Abstract
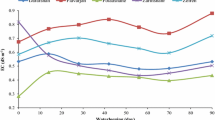
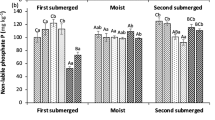
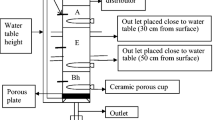
Soil samples from surface and sub-surface horizons in the well-drained and poorly-drained members of three soil catenas were incubated under submergence or at field capacity to study the effects of these incubation conditions and prior natural drainage on the solubility of four plant micro-nutrients. Iron, Mn, Zn and Cu were extracted by water using a 1∶1 water:soil ratio. The four micronutrient metals were also extracted by DTPA solutions buffered at either pH 5.3 or pH 7.3 to compare the effectiveness of these two extractants under these incubation conditions with acid soils. Generally the extractability of the nutrients was much affected by the horizon (A, E or B) with A horizons having the greatest amounts of all nutrients and undergoing greater changes in water- and DTPA-extractability during incubation. Soil drainage class (wellvs. poorly drained) had few effects. Incubation moisture regime had major effects on water extractable Fe and Mn with lesser effects on Zn and Cu. Submerged soils generally had the greatest levels of water extractable nutrients, though rice uptake did not reflect this. DTPA at pH 5.3 extracted 2 to 3 times as much Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu as did DTPA at pH 7.3 and about 50 to 100 times as much as did water. Correlations between DTPA extractable nutrients and rice uptake were significant only for Fe and Cu and declined during incubation. The changes in all variables during incubation were complex, being related to soil properties such as organic matter content, pH and mineralogy as well as to incubation conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grieve C M and Fujiyama H 1987 The response of two rice cultivars to external Na/Ca ratios. Plant and Soil 103, 245–250.
Haldar M and Mandal L N 1979 Influence of soil moisture regimes and organic matter application on the extractable Zn and Cu content in rice soil. Plant and Soil 53, 203–213.
Islam A and Islam W 1973 Chemistry of submerged soils and growth and yield of rice. I. Benefits from submergence. Plant and Soil 39, 555–565.
Islam A and Ullah S M 1973 Chemistry of submerged soils and growth and yield of rice II. Effect of additional application of fertilizers on soil at field capacity. Plant and Soil 39, 567–579.
Iu K L, Pulford I D and Duncan H J 1981 Influence of water-logging and lime or organic matter additions on the distribution of trace metals in an acid soil. I. Manganese and iron. Plant and Soil 59, 317–326.
Lindsay W L and Norvell W A 1978 Development of a DTPA soil test for Zn, Fe, Mn, and Cu. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 42, 421–428.
Mahapatra I C and Patrick W H Jr 1969 Inorganic phosphate transformation in waterlogged soils. Soil Sci. 107, 281–288.
Norvell W A 1984 Comparison of chelating agents as extractants for metals in diverse soil materials. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 48, 1285–1291.
Ponnamperuma F N 1965 Dynamic aspects of flooded soils and the nutrition of the rice plant.In International Rice Res. Institute. The mineral nutrition of the rice plant. pp 295–328. Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, Maryland.
Sah R N and Mikkelsen D S 1986 Transformations of inorganic phosphorous during the flooding and draining cycles of soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 62–67.
Sajawan K S and Lindsay W L 1985 Effects of redox on zinc deficiency in paddy rice. Soil. Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 1264–1269.
SAS Institute Inc 1982 SAS User's Guide: Statistics. 1982. Edition. SAS Instit. Inc. Cary, NC 584 pp.
Sims J T 1986 Soil pH effects on the distribution and plant availability of manganese, copper and zinc. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 50, 367–373.
Soil Conservation Services 1972 Soil survey laboratory methods and procedures for collecting soil samples. US Dept. Agric. Soil Survey Investigation Rep. No. 1. US Gov. Printing Office. Washington, DC.
Veneman P L M and Bodine S M 1982 Chemical and morphological soil characteristics in a New England drainage-Toposequence. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 46, 359–363.
Weil R R, Benedetto P W, Sikora L J and Bandel V A 1988 Influence of tillage practices on phosphorous distribution and forms in three Ultisols. Agron. J. 80, 503–509.
Yoshida S and Tanaka A 1969 Zinc deficiency of the rice plant in calcareous soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 15, 75–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weil, R.R., Holah, S.S. Effect of submergence on availability of certain plant nutrients in three Ultisol catenas. Plant Soil 114, 147–157 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02220793
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02220793