Summary
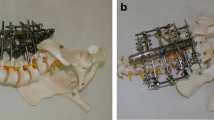
We studied the influence of instability of the spondylolisthesic segment upon anterior interbody fusion (AIF) rates. A one-level AIF of the lumbar spine by the modified extraperitoneal Bailey-Badgley fusion construct was performed in 26 patients with chronic or recurring acute low-back pain and/or other symptoms due to grades I and II spondylolisthesis. Sixteen were degenerative type, and 10 were isthmic type. Seventeen were female and 9, male. The average age was 41.2 years. The number of cases of spondylolisthesis at the level of L4–5 and L5-S1 as 18 and 8, respectively. In the 16 cases of degenerative type, 13 were grade I slip, and 3 were grade II slip, while in the 10 cases of isthmic type, 8 were grade I slip, and 2 were grade II slip. The average postoperative follow-up was 6 years (range 2–10 years). Solid fusion was obtained in 15 (93.8%) of the cases of degenerative spondylolisthesis and in 6 of the cases of isthmic type. Thus, the overall fusion rate was 80.7% (21 cases). However, some graft crumbling and redisplacement developed in 1 of the cases of degenerative type and 6 of the cases of isthmic type. Non-union developed in 4 (57.1%) of those 7 cases of graft crumbling (3 isthmic and 1 degenerative type). Fusion took 7 months on average (range 5–9 months). It is hypothesised that the isthmic-type spondylolisthesis has more instability than the degenerative one. Therefore, AIF in the case of degenerative spondylolisthesis is a useful procedure, while in the isthmic type it is not advisable as a routine procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng CL, Fang D, Lee PC, Leong JCY (1989) Anterior spinal fusion for spondylolysis and isthmic spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 71:264–267
Chow SP, Leong JCY, Ma A, Yau ACBC (1980) Anterior spinal fusion for deranged lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine 5:452
Evans JH (1992) Clinical biomechanics of the spine. In: Niwa S et al (eds) Biomechanics of orthopaedics. Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 31–45
Feffer HL, Wierel SW, Cuckler JM, Rotheman RH (1985) Degenerative spondylolisthesis — to fuse or not to fuse. Spine 10:287–289
Fredrickson BE, Baker D, McHolick WJ et al (1984) The natural history of spondylolysis and spondylohsthesis. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 66:699–707
Fujimaki A, Crock HV, Bedbrook GM (1982) The results of 150 anterior lumbar interbody fusion operations performed by two surgeons in Australia. Clin Orthop 165:164–172
Garfin SR, Heller S (1989) The operative reduction of spondylolisthesis: indication, results, complications. Semin Spine Surg 1:125–132
Inoue SI, Watanake T, Hirose A, Tanaka T, Matsu N, Saegusa O, Sho E (1984) Anterior discectomy and interbody fusion for lumbar disc herniation — a review of 350 cases. Clin Orthop 183:22–31
Inoue SI, Watanake T, Hirose A, Tanaka T, Matsui N, Saegusa O, Sho E (1988) Degenerative spondylolisthesis — pathophysiology and results of anterior interbody fusion. Clin Orthop 227:90–98
Kim NH, Choi JH (1988) Treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis by anterior interbody fusion (in Korean). J Korean Orthop Assoc 12:789–806
Luk DK (1984) Anterior discectomy and spinal fusion for deranged lumbar intervertebral disc. Thesis M Ch Orth, University of Liverpool
Monticelli G, Ascani E (1975) Spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. Acta Orthop Scand 46:498–506
Moon MS, Lee KS, Sung JH (1989) Surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis: clinical study on 49 cases. J Jpn Orthop Assoc 63:S-62
Raugstad TS, Harbo K, Hogberg A, Skeie S (1982) Anterior interbody fusion of the lumbar spine. Acta Orthop Scand 53: 561–565
Stauffer RN, Coventry MB (1972) Anterior interbody lumbar spine fusion: analysis of Mayo clinic series. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 54:756–768
Stewart TD (1953) The age incidence of neural arch defects in Alaskan natives, considered from the standpoint of etiology. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 35:937
Stokes IAF (1988) Mechanical function of facet joints in the lumbar spine. Clin Biomech 3:101–105
Takahashi K et al (1987) Clinical results of anterior lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolytic spondylolisthesis (in Japanese). J Jpn Orthop Assoc 61:1009
Turek SL (1984) Orthopaedics. Lippincott, Philadelphia, p 1537
Watkins R (1992) Anterior lumbar interbody fusion — surgical complication. Clin Orthop 284:47–62
Wiltse LL, Jackson DW (1976) Treatment of spondylolisthesis and spondylolysis in children. Clin Orthop 117:93–100
Yamamoto I, Kaneda K, Paujabi MM (1992) Three-dimensional kinematic analysis of the human whole lumbar spine and natural lumbosacral spondylolysis. In: Niwa S et al (eds) Biomechanics in orthopaedics. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 191–203
Zhang J, Yang KH (1993) Finite element modeling of anterior lumbar spinal fusion. Transactions of 39th annual meeting, Orthopaedic Research Society, February 15–18, 1993, San Francisco, p 66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moon, M.S., Kim, S.S., Sun, D.H. et al. Anterior spondylodesis for spondylolisthesis: Isthmic and degenerative types. Eur Spine J 3, 172–176 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02190582
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02190582