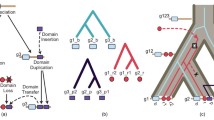
Summary
The relationships among 153 EF-hand (calcium-modulated) proteins of known amino acid sequence were determined using the method of maximum parsimony. These proteins can be ordered into 12 distinct subfamilies-calmodulin, troponin C, essential light chain of myosin, regulatory light chain, sarcoplasmic calcium binding protein, calpain, aequorin,Strongylocentrotus purpuratus ectodermal protein, calbindin 28 kd, parvalbumin, α-actinin, and S100/intestinal calcium-binding protein. Eight individual proteins-calcineurin B fromBos, troponin C fromAstacus, calcium vector protein fromBranchiostoma, caltractin fromChlamydomonas, cell-division-cycle 31 gene product fromSaccharomyces, 10-kd calcium-binding protein fromTetrahymena, LPS1 eight-domain protein fromLytechinus, and calcium-binding protein fromStreptomyces—are tentatively identified as unique; that is, each may be the sole representative of another subfamily. We present dendrograms showing the relationships among the subfamilies and uniques as well as dendrograms showing relationships within each subfamily.
The EF-hand proteins have been characterized from a broad range of organismal sources, and they have an enormous range of function. This is reflected in the complexity of the dendrograms. At this time we urge caution in assigning a simple scheme of gene duplications to account for the evolution of the 600 EF-hand domains of known sequence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken A, Klee CB, Cohen P (1984) The structure of the B subunit of calcineurin. Eur J Biochem 139:663–671
Aoki K, Imajoh S, Ohno S, Emori Y, Koike M,Kosaki G, Suzuki K (1986) Complete amino acid sequence of the large subunit of the low-Ca2+-requiring form of human Ca2+-activated neutral protease (μCANP) deduced from its cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett 205:313–317
Arimura C, Suzuki T, Yanagisawa M, Imamura M, Hamada Y, Masaki T (1988) Primary structure of chicken skeletal muscle and fibroblast α-actinins deduced from cDNA sequences. Eur J Biochem 177:649–655
Baba ML, Goodman M, Berger-Cohn J, Demaille JG, Matsuda G (1984) The early adaptive evolution of calmodulin. Mol Biol Evol 1:442–455
Babu YS, Sack JS, Greenhough TJ, Bugg CE, Means AR, Cook WJ (1985) Three-dimensional structure of calmodulin. Nature 316:37–40
Babu YS, Bugg CE, Cook WJ (1988) Structure of calmodulin refined at 2.2 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 204:191–204
Barker WC, Ketcham LK, Dayhoff MO (1977) Evolutionary relationships among calcium-binding proteins. In: Wasserman RH, Corradino R, Carafoli E, Kretsinger RH, Mac-Lennan D, Siegel F (eds) Calcium-binding proteins and calcium function. North-Holland, New York, pp 73–75
Baron MD, Davidson MD, Jones P, Critchley DR (1987) The sequence of chick α-actinin reveals homologies to spectrin and calmodulin. J Biol Chem 262:17623–17629
Barraclough R, Savin J, Dube SK, Rudland PS (1987) Molecular cloning and sequence of the gene for p9Ka. A cultured myoepithelial cell protein with strong homology to S-100, a calcium-binding protein. J Mol Biol 198:13–20
Barraclough R, Kimbell R, Rudland PS (1988) The identification of a normal rat gene located close to a gene for the potential myoepithelial cell calcium-binding protein, p9Ka. J Biol Chem 263:14597–14600
Barton PJR, Robert B, Cohen A, Garner I, Sassoon D, Weydert A, Buckingham ME (1988) Structure and sequence of the myosin alkali light chain gene expressed in adult cardiac atria and fetal striated muscle. J Biol Chem 263:12669–12676
Baudier J (1988) S100 proteins: structure and calcium binding properties. In: Gerday C, Gillis R, Bolis L (eds) Calcium and calcium binding proteins: molecular and functional aspects. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 102–113
