Summary
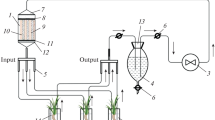
The importance of the Zn buffer power and its influence on the Zn concentration in soil solution was investigated in a simulatory experiment where the soil in question, previously treated with Zn and compacted to known bulk density, was eluted with 0.01M CaCl2 under constant hydraulic head. The data so obtained were correlated with Zn, uptake by maize. The correlation coefficient for effluent Znvs total Zn uptake improved, remarkably when the corresponding Zn buffer power was also incorporated into the computations. It is concluded from this and the earlier investigation2 that the Zn buffer power is the most important parameter governing Zn uptake by maize.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cottenie A, Verloo M and Velghe G 1980 La spectrométrie d'émission à plasma inductif appliquée à l'analyse des plantes. Spectra 2000, 63, 69–74.
Prabhakaran Nair K P 1984 Zinc buffer power as an important criterion for a dependable assessment of plant uptake. Plant and Soil 81, 209–215.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prabhakaran Nair, K.P., Ram, N. & Sharma, P.K. Quantitative relationship between zinc transport and plant uptake. Plant Soil 81, 217–220 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02197154
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02197154