazepam and the beta-carboline ZK 93423 during chronic treatment in amygdala-kindled rats. Eur J Pharmacol 143:403–414
McPherson GA (1983) A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Prog Biomed 17:107–114
Miller LG, Greenblatt DJ, Paul SM, Shader RI (1987a) Benzodiazepine receptor occupancy in vivo: correlation with brain concentrations and pharmacodynamic actions. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 240:516–522
Miller LG, Friedman H, Greenblatt DJ (1987b) Measurement of clonazepam by electron-capture gas-liquid chromatography with application to single-dose pharmacokinetics. J Anal Toxicol 11:55–57
Miller LG, Greenblatt DJ, Barnhill JG, Shader RI (1988a) Chronic benzodiazepine administration. I. Tolerance is associated with benzodiazepine receptor downregulation and decreased gamma-aminobutryic acidA receptor function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:170–176
Miller LG, Greenblatt DJ, Roy RB, Summer WR, Shade RI (1988b) Chronic benzodiazepine administration. II. Discontinuation syndrome is associated with upregulation of gamma-aminobutryic acidA receptor complex binding and function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 246:177–182
Miller LG, Woolverton S, Greenblatt DJ, Lopez F, Shader RI (1989a) Chronic benzodiazepine administration. IV. Rapid development of tolerance and receptor downregulation associated with alprazolam administration. Biochem Pharmacol 38:3773–3777
Miller LG, Roy RB, Weill CL (1989b) Chronic clonazepam administration decreases GABAA receptor function in cultured cortical neurons. Mol Pharmacol 36:796–802
Petursson H, Lader MH (1981) Benzodiazepine dependence. Br J Addict 76:133–145
Rosenberg HC, Tietz EL, Chiu TH (1989) Tolerance to anticonvulsant effects of diazepam, clonazepam, and clobazam in amygdala-kindled rats. Epilepsia 30:276–285
Scherkl R, Frey H-H (1986) Physical dependence on clonazepam in dogs. Pharmacology 32:18–24
Scherkl R, Scheuler W, Frey H-H (1985) Anticonvulsant effect of clonazepam in the dog. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 278:249–256
Schobben F (1979) Pharmacokinetics and therapeutics in epilepsy. Thesis, Catholic University of Nijmegen, Netherlands, pp 251–258
Sher PK, Machen VL (1987) Benzodiazepine receptor affinity alterations at physiologic temperature after chronic clonazepam exposure. Brain Dev 9:33–36
Specht U, Boenigk HE, Wolf P (1989) Discontinuation of clonazepam after long-term treatment. Epilepsia 30:458–463
Young NS, Lewis SJ, Harris QL, Jarrott B, Vajda FJE (1988) Differences in the development of tolerance to two anticonvulsant benzodiazepines in the amygdaloid kindled rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 40:365–367
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galpern, W.R., Lumpkin, M., Greenblatt, D.J. et al. Chronic benzodiazepine administration. Psychopharmacology 104, 225–230 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244183
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244183