Abstract
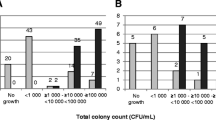
In the present study 25 infertile men delivered urine before and after prostatic massage. Expressed prostatic secretion (EPS) was obtained from 11 men. Aerobic and anaerobic bacterial analyses showed that a total of 33 isolates was found in samples of urine voided before massage as compared to 59 isolates after massage of the prostate. There was an increase in the number of anaerobes whereas there was no change in the number of aerobes. The occurrence of EPS did not influence the number of aerobic and anaerobic isolates in urine voided after massage of the prostate. The most often isolated anaerobes in urine voided after prostatic massage wereEubacterium lentum, Peptococcus asaccharolyticus andBacteroides species and the most common anaerobe in EPS wasPeptostreptococcus micros.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caldamore AA, Cocket ATK (1978) Infertility and genitourinary infection. Urology 12:304–312
Heimdahl A, Nord CE (1982) Effect of erythromycin and clindamycin on the indigenous human anaerobic flora and new colonization of the gastrointestinal tract. Eur J Clin Microbiol 1:38–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moberg, P.J., Nord, C.E. Anaerobic bacteria in urine before and after prostatic massage of infertile men. Med Microbiol Immunol 174, 25–28 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02123667
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02123667