Abstract
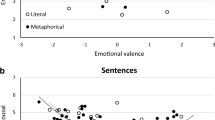
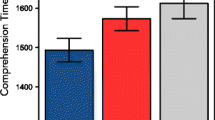
Three experiments examined whether sentences interpretable as metaphorical and literal expressions differed on three components of processing: perceptual decoding, sense selection, and integration of terms. In Experiments 1 and 2 metaphorical words were identified more readily than literal words on separate tests of perceptual identification and word recognition. In Experiment 3 the conveyed meaning of a metaphor was not recalled better than a literal interpretation of the same target sentence. It is concluded that metaphorical and literal sentences utilize separate perceptual and selectional decoding strategies, but do not differ with respect to comprehension processes once metaphorical and literal referents are instantiated. Discussion is given as to whether these differences constitute a separate metaphor strategy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burbules, N. C., Schraw, G., & Trathen, W. (1989). Metaphor, idiom and figuration.Metaphor and Symbolic Activity, 4, 93–110.
Fcustel, T. C., Shiffrin, R. M., & Salasoo, A. (1983). Episodic and lexical contributions to the repetition effect in word recognition.Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 112, 309–346.
Gerrig, R. J., & Healy, A. F. (1983). Dual process in metaphor understanding: Comprehension and appreciation.Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 9, 667–675.
Grice, H. P. (1975). Logic and conversation. In P. Cole & J. I. Morgan (Eds.),Syntax and semantics: Vol. 3. Speech acts (pp. 41–58). New York: Academic Press.
Inhoff, A. W., Lima, S. D. & Carroll, P. J. (1984). Contextual effects on metaphor comprehension in reading.Memory & Cognition, 12, 558–567.
Jacoby, L. L. (1983). Remembering the data: Analyzing interactive processes in reading.Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 22, 485–508.
Jacoby, L. L., & Dallas, M. (1981). On the relationship between autobiographical memory and perceptual learning.Journal of Experimental Psychology: General 3, 306–340.
Kucera, and Francis (1967).Computational analysis of present-day American English. Providence, RI: Brown University Press.
Ortony, A. (1979). Beyond literal similarity.Psychological Review, 86, 161–180.
Ortony, A., Schallert, D. L., Reynolds, R. E., & Antos, S. J. (1978). Interpreting metaphors and idioms: Some effects of context and comprehension.Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior, 17, 465–477.
Ortony, A., Vondruska, R. J., Foss, M. A., & Jones, L. E. (1985). Salience, similes, and the asymmetry of similarity.Journal of Memory and Language, 24, 569–594.
Reynolds, R. E., & Schwartz R. M. (1983). Relation of metaphoric processing to comprehension and memory.Journal of Educational Psychology, 75, 450–459.
Schacter, D. L. (1987). Implicit memory: History and current status.Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 13, 501–518.
Shinjo, M., & Myers, J. L. (1987). The role of context in metaphor comprehension.Journal of Memory and Language, 26, 226–241.
Tourangeau, R., & Sternberg, R. J. (1981). Aptness in metaphor.Cognitive Psychology, 13, 27–55.
Tversky, A. (1977). Features of similarity.Psychological Review, 84, 327–352.
Verbrugge, R. R., & McCarrell, N. S. (1977). Metaphoric comprehension: Studies in reminding and resembling.Cognitive Psychology, 9, 494–533.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Shinjo and Myers also described a fourth component process,retrieval, involved in the foregrounding of prime words used in their experiments.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schraw, G. Components of metaphoric processing. J Psycholinguist Res 24, 23–38 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02146098
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02146098