Abstract
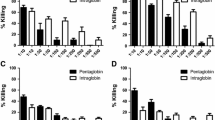
The combination effect of subinhibitory and inhibitory concentrations of ceftazidime, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) and polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNL) againstEscherichia coli was investigated. PMNL obtained from healthy volunteers were incubated with different concentrations of G-CSF and ceftazidime for 180 min. The addition of 0.25 × MIC of ceftazidime or 1 × MIC significantly enhanced the bactericidal activity of PMNL. G-CSF at a concentration of 6,000 units/ml led to only a slight improvement in the bactericidal activity of PMNL. The combination of 6,000 units/ml G-CSF and ceftazidime in inhibitory as well as subinhibitory concentrations, however, showed a significant synergistic effect (p<0.01) on the antibacterial activity of PMNL during the entire incubation period. Combinations of G-CSF and antibiotics could therefore be beneficial for infected patients, especially those with impaired cellular host defence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Groopman JE, Molina JM, Scadden DT: Hematopoietic growth factors. Biology and clinical applications. New England Journal of Medicine 1989, 321: 1449–1459.
Kitagawa S, Yuo A, Souza LM, Saito M, Miura Y, Takadu F: Recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances super-oxide release in human granulocytes stimulated by chemotactic peptide. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 1987, 144: 1143–1146.
Wang JM, Chen ZG, Colella S, Bonilla MA, Welte K, Bordignon C, Mantovani A: Chemotactic activity of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Blood 1988, 72: 1456–1460.
Cohen AM, Hines DK, Korach ES, Ratzkin BJ: In vivo activation of neutrophil function in hamsters by recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Infection and Immunity 1988, 56: 2861–2865.
Roilides E, Walsh TJ, Pizzo PA, Rubin M: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances the phagocytic and bactericidal activity of normal and defective human neutrophils. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1991, 163: 579–583.
Fabian I, Kletter Y, Bleiberg I, Gadish M, Naparsteck E, Slavin S: Effect of exogenous recombinant human granulocyte and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on neutrophil function following allogenic bone marrow transplantation. Experimental Hematology 1991, 19: 868–873.
Anding K, Kropec A, Schmidt-Eisenlohr E, Benzing A, Geiger K, Daschner F: Enhancement of in vitro bactericidal activity of neutrophils from trauma patients in the presence of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 1993, 12: 121–124.
Böyum A: Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of mononuclear cells by one centrifugation and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation 1968, 21, Supplement 97: 77–89.
Daschner FD, Langmaack H, Grehn M, Steffens A, Just M: Combination effect of piperacillin with four aminoglycosides on nonfermenting gram-negative bacteria. Chemotherapy 1981, 27: 39–43.
Gemell CG: Potentiation of phagocytosis of pathogenic bacteria by exposure to low concentrations of antibiotics. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1984, 13: 407–415.
Cuffini AM, Carlone NA, Xerri L, Pizzoglio MF: Synergy of ceftazidime and human macrophages on phagocytosis and killing ofStaphylococcus aureus andPseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1987, 20: 261–271.
Silver GM, Gamelli RL, O'Reilly MO: The beneficial effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) in combination with gentamycin on survival afterPseudomonas burn wound infection. Surgery 1989, 106: 452–456.
Matsumoto M, Matsubara S, Yokota T: Effect of combination therapy with recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (rG-CSF) and antibiotics in neutropenic mice unresponsive to antibiotics alone. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1991, 28: 447–453.
Yasuda H, Ajiki Y, Shlmozato T, Kasahara M, Kawada H, Iwata M, Shimizo K: Therapeutic efficacy of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor alone and in combination with antibiotics againstPseudomonas aeruginosa infections in mice. Infection and Immunity 1990, 58: 2502–2509.
van den Broek PJ: Antimicrobial drugs, microorganisms, and phagocytes. Clinical Infectious Diseases 1989, 11: 213–245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daschner, F.D., Grundmann, H., Anding, K. et al. Combined effect of human neutrophils, ceftazidime and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on killing ofEscherichia coli . Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 14, 536–539 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02113435
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02113435