Summary
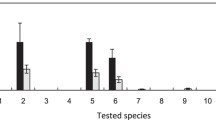
L-Canavanine, 2-amino-4-(guanidinooxy)butyric acid, and L-arginine incorporation into de novo synthesized proteins was compared in six organisms. Utilizing L-[guanidinooxy14C]canavanine and L-[guanidino14C]arginine at substrate saturation, the canavanine to arginine incorporation ratio was determined in de, novo synthesized proteins.Caryedes brasiliensis andSternechus tuberculatus, canavanine utilizing insects;Canavalia ensiformis, a canavanine storing plant; and to a lesser extentHeliothis virescens, a canavanine resistant insect, failed to accumulate significant canavanyl proteins. By contrast,Manduca sexta, a canavanine-sensitive insect, andGlycine max, a canavanine free plant, readily incorporated canavanine into newly synthesized proteins. This study supports the contention that the incorporation of canavanine into proteins in place of arginine contributes significantly to canavanine's antimetabolic properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell, E.A., Lackey, J.A., and Pohill, R.M., Biochem. Ecol. System6 (1978) 201.
Van Etten, C.H., Kwolek, W.F., Peters, J.E., and Barclay, A.S., J. Agric. Fd Chem.15 (1967) 1077.
Rosenthal, G.A., Q. Rev. Biol.52 (1977) 155.
Downum, K.R., Rosenthal, G.A., and Cohen, W.S., Pl. Physiol.73 (1983) 965.
Mitra, S.K., and Mehler, A.H., J. biol. Chem.242 (1967) 5490.
Boyar, A., and Marsh, R.E., J. Am. chem. Soc.104 (1982) 1995.
Greenstein, J.P., and Winitz, M., Chemistry of the Amino Acids. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York 1961.
Rosenthal, G.A., J. chem. Ecol.12 (1986) 1145.
Rosenthal, G.A., and Dahlman, D.L., Experientia38 (1982) 1034.
Dahlman, D.L., and Rosenthal, G.A., J. Insect Physiol.22 (1976) 265.
Rosenthal, G.A., and Dahlman, D.L., Comp. Biochem. Physiol.52A (1975) 105.
Berge, M.A., Rosenthal, G.A., and Dahlman, D.L., Pest. Biochem. Physiol.25 (1986) 319.
Bleiler, J.A., Rosenthal, G.A. and Janzen, D.H., Ecology 1987 (in press).
Rosenthal, G.A., and Dahlman, D.L., and Janzen, D.H., Science192 (1976) 256.
Rosenthal, G.A., J. chem. Ecol.9 (1983) 1353.
Rosenthal, G.A., Pl. Physiol.69 (1982) 1066.
Ozinskas, A.J., and Rosenthal, G.A., Bioorg. Chem.14 (1986) 157.
Rosenthal, G.A., Analyt. Biochem.77 (1977) 147.
Rosenthal, G.A., and Rhodes, D.L., Pl. Physiol.76 (1984) 541.
Rosenthal, G.A., and Dahlman, D.L., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. USA83 (1986a) 14.
Rosenthal, G.A., and Thomas, D.A., Analyt. Biochem.147 (1985) 428.
Rosenthal, G.A., and Dahlman, D.L., J. Insect Biochem. (1986b) in review.
Rosenthal, G.A., Sci. Am.249 (1983) 164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenthal, G.A., Berge, M.A., Bleiler, J.A. et al. Aberrant, canavanyl protein formation and the ability to tolerate or utilize L-canavanine. Experientia 43, 558–561 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02143585
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02143585