Abstract
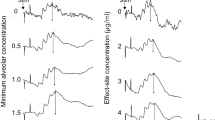
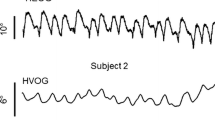
The effects of volatile anesthetics, i.e., methoxyflurane, halothane and enflurane, on the electroretinogram (ERG) were studied in 15 albino rabbits. The ERG was analyzed in terms of the a-wave, and the first oscillatory component (01) in the b-wave. The 01 peak latency showed a significant dose-related prolongation when anesthetic end-tidal concentrations were in excess of 0.8 minimum alveolar concentration (MAC). One MAC, a measure of anesthetic potency, is the end-tidal concentration of an anesthetic at 1 atmosphere that induces immobility in 50% of animals against a noxious stimulus. The amplitudes of the a-wave and the 01 decreased in dose-dependent manners, but their changes were less striking than those of the 01 latency. The peak latency of the a-wave remained unchanged. We conclude that the 01 peak latency is a useful monitor of the depth of inhalational anesthesia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown CH, Green DG (1984) Rod saturation in b-wave of the rat electroretinogram under two different anesthetics. Vision Res 24:87–90
Cheng SC, Brunner EA (1981a) Inhibition of GABA metabolism in the rat brain slices by halothane. Anesthesiology 55:26–33
Cheng SC, Brunner EA (1981b) Effects of anesthetic agents on synaptosomal GABA disposal. Anesthesiology 55:34–40
Demant E, Nagahara K, Niemeyer G (1982) Effects of changes in systemic blood pressure on the electroretinogram of the cat: evidence for retinal autoregulation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 23:683–687
Eger EI II (1974) Anesthetic uptake and action. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 2–6
Gerritsen BG (1970) The effect of anaesthetics on the electroretinogram and visually evoked response in the rabbit. Doc Ophthalmol 29:289–330
Granit R (1932) Isolation of components in the retinal action potential of the decerebrated dark-adapted cat. J Physiol 76:1–2
Niemeyer G, Nagahara K, Demant E (1982) Effects of changes in arterial pO2 and pCO2 on the electroretinogram in the cat. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 23:678–683
Norren DV, Padmos P (1975) Cone dark adaptation: the influence of halothane anesthesia. Invest Ophthamol 14:212–227
Raitta C, Karhunen U, Seppalainen AM, Naukkarinen M (1979) Changes in the electroretinogram and visual evoked potentials during general anesthesia. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 211:139–144
Raitta C, Karhunen U, Seppalainen AM (1982) Changes in the electroretinogram and visual evoked potentials during general anaesthesia using enflurane. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 218: 294–296
Tashiro C, Muranishi R, Gomyo I, Mashimo T, Yoshiya I (1983) Electroretinogram. A possible monitoring to brain hypoxia and anesthetic depth. Anesthesiology 59: A390
Uhl RR, Squires KC, Bruce DL, Starr A (1980) Effect of halothane anesthesia on the human cortical visual evoked response. Anesthesiology 53:273–276
Wachtmeister L, Dowling JE (1978) The oscillatory potentials of the mudpuppy retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 17:1176–1188
Yonemura D, Kawasaki K, Okumura T, Tanabe J (1977) Early deterioration in the temporal aspect of the human electroretinogram in diabetes mellitus. Folia Ophthalmol Jpn 28:379–388
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tashiro, C., Muranishi, R., Gomyo, I. et al. Electroretinogram as a possible monitor of anesthetic depth. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 224, 473–476 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02173367
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02173367