Abstract
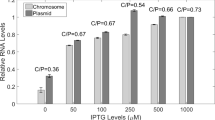
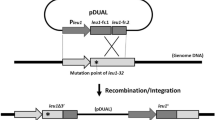
A k2/k1 plasmid gene shuffle system has been used to investigate linear plasmid promoter function inKluyveromyces lactis. By transplacing various ORF5 deletion constructs from the larger plasmid k2 onto k1, and analysing trans-complementation of an ORF5o deletion on k2, a 40 bp k2 fragment, including the UCS motif of ORF5 (UCS5), has been identified as a cis-acting promoter element essential for ORF5 gene function. Qualitative and quantitative transcript analyses of a UCS5-ScLEU2 fusion gene using Northern blot analysis and phosphor image technology revealed a plasmid-dependentLEU2 transcript distinct in size (1.55 kb) and regulation from its nuclear counterpart (1.35 kb): cytoplasmic, UCS5-driven expression of the marker gene was non-repressible by leucine and reduced five- to eight-fold compared to fully derepressed nuclear K1LEUC2 mRNA levels. Thus, the killer plasmids k2 and k1 appear to express low levels of transcript overall, when relative gene copy numbers (one for the nuclear allele versus 50–100 copies for the plasmid-borneLEU2 gene) are taken into account.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreadis A, Hsu YP, Hermodson M, Kohlhaw G, Schimmel P (1984) YeastLEU2: repression of mRNA levels by leucine and primary structure of the gene product. J Biol Chem 259:8058–8062
Birnboim HC, Doly J (1979) A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 7:1513–1523
Bolen PL, Eastman EM, Cihak PL, Hayman GT (1994) Isolation and sequence analysis of a gene from the linear DNA plasmid pPac1-2 ofPichia acaciae that shows similarity to a killer toxin gene ofKluyveromyces lactis. Yeast 10:403–414
Church, GM, Gilbert W (1984) Genomic sequencing Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1991–1995
Cong Y-S, Wesolowski-Louvel M, Fukuhara H (1994) Creation of a functional promoter by rearrangement inKluyveromyces lactis linear plasmid. Gene 147:125–129
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Gallo E, Galeotti CL (1990) Transplacement of a nuclear gene into the cytoplasmic killer plasmid ofKluyveromyces lactis. Abst 15th Int Conf Yeast Genet Mol Biol
Gietz D, St Jean A, Woods RA, Schiestl RH (1992) Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res 20:1425
Gough JA, Murray NE (1983) Sequence diversity among related genes for recognition of specific targets in DNA molecules. J Mol Biol 166:1–19
Gunge N, Tamaru A, Ozawa F, Sakaguchi K (1981) Isolation, characterisation of linear deoxyribonucleic acid plasmids fromKluyveromyces lactis and the plasmid-associated killer character. J Bacteriol 145:382–390
Hishinuma F, Hirai K (1991) Genome organisation of the linear plasmid pSKL isolated fromSaccharomyces kluyveri. Mol Gen Genet 226:97–106
Kämper J, Meinhardt F, Gunge N, Esser K (1989a) New recombinant linear DNA elements derived fromKluyveromyces lactis killer plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res 17:1781
Kämper J, Meinhardt F, Gunge N, Esser K (1989b) In vivo construction of linear vectors based on killer plasmids fromKluyveromyces lactis: selection for a nuclear gene results in attachment of telomeres. Mol Cell Biol 9:3931–3937
Kämper J, Esser K, Gunge N, Meinhardt F (1991) Heterologous expression on the linear DNA killer plasmid fromKluyveromyces lactis. Curr Genet 19:109–118
Kolodziej PA, Young RA (1991) Epitope-tagging and protein surveillance. Methods Enzymol 194:508–519
Meinhardt F, Rohe M (1993) Extranuclear inheritance: linear protein-primed replicating genomes in plants and microorganisms. In Behnke HD, Esser K, Kubitzki K, Runge M, Ziegler H, (eds) Progress in Botany vol. 54. Springer Verlag, Berlin/Heidelberg/New York, pp 334–357
Meinhardt F, Kempken F, Kämper J, Esser K (1990) Linear plasmids among eukaryotes: fundamentals and applications Curr Genet 17:89–95
Meinhardt F, Wodara C, Larsen M, Schickel J (1994) A novel approach to express a heterologous gene fromKluyveromyces lactis linear killer plasmids: expression of the bacterialaph gene from a cytoplasmic promoter fragment without in-phase fusion to the plasmid open reading frame Plasmid 32:318–327
Remboutsika E, Kohlhaw GB (1994) Molecular architecture of a Leu3p-DNA complex in solution: a biochemical approach. Mol Cell Biol 14:5547–5557
Rohe M, Schründer J, Tudzinsky P, Meinhardt F (1992) Phylogenetic relationships of linear, protein-primed replicating genomes. Curr Genet 21:173–176
Romanos M, Boyd A (1988) A transcriptional barrier to expression of cloned toxin genes of the linear plasmid k1 ofKluyveromyces lactis: evidence that native k1 has novel promoters. Nucleic Acids Res 16:7333–7350
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbour, New York
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Schaffrath R, Meacock PA (1995)Kluyveromyces lactis killer plasmid pGKL2: molecular analysis of an essential gene, ORF5 Yeast 11:615–628
Schaffrath R, Stark MJR, Gunge N, Meinhardt F (1992)Kluyveromyces lactis killer system:ORF1 of pGKL2 has no function in immunity expression and is dispensable for killer plasmid replication and maintenance Curr Genet 21:357–363
Schaffrath R , Soond SM, Meacock PA (1995) Cytoplasmic gene expression in yeast: a plasmid-encoded transcription system inKluyveromyces lactis. Biochem Soc Transactions 23:128S
Schmitt ME, Brown TA, Trumpover BA (1990) A rapid and simple method for preparation of RNA fromSaccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res 18:3091–3092
Schründer J, Meinhardt F (1995) An extranuclear expression system for analysis of cytoplasmic promoters of yeast linear killer plasmids. Plasmid 33:139–151
Sherman F (1991) Getting started with yeast. Methods Enzymol 194:3–21
Stam JC, Kwakman J, Meijer M, Stuitje AR (1986) Efficient isolation of the linear DNA killer plasmid ofKluyveromyces lactis: evidence for location and expression in the cytoplasm and characterisation of their terminally bound proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 14:6871–6884
Stark MJR, Milner JS (1989) Cloning and analysis of theKluyveromyces lactis TRP1 gene: a chromosomal locus flanked by genes encoding inorganic pyrophosphatase and histone H3. Yeast 6:35–50
Stark MJR, Boyd A, Mileham AJ, Romanos MA (1990) The plasmid encoded killer system ofKluyveromyces lactis: a review. Yeast 6:1–29
Tanguy-Rougeau C, Chen XJ, Wesolowski-Louvel M, Fukuhara H (1990) Expression of a foreign KmR gene in a linear killer DNA plasmid in yeast. Gene 91:43–50
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Wilson DW, Meacock PA (1988) Extranuclear gene expression in yeast: evidence for a plasmid-encoded RNA polymerase of unique structure. Nucleic Acids Res 16:8097–8112
Zhang Y-P, Chen X-J, Li Y-Y, Fukuhara H (1992)LEU2 gene homolog inKluyveromyces lactics. Yeast 8:801–804
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by C. P. Hollenberg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schaffrath, R., Meacock, P.A. & Meinhardt, F. Yeast killer plasmid pGKL2: molecular analysis of UCS5, a cytoplasmic promoter element essential for ORF5 gene function. Molec. Gen. Genet. 250, 286–294 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02174386
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02174386