Summary
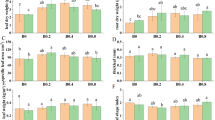
The effects of deficient and toxic levels of boron on various aspects of nitrogen metabolism in sugar beet are studied. Plant analysis shows a nitrate ion accumulation, a decrease in the activity of the nitrate reductase enzyme and a lower molybdenum absorption.
The effect of boron levels on the plant and root sugar concentration has also been studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliography
Albert, L. S. 1965 Ribonucleic acid content, boron deficiency symptoms and elongation of tomato root tips. Plant Physiol.40, 649–654.
Arnon, D. I. and Hoagland, D. R. 1950 The water culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stn. Circ.347.
Association of official Analytical Chemist 1975 Official methods of analysis. P.O. Box 540, Benjamin Franklin Station, Washington DC 20044.
Bar Akiva, A. and Sterbaun, S. 1965 Possible use of nitrate reductase activity of leaves as a measure of the nitrogen requirement of citrus trees. Plant Cell. Physiol.6, 575–577.
Cadahia, C.; Piñero, M. T. 1974 Determinación de glúcidos en plantas por fotocolorimetría. Estudio comparativo de métodos clásicos y automáticos. Anal. Edafol. Agrobiol.XXXIII, 9–10.
Comité Inter-Institutos de Análisis foliares 1969 Métodos de referencia para la determinación de elementos minerales en vegetales. Anal. Edafol. Agrobiol.XXVIII, 410 y sig.
Dugger, W. M. 1973 Functional aspects of boron in plantas.In Trace elements in the environment. Ed. F. L. Kotnny, Advances in Chemistry Series123. American Chemical. Soc. Washington D.C. pp 112–129
Gamboa, A. 1976 La remolacha azucarera y el abonado potásico Rev. para el campo no 22. Otoño 76.
Gauch, H. G. 1972 Organic plant nutrition. Ed. Dowden. Hutchinson 8 Ross. Inc. Stronburg, Pennsylvania. 183600. pp 243–259.
Hernando, V., Cadahia, C. 1973 El análisis de savia como índice de fertilización. Manuales de Ciencia Actual, 7, C. S. I. C. Vitrubio8, Madrid.
Kouchi, H. and Kumazawa, K. 1975 Anatomical responses of root tips to boron deficiency I. Soil. Sci. Plant. Nutr.21, 21–28.
Kouchi, H. and Kumazawa, K. 1975 Anatomical responses of roots tips to boron deficiency. II. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr.21, 137–150.
Marcos de Lanuza, L. 1966 Nutrición hidropónica con microelementos Mg, B, Mo, en Pinus radiata. Minist. Agric. Direc. General Montes. Caza y Pesca Fluvial. IFIE Madrid.
Skol'Nik, M. J. 1965 Translated from proceedings of the International Symp. on Mineral Nutrition of plants and Animals. Jena November. 15 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonilla, I., Cadahía, C., Carpena, O. et al. Effects of boron on nitrogen metabolism and sugar levels of sugar beet. Plant Soil 57, 3–9 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02139636
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02139636