Summary
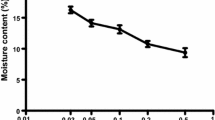
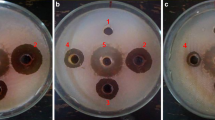
Alachlor was more inhibitory toRhizoctonia solani growth than fluchloralin in potato dextrose broth (PDB). Infective capacity of the pathogen was not altered by growing it in a medium containing either of the herbicides. Cowpea seedlings grown in alachlor-treated soil were more susceptible toR. solani than those treated with fluchloralin and the untreated seedlings. Pre-sowing application of alachlor in soil (5 μl a.i./kg) aggravated damping-off whereas fluchloralin decreased the disease incidence to nearly half of that in untreated soil in greenhouse pot tests (av. temperature 31±5°C). Both herbicides reduced damping-off in pots kept at constant temperature of 30°C and increased the disease incidence at 20°C. Fungus growth in culture was stimulated at 20° but was strongly inhibited at 30°C by both herbicides. Growth inhibition by herbicides was maximum in PDB of pH 8 and decreased steadily up to pH 5.
Impact of fluchloralin and alachlor onR. solani damping-off of cowpea appears to be due to the predisposing effect by the herbicides on the susceptibility of the host and is influenced by atmospheric temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman J 1972 Increased glucose exudate and damping-off in sugarbeets in soils treated with herbicides. Phytopathology 62, 743.
Altman J and Campbell C L 1977 Effect of herbicides on plant diseases. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 15, 361–385.
Chandler J M and Santelmann P W 1968 Interactions of four herbicides withRhizoctonia solani on seedling cotton. Weed Sci. 16, 453–456.
Hill R L and Wright J L 1978 Pesticide Microbiology. Academic Press, London & New York.
Kataria H R and Dodan D S 1981 Pathogenesis ofPythium butleri on cowpea as influenced by two herbicides. Z. Pfl. krankh. Pfl. schutz. 88, 734–743.
Kataria H R and Dodan D S 1982 The influence of two herbicides on antifungal activity of some fungicides againstPythium butleri andRhizoctonia solani causing damping-off of cowpea. Pestic. Sci. 13, 583–588.
Neubauer R and Avizohar-Hershenson Z 1973 Effect of the herbicide, trifluralin, onRhizoctonia disease in cotton. Phytopathology 63, 651–652.
Romig W R and Sasser M 1972 Herbicide predisposition of snapbeans toRhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology 62, 785–786.
Wyse D L, Meggitt W F and Penner D 1976 Effect of herbicides on the development of root rot on navy bean. Weed Sci. 24, 11–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kataria, H.R., Dodan, D.S. Impact of two soil-applied herbicides on damping-off of cowpea caused byRhizoctonia solani . Plant Soil 73, 275–283 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02197723
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02197723