Summary
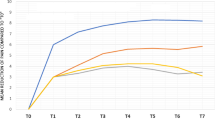
A new PGE2-gel, based on a cross-linked starch powder, has been developed. This gel seems to have solved several of the pharmaceutical and practical problems connected with local administration of prostaglandins. In a three-center study 120 nulliparous patients were given 0.5 mg PGE2 in 2.2 ml gel intracervically prior to dilatation of the cervix and evacuation of the uterus in late first trimester. Considerable cervical dilatation was obtained within 15 h. The frequency of side effects, including pain and gastro-intestinal discomfort was low. The technique can be recommended for outpatients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brenner WE, Dingfelder JR, Staurovsky LG, Hendricks CH (1973) Vaginally administered PGF2α for cervical dilatation in nulliparous prior to suction curettage. Prostaglandins 4: 819
Bygdeman M, Gréen K, Bergström S, Bundy G, Kimball F (1979) New prostaglandin E2 analogue for pregnancy termination. Lancet 1: 1136
Bygdeman M, Bremme K, Christensen N, Lundström V, Gréen K (1980) A comparison of two stable prostaglandin E analogues for termination of early pregnancy and for cervical dilatation. Contraception 22: 471
Calder AA, Embrey MP, Tait T (1977) Ripening of the cervic with extra-amniotic prostaglandin E2 in viscous gel before induction of labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 84: 264
Embrey MP (1979) Induction of labour. Br Med J 2: 793
Harris AS, Kirstein-Pedersen A, Stenberg P, Ulmsten U, Wingerup L (1980) The preparation, characterization and stability of a new prostaglandin E2 gel for local administration. J Pharm Sci 69: 1271
Karim SMM, Ng SC, Ratman SS (1980) Termination of abnormal intrauterine pregnancy with prostaglandins. Singapore J Obstet Gynaecol 11: 7
Klinger A (1970) Demographic consequences of the legalization of induced abortion in eastern Europe. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 8: 680
Liggins GC (1978) Ripening of the cervix. Semin Perinatol 2: 261
Lippert TH (1979) The use of prostaglandin gel in obstetrics and gynecology. Arch Gynecol 227: 171
Lippert TH, Modly T (1973) Induction of abortion by the extra-amniotic administration of prostaglandin gels. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 80: 1025
MacKenzie IZ, Embrey MP (1977) Cervical ripening with intravaginal prostaglandin E2 gel. Br Med J 2: 1381
Mitchell MD, Flint APF, Bibby J, Brunt J, Arnold JM, Anderson ABM, Turnbull AC (1977) Rapid increases in plasma prostaglandin concentrations after vaginal examination and amniotomy. Br Med J 2: 1183
Moberg P (1976) Uterine perforation in connection with vacuum aspiration for legal abortion, Int J Gynaecol Obstet 14: 77
Robinson HP (1973) Sonar measurement of fetal crown-rump length as means of assessing maturity in first trimester of pregnancy. Br Med J 4: 28
Stys SJ, Clewell WH, Meschia G (1978) Changes in cervical compliance at parturition independent of uterine activity. Am J Obstet Gynecol 130: 414
Tietze C, Lewit S (1972) Joint program for the study of abortion (JPSA): Early medical complications of legal abortion. Stud Fam Plann 3: 97
Toppozada M, Bygdeman M, Papageorgiou C, Wiqvist N (1973) Administration of 15-methyl-prostaglandin F2α as a preoperative means of cervical dilatation. Prostaglandins 4: 371
Ulmsten U, Kirstein-Pedersen A, Stenberg P, Wingerup L (1979) A new gel for intracervical application of prostaglandin E2. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand [Suppl] 84: 19
Ulmsten U, Wingerup L, Andersson K-E (1979) Comparison of prostaglandin E2 and intravenous oxytocin for induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol 54: 581
Ulmsten U, Wingerup L (1980) Clinical experiences with a new gel for intracervical application of prostaglandin E2 before therapeutic abortion or induction of term labor. Prostaglandins 20: 533
(1979) WHO Task Force on sequele of abortion. Gestation, birth weight, and spontaneous abortion in pregnancy after induced abortion. Lancet 1: 142
(1981) WHO Task Force on prostaglandins for fertility regulation. Vaginal administration of 15-methyl-PGF2α methyl ester for preoperative cervical dilatation. Contraception 23: 251
Wingerup L, Andersson K-E, Ulmsten U (1978) Ripening of the uterine cervix and induction of labour at term with prostaglandin E2 in viscous gel. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 57: 403
Wingerup L, Ulmsten U, Andersson K-E (1979) Ripening of the cervix by intracervical application of PGE2-gel before termination of pregnancy with dilatation and evacuation. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand [Suppl] 84: 15
Editorial (1979) The unripe cervix. Lancet 1: 364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wingerup, L., Ulmsten, U., Bygdeman, M. et al. A new prostaglandin E2-gel for pretreatment of the cervix in nulliparous patients having a late first trimester termination of pregnancy. Arch. Gynecol. 231, 1–6 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02110018
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02110018