Abstract
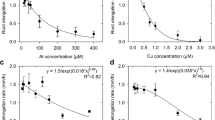
The effects of the divalent metal ions Zn, Cd, Hg, Cu and Pb on the ATPase activity of a plasma membrane fraction isolated from roots ofZea mays have been investigated. When Mg-ions (3 mM), with or without K-ions (50mM) are included in the reaction medium, inhibition of ATPase activity was found in all cases, the relative order of the inhibitors over the concentration range 10 to 100μM, being Hg>>Cu∼Cd>Zn∼Pb. Below 1.0μM only Hg caused substantial inhibition. In the absence of Mg ions, Zn and to a lesser extent Cd, activated the enzyme up to a concentration of 1 mM, activity being further stimulated in the presence of K-ions (50mM). No activation of ATPase activity was found for Hg, Cu or Pb. It was concluded that Zn-ATP and Cd-ATP are both alternative substrates for the enzyme. Further experiments showed that both Km and Vmax for the substrates Zn-ATP and Cd-ATP are very much lower than for the usual substrate Mg-ATP.
These present results are discussed in relation to the known actions of these divalent cations on the trans-root potential and H-ion efflux in excised maize roots (Kennedy and Gonsalves, 1987).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DTT:
-
DL-dithiothreitol
- EDTA:
-
Ethylene diamine tetra-actetic acid, disodium salt
- MES:
-
2-[N-morpholino] ethanesulphonic acid
- TES:
-
2([-hydroxyl-1, 1-bis(hydroxymethylethyl)] amino) ethanesulphonic acid
- TRIS:
-
2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl) 1,3-propandiol
- TRP:
-
trans-root potential
References
Beffagna N, Marrè E and Cocucci S 1979 Cation activated ATPase activity of plasmalemma enriched membrane preparations from maize coleoptiles. Planta 146, 387–391.
Bowling DJF and Dunlop J 1978 Uptake of phosphate by white clover. I. Evidence for an electrogenic phosphate pump. J. Exp. Bot. 29, 1139–1146.
Briskin DP and Leonard RT 1982 Phosphorylation of the ATPase in the deoxycholate treated plasma membrane fraction from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 70, 1459–1464.
Churchill KA and Sze H 1984 Anion-sensitive H+-pumping ATPase of oat roots. Plant Physiol. 76, 490–497.
Dixon M and Webb EC 1979aIn Enzymes. pp. 315–316. Longman Group Limited, London, U.K.
Dixon M and Webb EC 1979In Enzymes. pp. 72–75. Longman Group Limited, London, U.K.
Dunlop J and Bowling DJF 1978 Uptake of phosphate by white clover. II. The effect of pH on the electrogenic phosphate pump. J. Exp. Bot. 29, 1147–1153.
DuPont FM, Burk LL and Spanswick RM 1981 Characterisation of a partially purified ATPase from a corn root plasma membrane fraction. Plant Physiol. 67, 59–63.
DuPont FM, Giorgi D and Spanswick RM 1982 Characteristics of a proton-translocating ATPase in microsomal vesicles from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 70, 1694–1699.
Fiske CH and Subbarow Y 1925 The colorimetric determination of phosphorous. J. Biol. Chem. 66, 375–400.
Gerhardt B and Beevers H 1968 Influence of sucrose on protein determination by the Lowry procedure. Anal. Biochem. 24, 337–352.
Gerritse RG and Van Driel W 1984 The relationship between adsorption of trace elements, organic matter and pH in temperate soils. J. Environ. Qual. 13, 197–204.
Giordano PM, Noggle JC and Mortvedt JJ 1974 Zinc uptake by rice as affected by metabolic inhibitors and competing cations. Plant and Soil 41, 637–646.
Hodges TK and Leonard RT 1972 Purification of a plasma membrane-bound adenosine triphosphatase from plant roots.In Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 32. Eds. SP Colowick and NO Kaplan. pp. 392–406. Academic Press, New York, London.
Jung KD, Lüttge V and Fisher E 1982 Uptake of neutral and acidic amino acids byLemna gibba correlated with the H+ electro-chemical gradient at the plasmalemma. Physiol. Plant. 55, 351–355.
Kennedy CD and Gonsalves FAN 1987 The action of divalent zinc, cadmium, mercury, copper and lad on the trans-root potential and H+ efflux of excised roots. J. Exp. Bot. 38, 800–817.
Kennedy CD and Stewart RA 1982 Glucose induced H+ influx and transient currents in excised roots, Particularly those ofZea mays. J. Exp. Bot. 33, 1220–1238.
Kinraide TB and Etherton B 1980 Electrical evidence for different mechanisms of uptake for basic, neutral and acidic amino acids in oat coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 65, 1085–1089.
Larsson C, Kjellbom P, Widell S and Lundborg T 1984 Sidedness of plant plasma membrane vesicles purified by partitioning in aqueous two-phase systems. FEBS Lett. 171, 271–276.
Leonard RT and Hodges TK 1973 Characterisation of plasma membrane associated ATPase activity of oat roots. Plant Physiol. 52, 6–12.
Leonard RT and Hotchkiss WJ 1976 Cation stimulated ATPase activity and cation transport in corn roots. Plant Physiol. 57, 105–114.
Lindberg SE, Jackson DR, Huckabee JW, Janzen SA, Levin MJ and Lund JR 1979 Atmospheric emission and plant uptake of mercury from agricultural soils near the Almedén mercury mine. J. Environ. Qual. 8, 572–578.
Lowry DH, Rosenbraugh NJ, Farr AL and Randall RJ 1951 Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 192, 265–275.
Marschner H 1983 General introduction to the mineral nutrition of plants.In Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology, New Series, Vol. 15A. Inorganic Plant Nutrition. Eds. A, Läuchli and RL Bieleski. pp. 5–60. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, Tokyo.
Saunders JR and Adams J McM 1987 The effects of pH and soil type on the concentration of zinc, copper and nickel extracted by calcium chloride. Environ. Pollut. 43, 219–228.
Sze H 1983 Proton-pumping adenosine triphosphatase in membrane vesicles of tobacco callus. Sensitivity to vanadate and K+. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 732, 586–594.
Sze H 1984 H+ translocating ATPase of the plasma membrane and tonoplast of plant cells — a mini-review. Physiol. Plant. 61, 683–691.
Ure AM and Berrow ML 1982 The elemental constituents of soils.In Environmental Chemistry. Vol. 2. pp. 94–204. Specialist Periodical Report, The Royal Society of Chemistry, London.
Wainwright SJ and Woolhouse HW 1977 Some physiological aspects of copper and zinc tolerance inAgrostis tenuis Sibth. Cell elongation and membrane damage. J. Exp. Bot. 28, 1029–1036.
Wong MH and Lau WM 1983 Effects of roadside soil extracts on seed germination and root elongation of edible crops. Environ. Pollut. (Series A) 31, 203–215.
Woolhouse HW 1983 Toxicity and tolerance in the response of plants to metals.In Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology, New Series, Vol. 12C. Physiological Plant Ecology III. Eds. O. L. Lange, P.S. Boble, C. B. Osmond, and H. Ziegler, pp. 245–300. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
Zocchi G and Hanson JB, 1983 Calcium transport and ATPase activity in a microsomal vesicle fraction from corn roots. Plant Cell Environ. 6, 203–209.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kennedy, C.D., Gonsalves, F.A.N. The action of divalen Zn, Cd, Hg, Cu and Pb ions on the ATPase activity of a plasma membrane fraction isolated from roots ofZea mays . Plant Soil 117, 167–175 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02220709
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02220709