Summary
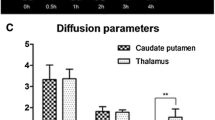
The local concentration and distribution of methotrexate following intraventricular administration were studied in the brains of New Zealand White rabbits. Tritiated methotrexate was injected through subcutaneous reservoirs connected to ventricular catheters, the animals were sacrificed one hour after administration of the drug, and the distribution of the radiolabelled compound was assessed using quantitative autoradiographic techniques. The intracerebral distribution of tritiated inulin delivered in an identical fashion was studied for comparison. One hour after intraventricular administration of radiolabelled methotrexate or inulin approximately 40% of the area of the brain sections contained appreciable concentrations of the radiolabelled tracer. Gray matter adjacent to the cerebrospinal fluid, including the hippocampus, thalamus, caudate nucleus, and periaquaductal gray contained the highest concentrations of3H-methotrexate. Large white matter tracts contained smaller amounts of tracer activity. The rapid and extensive penetration of intraventricularly administered methotrexate and inulin into normal brain parenchyma and the high methotrexate concentrations in specific regions of the brain provide insight into the pathogenesis of methotrexate-induced neurotoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wasserstrom WR, Glass PJ, Posner JB: Diagnosis and treatment of leptomeningeal metastases from solid tumors: experience with 90 patients. Cancer 49: 759–772, 1982
Shapiro WR, Young DR, Mehta BM: Methotrexate: Distribution in cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous, ventricular and lumbar injections. N Engl J Med 293: 161–166, 1975
Bleyer WA: Current status of intrathecal chemotherapy for human meningeal neoplasms. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 46: 171–178, 1977
Bleyer WA, Poplack DG: Intraventricular versus intralumbar methotrexate for central-nervous-system leukemia: Prolonged remission with the Ommaya reservoir. Med Pediatr Oncol 6: 207–213, 1979
Kay HEM, Knapton PJ, O'Sullivan JP, et al.: Encephalopathy in acute leukemia associated with methotrexate therapy. Arch Dis Child 47: 344–354, 1972
Bresnan MD, Gilles FH, Lorenzo AV, et al.: Leukoencephalopathy following combined irradiation and intraventricular methotrexate therapy of brain tumors in childhood. Trans Am Neurol Assoc 97: 204–206, 1972
Rubenstein LJ, Herman MM, Long TG, et al.: Disseminated necrotizing leukoencephalopathy: A complication of treated central nervous system leukemia and lymphoma. Cancer 35: 291–305, 1975
Hendin B, DeVivo DC, Torack R, et al.: Parenchymatous degeneration of the central nervous system in childhood leukemia. Cancer 33: 468–482, 1974
Grossman SA, Ahn H, Trump D, et al.: Improved treatment results and leukoencephalopathic changes in patients with neoplastic menigitis treated with intrathecal methotrexate and thiotepa. Proc ASCO 1: 73, 1982
Girgis M, Shih-Chang W: Stereotaxic atlas of the rabbit brain. St. Louis, Missouri, W.H. Green, Inc., 1981
Hayniuk WM, Bertino JR: Treatment of leukemia with large doses of methotrexate and folinic acid: clinical-biochemical correlates. J Clin Invest 48: 2140–2155, 1969
Tennyson VM, Pappius GD. Ependyma. In: Minckler J (ed) Pathology of the Nervous System. Vol. 1, New York. McGraw-Hill, 1968, pp 518–530
Knigge KM, Scott DE, Kobayashi H et al. (eds) Brainendocrine interaction II. Basel S. Karger, 1975
Weindl A, Joynt RJ: Ultrastructure of the ventricular walls: three-dimensional study of regional specialization. Arch Neurol 26: 420–427, 1972
Brightman MW, Prescott L, Reese TS et al.: Intercellular junctions of special ependyma. In Knigge KM et al. (eds) Brain-endocrine interaction II. The ventricular system in neuroendocrine mechanisms. Basel S. Karger, 1975, pp 146–165
Rall DP, Oppelt WW, Patlak CS: Extracellular space of brain as determined by diffusion of inulin from the ventricular system. Life Sci 2: 43–48, 1962
