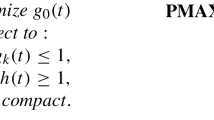Abstract
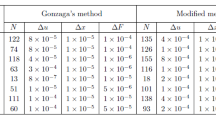
This work examines the generalization of a certain interior-point method, namely the method of analytic centers, to semi-infinite linear programming problems. We define an analytic center for these problems and an appropriate norm to examine Newton's method for computing this center. A simple algorithm of order zero is constructed and a convergence proof for that algorithm is given. Finally, we describe a more practical implementation of a predictor-corrector method and give some numerical results. In particular we concentrate on practical integration rules that take care of the specific structure of the integrals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.J. Davis and P. Rabinowitz,Methods of Numerical Integration (Academic Press, New York, 1975).
A.V. Fiacco and K.O. Kortanek,Semi-infinite Programming and Applications, An International Symposium, Austin, TX, 1981, Lecture Notes in Economics and Mathematical Systems Vol. 215 (Springer, Berlin, 1983).
M. C. Ferris and A.B. Philpott, An interior point algorithm for semi-infinite linear programming, Mathematical Programming 43(1989)257–276.
M.C. Ferris and A.B. Philpott, On affine scaling and semi-infinite programming, Mathematical Programming 56(1992)361–364.
K. Glashoff and S.Å. Gustafson,Einführung in die lineare Optimierung (Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft, Darmstadt, 1978).
C.C. Gonzaga, An algorithm for solving linear programming problems inO(n 3 L) operations, Memo No. UCB/ERL M87/10, College of Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 (1987).
R. Hettich, A comparison of some numerical methods for semi-infinite programming, in:Semiinfinite Programming, Proc. Workshop, ed. R. Hettich, Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences, Vol. 15 (1978) pp. 112–125.
R. Hettich and P. Zencke,Numerische Methoden der Approximation und semi-infiniten Optimierung (B.G. Teubner, Stuttgart, 1982).
F. Jarre,The Method of Analytic Centers for Smooth Convex Programs, Dissertation, Universität Würzburg (Grottenthaler Verlag, Bamberg, 1989).
F. Jarre, G. Sonnevend and J. Stoer, An implementation of the method of analytic centers, in:Analysis and Optimization of Systems, ed. A. Bensoussan and J.L. Lions, Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences, Vol. 111 (1988).
N. Karmarkar, A new polynomial-time algorithm for linear programming, Combinatorica 4 (1984)373–395.
J. Mennicken, Implementation of a first order central path following algorithm for solving large linear programs, Report No. 202, Schwerpunktprogramm der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft — Anwendungsbezogenen Optimierung und Steuerung, Institut für Angewandte Mathematik und Statistik der Universität Würzburg, Germany (1990).
M.R. Osborne and G.A. Watson, A note on singular minimax approximation problems, J. Math. Anal. Appl. 25(1969)692–700.
J. Renegal, A polynomial time algorithm based on Newton's method for linear programming, Mathematical Programming 40(1988)59–93.
U. Schättler, An interior-point method for semi-infinite programming problems Ph.D. Thesis, Institut für Angewandte Mathematik und Statistik der Universität Würzburg, Germany (1992).
G. Sonnevend, An “analytical centre” for polyhedrons and new classes of global algorithms for linear (smooth, convex) programming, in:Proc. 12th IFIP Conf. on System Modelling and Optimization, Lecture Notes in Control and Information Sciences, Vol. 84 (Springer, 1986) pp. 866–876.
G. Sonnevend and J. Stoer, Global ellipsoidal approximations and homotopy methods for solving convex analytic programs, Applied Mathematics and Optimization 21(1990)139–165.
G. Sonnevend, J. Stoer and G. Zhao, On the complexity of following the central path of linear programs by linear extrapolation II, in:Proc. Conf. on Interior Point Methods in Linear Programming, ed. C. Roos and J.P. Vial, to appear in Mathematical Programming, Study Series B.
M.J. Todd, Interior point algorithms for semi-infinite programming, Technical Report No. 978, College of Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853-3801 (August 1991).
L. Tunçel and M.J. Todd, Asymptotic behavior of interior-point methods: A view from semiinfinite programming, Technical Report 1031, School of Operations Research and Industrial Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853-3801 (September 1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schättler, U. An interior-point method for semi-infinite programming problems. Ann Oper Res 62, 277–301 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02206820
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02206820