Abstract
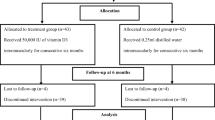
Twelve children (8 boys and 4 girls) with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), aged 9–15 years, received 1α-hydroxyvitamin D3 (1α-OHD3) in a dose of 0.05 μg/kg per day for 1 year. Duration of disease varied between 2.8 and 9 years. Bone density was determined in the distal third of forearm using single photon absorptiometry, and was expressed as standard scores (±SD) with respect to sex- and agemateched controls. Bone density measurements and ultrasound studies of the kidneys were performed at 0,6 and 12 months. Serum calcium, ionized calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, creatinine, alkaline phosphatase, glycosylated haemoglobin in morning blood samples and urinary Ca, P, Mg, and hydroxyproline were regularly determined. One patient was excluded from the study because of hypercalciuria and one because of lack of compliance. Bone density increased significantly after 6 and 12 months of 1α-OHD3 administration (P=0.015,P<0.001 respectively). None of the biochemical parameters changed significantly.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1α-OHD 3 :
-
1α-hydroxyvitamin D3
- 1,25 (OH) 2D 3 :
-
1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3
- BD :
-
bone density
- IDDM :
-
insulindependent diabetes mellitus
- UCa/Ucr :
-
urinary calcium creatinine ratio
- UMg/UCr :
-
urinary magnesium creatinine ratio
- UOH-Pr/UCr :
-
urinary hydroxyproline creatinine ratio
- UP/UCr :
-
urinary phosphorus creatinine ratio
References
Al-Qadreh A, Delis D, Voskaki I, Kassiou C, Bartsocas CS (1992) A prospective study of bone density in patients with IDDM (Abstract). Diabetes Young 28: 28
Bouillon R (1991) Diabetic bone disease. Calcif Tissue Int 49: 55–160
Chesney RW, Shore RM (1982) The non-invasive determination of bone mineral content by photon absorptiometry. Am J Dis Child 136: 578–580
Frazer TE, White NH, Hough S, Santiago JV, McGee BR, Bryce G, Mallon J, Aniol LV (1981) Alteration in circulating vitamin D metabolites in young insulin-dependent diabetics. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 53: 1154–1159
Hiu LH, Epstein S, Johston CC (1985) A prospective study of bone mass in patients with type I diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 60: 74–77
Hough FS (1987) Alteration of bone mineral metabolism in diabetes mellitus, clinical studies in 206 patients with type I diabetes mellitus. S Afr Med J 72: 120–126
Hough S, Fausto A, Sonn Y, Dong JOK, Birge SL, Avioli LV (1983) Vitamin D metabelism in chronic streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat. Endocrinology 113: 790–796
Kanc-Hanzel K, Prezelj J, Gantar-Rott U, Kocijancic A (1993) Treatment of osteoporosis in type I diabetic women: the effect of calcitonin and calcium (Abstract). Diabetologia Aug; 36 (1)
Leon M, Larrodera L, Liedo G, Howkins F (1989) Study of bone loss in diabetes mellitus type I. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 6: 237–242
McNair P, Madsbad S, Christiansen C, Farber OK, Transbol I, Binder C (1978) Osteopenia in insulin treated diabetes mellitus. Its relation to age at onset, sex and duration of disease. Diabetologia 15: 87–90
Rico H, Hernandez ER, Cabranes JA, Gomez-Castresan F (1989) Suggestions of deficient osteoblastic function in diabetes mellitus the possible cause of osteopenia in diabetics. Calcif Tissue Int 45: 71–73
Rodland O, Markestad T, Aksens L, Aarskog D (1985) Plasma concentrations of vitamin D metabolites during puberty of diabetic children. Diabetologia 28: 663–666
Rosenbloom A (1984) Skeletal and joint manifestations of childhood diabetes. Pediatr Clin North Am 31: 569–589
Rosenbloom AL, Lezotte DC (1981) Diminution of bone mass in childhood diabetes. Diabetes 26: 1052–1055
Sagges G, Beretellonis S, Baroncelli AG, Federico G, Galisti L (1989) Bone demineralization and impaired metabolism in IDDM. Helv Pediatr Acta 43: 405–414
Shore RM, Chesney RW, Mazess RB, Rose PC, Bargman GJ (1981) Osteopenia in juvenile diabetes. Calcif Tissue Int 33: 455–457
Spencer EM, Khalil M, Tobiassen O (1980) Experimental diabetes in the rat causes an insulin-reversible decrease in renal 25-OH vitamin D3-1α-hydroxylase activity. Endocrinology 107: 300–305
Verhaeghe J, Van Herck E, Visser WJ, Suiker AMH, Thomasset M, Einhorn TA, Faierman E, Bouillon R (1990) Bone mineral metabolism in BB rats with long-term diabetes. Decreased bone turnover nad osteoporosis. Diabetes 39: 477–482
Verrotti A, Chiarelli F, Capani F, Morgese G (1992) Calcium metabolism in type I diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Nutr Metab 5: 231–236
Weintroub S, Eisenberg D, Tardiman R, Weisman SI, Salama R (1990) Is diabetic osteoporosis due to microangiopathy? Lancet II: 983
Wiske PS, Wentworth SM, et al (1982) Evaluation of bone mass and growth in young diabetics. Metabolism 31: 848
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Qadreh, A., Voskaki, I., Kassiou, C. et al. Treatment of osteopenia in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: The effect of 1α-hydroxyvitamin D3 . Eur J Pediatr 155, 15–17 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02115619
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02115619