Blasberg RG, Patlak C, Fenstermacher JD: Intrathecal chemotherapy: brain tissue profiles after ventriculo-cisternal perfusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 195: 73–83, 1975
Blasberg RG: Methotrexate, cytosine arabinoside, and BCNU concentration in brain after ventriculocisternal perfusion. Cancer Treat Rep 61: 625–631, 1977
Dorr RT, Fritz WL: Cancer Chemotherapy Handbook, Elsevier North Holland, Inc., New York, p 163, 1980
Grossman SA, Trump DL, Chen DCP et al.: Cerebrospinal fluid flow abnormalities in patients with neoplastic meningitis. An evaluation using111Indium-DTPA ventriculography. Am J Med 73: 641–647, 1982
Morse M, Balis F, Poplack D et al.: Altered central-nervous-system pharmacology of methotrexate in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: another sign of CNS relapse. Proc ASCO 3: 30, 1984
Huffman DH, Wan SH, Azarnoff DL et al.: Pharmacokinetics of methotrexate. Clin Pharmacol Ther 14: 572–579, 1973
Bleyer WA, Dedrick R: The clinical pharmacology of intrathecal methotrexate (NSC-740). I. Pharmacokinetics in nontoxic patients after lumbar injection. Cancer Treat Rep 61: 703–708, 1977
Price RA, Jamieson PA: The central nervous system in childhood leukemia III. Subacute leukoencephalopathy. Cancer 35: 306–318, 1975
Shapiro WR, Chernoff NL, Posner JB: Necrotizing encephalopathy following intraventricular instillation of methotrexate. Arch Neurol 28: 96–102, 1973
Norrell H, Wilson CB, Slagel DE et al.: Leukoencephalopathy following the administration of methotrexate into the cerebrospinal fluid in the treatment of primary brain tumors. Cancer 33: 923–932, 1974
Fusner JE, Poplack DG, Pizzo PA et al.: Leukoencephalopathy following chemotherapy for rhabdomyosarcoma; reversibility of cerebral changes demonstrated by computed tomography. J Pediatr 91: 77–79, 1977
Wendling LR, Bleyer WA, DiChiro G et al.: Transient severe periventricular hypodensity after leukemia prophylaxis with cranial irradiation and intrathecal methotrexate. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2: 502–505, 1978
Liu HM, Mauer HS, Vongsvivut S et al.: Methotrexate encephalopathy, a neuropathologic study. Human Pathol 9: 635–648, 1978
Russel DS, Rubenstein LJ: Pathology of tumors of the nervous system. 4th Edition. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, p 102, 1977
Peylan-Ramu N, Poplack DG, Pizzo PA et al.: Abnormal CT scans of the brain in asymptomatic children with acute lymphocytic leukemia after prophylactic treatment of the central nervous system with radiation and intrathecal chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 298: 815–818, 1978
McIntosh S, Klatskin EH, O'Brien RT et al.: Chronic neurologic disturbance in childhood leukemia. Cancer 37: 853–857, 1976
Burch P, Grossman SA, Reinhard C: Spinal cord penetration of intrathecally administered cytosine arabinoside and methotrexate: A quantitative autoradiographic study. JNCI 80: 1211–1216, 1988
Shubert P, Teschemacher H, Kreutzberg GW et al.: Intracerebral distribution pattern of radioactive morphinelike drugs after intraventricular and intrathecal injection. Histochemie 22: 277–288, 1970
Alexander GM, Schwartzman RJ, Bell RD et al.: Quantitative measurement of local cerebral metabolic rate for glucose utilizing tritiated 2-deoxyglucose. Brain Res 223: 59–67, 1981
Orzi F, Kennedy C, Jehle J et al.: Measurement of local glucose utilization with 2-[3H]deoxyglucose in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3(1): 77–78, 1983
Schoolar JC, Barlow CF, Roth LJ: The penetration of carbon-14 urea into the cerebrospinal fluid and various areas of the cat brain. J Neuropath Exp Neurol 19: 216–227, 1960
Gilbert MR, Grossman SA: Methotrexate Neurotoxicity:In Vitro Studies using Cerebellar Explants. Cancer Res 49: 2502–2505, 1989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grossman, S.A., Reinhard, C.S. & Loats, H.L. The intracerebral penetration of intraventricularly administered methotrexate: A quantitative autoradiographic study. J Neuro-Oncol 7, 319–328 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02147089
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02147089