Summary
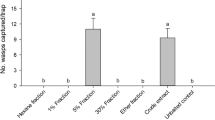
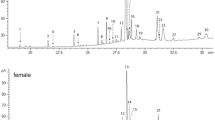
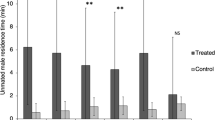
The presence of sex pheromones in six Japanese species of the genusVespa was demonstrated by laboratory assyas using intact queens and their ether extracts. Clear interspecific cross-activities of the pheromones was found for all pairwise combinations between five of the six sympatric species,V. analis, V. mandarinia, V. tropica, V. simillima xanthoptera andV. crabro.
Zusammenfassung
Geschlechtsphromone wurden bei sechs japanischenVespa-Arten in Laborversuchen nachgewiesen, wobei sowohl intakte Königinnen wie auch deren Atherextrakte getestet wurden. Eine deutliche interspezifische Wirksamkeit der Pheromone wurde bei allen paarweisen Kombinationen zwischen fünf der sechs sympatrischen rten gefunden, und zwar beiV. analis, V. mandarina, V. tropica, V. simillima xanthoptera undV. crabro.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batra S.W.T., 1980.—Sexual behavior and phromones of European hornet,Vespa crabro germana (Hymenoptera; Vespidae).J. Kan. entomol. Soc., 53, 461–469.
Bulter C.G., Calam D.H., Callow R.K., 1967.—Attraction ofApis mellifera drones by the odours of the queen of two other species of honeybees.Nature, 213, 423–424.
Engels E., Engels W., 1984.—Drohnen-Ansammlungen bei Nestern der Stachellosen BieneScaptotrigona postica.Apidologie, 15, 315–328.
Gary N.E., 1962.—Chemical mating attractants in the queen honeybee.Science, 136, 773–774.
Hölldobler B., 1971.—Sex pheromone in the antXenomyrmex floridanus.J. Insect Physiol., 17, 1497–1499.
Hölldobler B., 1976.—The behavioral ecology of mating in harvester ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae:Pogonomyrmex).Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol., 1, 405–423.
Hölldobler B., 1985.—Evolution of insect communication.In:Insect communication, ed. T. Lewis, pp.349–377, Academic Press. London, 414 p.
van Honk C.G.J., Velthuis H.H.W., Wöseler P.F., 1978.—A sex pheromone from the mandibular glands in bumblebee queens.Experientica, 34, 838–839.
Koeniger N., Wijayagunasekera H.N.P., 1976.—Time of drome flight in the three Asiatic honeybee species (Apis cerana, Apis florea, Apis dorsata).J. apic. Res., 15, 67–71.
Matsuura M., 1984.—Comparative biology of the five Japanese spcies of the genusVespa (Hymenoptera, Vespidae).Bull. Fac. Agr. Mie Univ., 69, 1–131.
Morse R.A., 1985.—Some questions about reproduction in honey bees.Honeybee Science, 6, 49–52 (In Japanese).
Ono M., Sasaki M., Okada I., 1985.—Mating behavior of the giant hornet,Vespa mandarinia Smith and its pheromonal regulation.Proc. 30th Int. Apicult. Cong., Nagoya, Japan, 255–259.
Post D.C., Jeanne R.L., 1983.—Venom source of a sex pheromone in the social waspPolistes fuscatus (Hymenoptera: Vespidae).J. Chem. Ecol., 9, 259–266.
Post D.C., Jeane R.L., 1984.—Venom as an interspecific sex pheromone, and species recognition by a cuticular pheromone in paper wasps (Polistes, Hymenoptera: Vespidae).Physiol. Entomol., 9, 65–75.
Post D.C., Jeanne R.L., 1985.—Sex pheromone inPolistes fuscatus (Hymenoptera: Vespidae): Effect of age, caste and mating.Insect. Soc., 32, 70–77.
Ruttner F., 1973.—Drohnen vonApis cerana Fabr. auf einem Drohnensammelplatz.Apidologie, 4, 41–44.
Ruttner F., Kaissling K.E., 1968.—Über die interspezifische Wirkung des Sexuallockstoffes vonApis mellifera undApis cerana.Z. veergl. Physiol., 59, 362–370.
Ruttner F., Maul V., 1983.—Experimental analysis of reproductive interspecies isolation ofapis mellifera L. andApis cerana FabrApidologie, 14, 309–327.
Sannasi A., Rajulu G., 1971.—9-oxodec-rrans-2-enoic acid in the honeybees.Life Sciences, 10, 195–201.
Shearer D.A., Boch R., Morse R.A., Laigo F.M., 1970.—Occurrence of 9-oxodec-trans-2-enoic acid in queens ofApis dorsata, Apis cerana, andApis mellifera.J. Insect Physiol., 16, 1437–1441.
Strambi A., 1985.—Physiological aspects of casta differentiation in social wasps.In:Caste differentiation in social insects, eds. J.A.L.Watson, B.M. Okot-Kotber, C.T. Noirot, pp. 371–384, Pergamon Press, Oxford, 405 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ono, M., Sasaki, M. Sex pheromones and their cross-activities in six Japanese sympatri species of the genus Vespa. Ins. Soc 34, 252–260 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02224357
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02224357