Summary
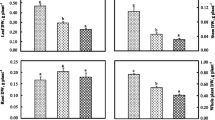
Iron chlorosis of 4 year old Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) in comparison to areas of adjacent healthy growth on calcareous prairie soil, was associated with slight increases in the soluble ion content of the saturation paste extract. Such increases in soluble ions (mainly calcium sulphate) were associated with significant increases in ash, cation (including iron) and organic anion content of the chlorotic needles. Increasing levels of available soil nitrate were also related to increase in organic anions. Nitrogen and phosphorus assimilation was adversely affected under conditions of iron chlorosis. These observations support the theory of induced iron deficiency associated with elevated levels of organic anions or translocated cations and are applicable to plantings of conifers on prairie soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canada Soil Survey Committee 1978 Manual on Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis. Ed. J. A. McKeague. Soil Research Inst., Ottawa.
Carter, M. R. 1979 Soil and plant nutrition projects. Annu. Rep. 1979. PFRA Tree Nursery, Indian Head, Saskatchewan.
Clement, A. 1977 Comparison between the mineral nutrition ofPinus nigra nigricans andPicea excelsia in very calcareous, calcareous and non-calcareous soils, effects of mineral and organic anions on metabolism. Ann. Sci. For.34, 293–309.
Cram, W. H. and Luken, H. 1961 Salinity tolerance of conifers. Paper presented at Can. Soc. Hortic. Sci. Regina, Saskatchewan.
Dale, J., McComb, A. L. and Loomis, W. E. 1955 Chlorosis, mycorrhizae and the growth of pines on a high-lime soil. For. Sci.1, 148–157.
Hacskaylo, J., Finn, R. F. and Vimmerstedt, J. P. 1969 Deficiency Symptoms of Some Forest Trees. Ohio Agric. Res. Development Center, Wooster, Ohio Res. Bull. 1015.
Kirby, E. A. and Knight, A. H. 1977 Influence of the level of nitrate nutrition on ion uptake and assimilation, organic acid accumulation, and cation-anion balance in whole tomato plants. Plant Physiol.60, 349–353.
Le Tacon, F. 1978 The presence of calcium carbonate in soil. Influence on the behaviour of Norway spruce (Picea excelsa) and Austrian pine (Pinus nigra nigricans). Ann. Sci. Forest35, 165–174.
Meek, B. D., Graham, L. E., Donovan, T. J. and Mayberry, K. S. 1979 Phosphorus availability in a calcareous soil after high loading rates of animal manure. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J.43, 741–744.
Nelson, L. E. and Selby, R. 1974 The effect of nitrogen sources and iron levels on the growth and composition of Sitka spruce and Scots pine. Plant and Soil41, 573–588.
Pierre, W. H. and Banwart, W. L. 1973 Excess-base and excess-base/nitrogen ratio of various crop species and parts of plants. Agron. J.65, 91–96.
Richards, B. N. and Wilson, G. L. 1963 Nutrient supply and mycorrhiza development in Caribbean pine. For. Sci.9, 405–412.
Stoeckler, J. H. 1965 Conifer Nursery Practive in the Prairie Plains. USDA For. Serv. Agric. Handbook No.279 p. 19.
Tiffin, L. O. 1972 Translocation of micronutrients in plants.In Micronutrients in Agriculture, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Madison, Wisconsin, p. 199–299.
Van Den Driessche, R. 1978 Response of Douglas fir seedlings to nitrate and ammonium nitrogen sources at different levels of pH and iron supply. Plant and Soil49, 607–623.
Wallace, A., Wood, R. A. and Soufi, S. M. 1976 Cation-anion balance in lime-induced chlorosis. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal.7, 15–26.
Yaalon, D. H. 1957 Problems of soil testing on calcareous soils. Plant and Soil8, 275–288.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carter, M.R. Association of cation and organic anion accumulation with iron chlorosis of Scots pine on prairie soils. Plant Soil 56, 293–300 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02205858
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02205858