Abstract
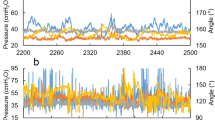
Our aims were to measure antral axial forces in patients with suspected upper gut dysmotilities and to compare the number of antral contractions detected by an axial force catheter and by manometric sensors in the distal antrum and pylorus. Fifteen patients (2 men, 13 women; mean age 42 years) underwent studies for 3 hr fasting, 2 hr postprandially, and up to 60 min after intravenous erythromycin (3 mg/kg). Seven patients had gastroparesis or chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction, five functional disease, and three subacute obstruction. Postprandially, the number of peaks detected by the two methods was not significantly different; however, after erythromycin, the axial catheter detected more contractions (P=0.02). Erythromycin significantly increased the number of postprandial axial forces (from 1.2±0.3/min to 2.5±0.3/min,P≤0.01) in the whole group and in the organic dysmotility group (P=0.01). Erythromycin significantly increases the number of axial forces in functional and organic upper gut dysmotilities, but the axial force catheter is not advantageous over manometry for postprandial measurements of antral motility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Camilleri M, Malagelada J-R, Brown ML, Becker G, Zinsmeister AR: Relation between antral motility and gastric emptying of solids and liquids in humans. Am J Physiol 249:G580-G585, 1985
Camilleri M, Brown ML, Malagelada J-R: Relationship between impaired gastric emptying and abnormal gastrointestinal motility. Gastroenterology 91:94–99, 1986
Vassallo M, Camilleri M, Prather CM, Hanson RB, Thomforde GM: Measurement of axial forces during emptying from the human stomach. Am J Physiol 263:G230-G239, 1992
Prather CM, Camilleri M, Thomforde GM, Forstrom LA, Zinsmeister AR: Gastric axial forces in experimentally-delayed and accelerated gastric emptying. Am J Physiol 264:G928-G934, 1993
Hveem K, Sun WM, Hebbard GS, Horowitz M, Dent J: Insights into stomach mechanisms from concurrent gastric ultrasound and manometry. Gastroenterology 107:A1236, 1994
Fraser RJ, Horowitz M, Maddox AF, Dent J: Postprandial antropyloroduodenal motility and gastric emptying in gastroparesis—effects of eisapride. Gut 35:172–178, 1994
Williams D, Thompson DG, Heggie L, O'Hanrahan T, Bancewicz J: Esophageal clearance function following treatment esophagitis. Gastroenterology 106:108–116, 1994
Williams D, Thompson DG, Marples M, Heggie L, O'Hanrahan T, Mani V, Bancewicz J: Identification of an abnormal esophageal clearance response to intraluminal distension in patients with esophagitis. Gastroenterology 103:943–953, 1992
Camilleri M, Malagelada J-R, Stanghellini V, Zinsmeister AR, Kao PC, Li CH: Dose-related effects of synthetic human β-endorphin and naloxone on fed upper gastrointestinal motility. Am J Physiol 251:G147-G154, 1986
Annese V, Janssens J, Vantrappen G, Tack J, Peeters TL, Willemse P, Van Cutsem E: Erythromycin accelerates gastric emptying by inducing antral contractions and improved gastroduodenal coordination. Gastroenterology 102:823–828 1992
Bruley des Varannes S, Parys V, Ropert A, Chayvialle JA, Roze C, Galmiche JP: Erythromycin enhances fasting and postprandial proximal gastric tone in humans. Gastroenterology 109:32–39, 1995
Keshavarzian A, Isaae RM: Erythromycin accelerates gastric emptying of indigestible solids and transpyloric migration of the tip of an enteral feeding tube in fasting and fed states. Am J Gastroenterol 88:193–197, 1993
Ahluwalia NK, Thompson DG, Barlow J, Heggie L: Human small intestinal contractions and aboral traction forces during fasting and after feeding. Gut 35:625–630, 1994
Tack J, Janssens J, Vantrappen G, Peeters T, Annese V, Depoortere I, Muls E, Bouillon R: Effect of erythromycin on gastric motility in controls and in diabetic gastroparesis. Gastroenterology 103:72–79, 1992
Fraser R, Shearer T, Fuller J, Horowitz M, Dent J: Intravenous erythromycin overcomes small intestinal feedback on antral, pyloric, and duodenal motility. Gastroenterology 103:114–119, 1992
Camilleri M: Study of human gastroduodenojejunal motility: Applied physiology in clinical practice. Dig Dis Sci 38:785–794, 1993
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surrenti, E., Camilleri, M., Kammer, P.P. et al. Antral axial forces postprandially and after erythromycin in organic and functional dysmotilities. Digest Dis Sci 41, 697–704 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02213125
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02213125