Summary
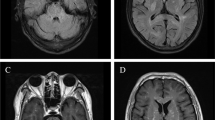
The course of a patient suffering from superficial siderosis of the central nervous system for 37 years is presented and diagnostic and therapeutic approaches are evaluated. The syndrome is clinically defined by slowly progressing deafness, cerebellar ataxia, myelopathy and neuropsychological deficits in combination with recurrent xanthochromia of the cerebrospinal fluid with siderophages. The diagnosis may be confirmed by computed tomography, which shows degeneration of the cerebellar vermis, and by magnetic resonance imaging, demonstrating iron deposits on the surface of brain, brain stem and spinal cord. Therapy should seek to identify and remove the source of bleeding, since pharmacotherapy with iron-depleting drugs is of limited effectiveness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braham J, Wolman M (1965) Subpial siderosis of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 4:559–562
Cammermeyer J (1947) Deposition of iron in paraventricular areas of the human brain in haemochromatosis. J Neuropath Exp Neurol 6:111
Castaigne P, Escourolle R, Laplane D, Berger B, Augustin P (1967) Étude anatomo-clinique d'un cas de sidérose marginale du système nerveux central. Rev Neurol (Paris) 116:105–118
Dastur DK, Sinh G (1962) Toxic iron and the nervous system. Siderotic necrosis of spinal root sheaths, ganglia and nerve, and siderosis of central nervous border-zones, in a case of “pinealoma”. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 2:161–176
Garcin R, Lapresle JI (1957) Sur un cas de surcharge ferrique du système nerveux central. Rev Neurol (Paris) 97:417–432
Gomori JM, Grossman RI, Bilaniuk LT, Zimmerman RA, Goldberg HI (1985) High field MR imaging of superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. J Comput Assist Tomogr 9:972–975
Gomori JM, Grossman RI, Goldberg HI, Hackney DB, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT (1987) High-field spin-echo MR imaging of superficial and subependymal siderosis secondary to neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage. Neuroradiology 29:339–342
Hughes JT, Oppenheimer DR (1969) Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. A report on nine cases with autopsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 13:56–74
Katsuragi S, Sakai T, Watanabe T, Shimoji A, Deshimaru M, Kuramoto R, Miyamoto K, Yamashita K, Miyakawa T (1988) An autopsy case of idiopathic superficial hemosiderosis of the central nervous system: a microscopic and immunohistochemical study. Clin Neuropathol 7:87–92
Koeppen AHW, Barron KD (1971) Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. A histological, histochemical and chemical study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 30:448–469
Koeppen AH, Dentinger, MP (1988) Brain hemosiderin and superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 47:249–270
Lewey FH, Govons SR (1942) Hemochromatotic pigmentation on the central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1:129–138
McGee DA, Patter HJ van, Morotta J, Olszewski J (1962) Subpial cerebral siderosis. Neurology 12:108–113
Neumann MA (1948) Hemochromatosis of the central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 7:19–34
Neumann MA (1956) Hemochromatotic pigmentation of the central nervous system. Arch Neurol 76:355–368
Noetzel H (1940) Diffusion von Blutfarbstoff in der inneren Randzone und äußeren Oberfläche des Zentralnervensystems bei subarachnoidaler Blutung. Arch Psychiatr 111:129–138
Noetzel H, Ohlmeier R (1963) Zur Frage der Randzonensiderose des Zentralnervensystems (Tierexperimentelle Untersuchung). Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 13:164–183
Pinkston JW, Ballinger WE, Lotz PR, Friedman WA (1983) Superficial siderosis: a cause of leptomeningeal enhancement on computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 7:1073–1076
Rosenthal P (1958) Siderose der Randzonen des Zentralnervensystems. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd 178:431–472
Sherwin I, Toll K (1972) Superficial hemosiderosis of the central nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 18:413–417
Tomlinson BE, Walton JN (1964) Superficial haemosiderosis of the central nervous system. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 27:332–339
Ulrich J, Isler W, Vassalli L (1965) L'effet d'hémorragies leptoméningées répétées sur le système nerveux (la sidérose marginale du système nerveux central). Rev Neurol (Paris) 112:466–471
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stevens, I., Petersen, D., Grodd, W. et al. Superficial siderosis of the central nervous system. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Nuerosci 241, 57–60 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02193756
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02193756