Abstract
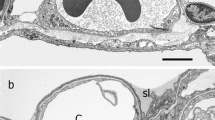
Pulmonary ultrastructural abnormalities were studied in squirrel monkeys exposed to 30 ppm NO2 or 3 ppm O3 for three hours with intermittent exercise. The lung tissues were processed either immediately after exposure or 1, 4 or 7 days later. Both the transmission and scanning electron microscopes were used for observation. Initial changes caused by the NO2 were the presence of fibrin in the alveoli, blebbing of the alveolar epithelium and the removal of cilia from the terminal bronchiolar epithelium. Seven days after exposure the tissues appeared to be recovering. Three ppm O3 was more damaging to alveoli than the 30 ppm NO2. The epithelial lining was degenerating or completely gone in many loci. Where intact, the width of the blood-air barrier increased with exposure and further with delay of sacrifice. Abnormal porosity of the alveolar walls was generally observed and remained through seven days after exposure. An unusual number of “paired” type 2 epithelial cells were present and contained a few to many homogeneous spherical inclusions of medium density. The results observed indicate that quantitation of morphological changes will be possible even at ambient exposures of atmospheric pollutants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T. F.: Techniques for the preservation of three-dimensional structure in preparing specimens for the electron microscope. Trans NY Acad Sci13, 130–141 (1951)
Bils, R. F.: Ultrastructural alterations of alveolar tissue of mice. I. Due to heavy Los Angeles smog. Arch Environ Health12, 689–697 (1966)
Bils, R. F.: Ultrastructural alterations of alveolar tissue of mice. III. Ozone. Arch Environ Health20, 468–480 (1970)
Bils, R. F.: Lung Ultrastructure of Exercising Monkeys After Nitrogen Dioxide Exposure. Proc Electron Micros Soc Amer pp 314–315 (1973)
Bils, R. F., Evans, M. E.: The effects of ozone, nitrogen dioxide and other gaseous air pollutants on mammalian respiratory tissues: A review of light and electron microscope studies. Read before the 61st annual meeting of the Air Pollution Control Association, St. Paul, 1968
Bils, R. F., Romanovsky, J. C.: Ultrastructural Alterations of Alveolar Tissue of Mice. II. Synthetic photochemical smog. Arch Environ Health14, 844–858 (1967)
Bils, R. F., Wightman, L.: A practical small animal controlled exercise cage. (In preparation)
Boatman, E. S., Sato, S., Frank, R.: Structural Changes in Animal Lungs Exposed to Low Concentrations of Ozone. Proc. Electron Micros Soc. Amer. (1973)
Brinkman, R., Lamberts, H. B., Veninga, T. S.: Radiomimetic toxicity of ozonized air. Lancet1, 133–136 (1964)
Bruch, J. Schlipköter, H.: Changes in the Pulmonary Alveoli in Mouse Following Chronic Exposure to a Low Concentration of Ozone. Virchows Arch 355–368 (1973)
Cooper, W. C., Tabershaw, I. R.: Biologic effects of nitrogen dioxide in relation to air quality standards. Arch. Environ Health12, 522–530 (1966)
Dowell, A. R. Kilburn, K. H., Pratt, P. C.: Short-Term Exposure to Nitrogen Dioxide. Arch Intern Med128, (1971)
Ehrlich, R.: Effect of Nitrogen Dioxide on Resistance to Respiratory Infection. Bacteriological Reviews30, 604–614 (1966)
Freeman, G., Stephens, R. J., Coffin, D. L., Stara, J. F.: Changes in Dogs' Lungs After Long-Term Exposure to Ozone. Arch Environ Health26, 209–216 (1973)
Hine, C. H., Meyers, F. H., Wright, R. W.: Pulmonary Changes in Animals Exposed to Nitrogen Dioxide, Effects of Acute Exposures. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol16, 201–213 (1970)
Jaffe, L. S.: The biological effects of ozone on man and animals. Amer Industr Hyg Assoc J28, 267–277 (1967)
Kapanci, Y., Weibel, E. R., Kaplan, H. P., Robinson, F. R.: Pathogenesis and reversibility of the pulmonary lesions of oxygen toxicity in monkeys. Lab Invest20, 101–118 (1969)
Parkinson, D. R., Stephens, R. J.: Morphological surface changes in the terminal bronchiolar region of NO2-exposed rat lung. Environ Res6, 37–51 (1973)
Plopper, C. G., Dungworth, D. L., Tyler, W. S.: Ultrastructure of pulmonary alveolar macrophagesin situ in lungs from rats exposed to ozone. Am Rev Resp Dis108, 632–638 (1973)
Scheel, L. D., Dobrogorski, O. J., Mountain, J. T.et al.: Physiologic, biochemical, immunologic and pathologic changes following ozone exposure. J Appl Physiol14, 67–80 (1959)
Schlipköter, H., Bruch, J.: Functional and morphological alterations caused by exposition to ozone. Zbl Bakt Hyg 1:156, 486–499 (1973)
Stephens, R. J., Freeman, G., Evans, M. J.: Early response of lungs to low levels of nitrogen dioxide. Arch Environ Health24, 160–179 (1972)
Stokinger, H. E., Coffin, F. L.: Biologic effects of air pollutants, in Stern AC (ed). Air Pollution 1 (1968)
Stokinger, H. E., Wagner, W. D., Wright, P. G.: Studies of ozone toxicity. Arch Ind Health14, 158–162 (1956)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by SCOR HL-15098, National Heart and Lung Institute, USPHS.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bils, R.F. Effects of nitrogen dioxide and ozone on monkey lung ultrastructure. Pneumologie 150, 99–111 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02179307
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02179307