Abstract
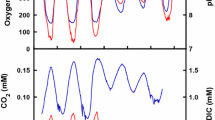
This paper examines the influence of aSargassum forest on distributions of illuminance, dissolved oxygen content and pH in a small cove facing Wakasa Bay. Spatial distributions of illuminance, dissolved oxygen content, water density and pH were observed for June 1982 during the season of luxuriant seaweed growth, and for August 1982 during the season of little growth. Observations of dissolved oxygen content, water density and pH were made during the day and at night. The values of illuminance at the sea surface were decreased to less than 40% inside theSargassum forest when the sun was highest in the sky during the season of luxuriant growth. Density stratification occurred during every observation. Dissolved oxygen content and pH showed similar patterns of spatial distribution. Their horizontal distributions reversed from day to night, and consisted of two types: (1) higher values inshore and lower values offshore in the upper layer during the day with (2) lower values inshore and higher values offshore at night. Distributions of illuminance about noon, and dissolved oxygen content and pH at night showed patterns corresponding to the vertical distribution of algal density of theSargassum forest. Dissolved oxygen was supersaturated at every observation point during the daytime, but at night it was undersaturated in the lower part of the forest or along the bottom in June and August, respectively. Processes that brought about these spatial distributions are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buch, K. and O. Nyäs (1939): Studien über neuere pH Methodik mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Meerwassers. Acta Acad. Mathe. Physi.,12, 1–41.
Horibe, S. and H. Tsubota (1970): Seawater as a solution. p. 26–81.In: Chemistry of Seawater. Basic Series on Marine Science, Vol. 10, ed. by S. Horibe, Tokai Univ. Press, Tokyo. (in Japanese).
Komatsu, T., H. Ariyama, H. Nakahara and W. Sakamoto (1982): Spatial and temporal distributions of water temperature in aSargassum forest. J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan,38, 63–72.
Komatsu, T. (1985): Temporal fluctuations of water temperature in aSargassum forest. J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan,41, 235–243.
Komatsu, T. and H. Kawai (1986): Diurnal changes of pH distributions and the cascading of shore water in aSargassum forest. J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan,42, 447–459.
Ohno, M. (1981): Environmental factors inSargassum beds. p. 75–92.In: Seaweed beds, ed. by Japan. Soc. Sci. Fish., Koseishakoseikaku, Tokyo, (in Japanese).
Sugiura, Y. (1970): Gases. p. 231–241.In: Chemitry of Seawater. Basic Series on Marine Science, Vol. 10, ed. by S. Horibe, Tokai Univ. Press, Tokyo. (in Japanese).
Umezawa, S., M. Ohno and T. Yamamoto (1977): An ecological study on the model of a seaweed belt. Daily variations of the environmental factors with reference to the behavior of fish. Rep. Usa Mar. Biol. Stat., Kochi Univ.,24, 13–26 (in Japanese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Komatsu, T. Day-night reversion in the horizontal distributions of dissolved oxygen content and pH in aSargassum forest. Journal of the Oceanographical Society of Japan 45, 106–115 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02108884
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02108884