Baudier J, Gerard D (1986) Ions binding to S100 proteins. II. Conformational studies and calcium-induced conformational changes in S100αα protein: the effect of acidic pH and calcium incubation on subunit exchange in S100a (αβ) proteins. J Biol Chem 261:8204–8212
Baudier J, Glasser N, Gerard D (1986) Ions binding to S100 proteins. I. Calcium- and zinc-binding properties of bovine brain S100(αα), S100a(αβ), and S100b(ββ) protein: Zn2+ regulates Ca2+ binding on S100b protein. J Biol Chem 261:8192–8203
Baum P, Furlong C, Byers B (1986) Yeast gene required for spindle pole body duplication: homology of its product with Ca2+-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:5512–5516
Bender PK, Dedman JR, Emerson CP Jr (1988) The abundance of calmodulin mRNAs is regulated in phosphorylase kinase-deficient skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 263:9733–9737
Berchtold MW (1988) Structural organization of the human parvalbumin gene. In: Hidaka H (ed) Ca2+ protein signaling. Plenum Press, New York (in press)
Berchtold MW, Heizmann CW, Wilson KJ (1982) Primary structure of parvalbumin from rat skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem 127:381–389
Berchtold MW, Epstein P, Beaudet AL, Payne ME, Heizmann CW, Means AR (1987) Structural organization and chromosomal assignment of the parvalbumin gene. J Biol Chem 262:8696–8701
Bruggen J, Tarcsay L, Cerletti N, Odink K, Rutishauser M, Hollander G, Sorg C (1988) The molecular nature of the cystic fibrosis antigen. Nature 331:570
Calabretta B, Battini R, Kaczmarek L, de Riel JK, Baserga R (1986) Molecular cloning of the cDNA for a growth factor-inducible gene with strong homology to S-100, a calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem 261:12628–12632
Capony J-P, Ryden L, Demaille J, Pechére J-F (1973) The primary structure of the major parvalbumin from hake muscle. Overlapping peptides obtained with chemical and enzymatic methods. The complete amino acid sequence. Eur J Biochem 32:97–108
Capony J-P, DeMaille J, Pina C, Pechére J-F (1975) The amino-acid sequence of the most acidic major parvalbumin from frog muscle. Eur J Biochem 56:215–227
Capony J-P, Pina C, Pechére J-F (1976) Parvalbumin from rabbit muscle: isolation and primary structure. Eur J Biochem 70:123–135
Carpenter CD, Bruskin AM, Hardin PE, Keast MJ, Anstrom J, Tyner AL, Brandhorst BP, Klein WH (1984) Novel proteins belonging to the troponin C superfamily are encoded by a set of mRNAs in sea urchin embryos. Cell 36:663–671
Charbonneau H, Walsh KA, McCann RO, Prendergast FG, Cormier MJ, Vanaman TC (1985) Amino acid sequence of the calcium-dependent photoprotein aequorin. Biochemistry 24: 6762–6771
Chen Q, Taljanidisz J, Sarkar S, Tao T, Gergely J (1988) Cloning, sequencing and expression of a full-length rabbit fast skeletal troponin-C cDNA. FEBS Lett 228:22–26
Chien Y-H, Dawid IB (1984) Isolation and characterization of calmodulin genes fromXenopus laevis. Mol Cell Biol 4:507–513
Coffee CJ, Bradshaw RA (1973a) Carp muscle calcium-binding protein. I. Characterization of the tryptic peptides and the complete amino acid sequence of component B. J Biol Chem 248:3305–3312
Coffee CJ, Bradshaw RA (1973b) Erratum. J Biol Chem 248:6576
Coffee CJ, Bradshaw RA, Kretsinger RH (1974) The coordination of calcium ions by carp muscle calcium binding proteins A, B and C. Adv Exp Med Biol 48:211–233
Collins, JH (1976a) Structure and evolution of troponin C and related proteins. In: Calcium in biological systems, Soc Exp Biol Symp XXX, Cambridge University Press, London, pp 303–334
Collins JH (1976b) Homology of myosin DTNB light chain with alkali light chains, troponin C and parvalbumin. Nature 259:699–700
Collins JH, Greaser ML, Potter JD, Horn MJ (1977) Determination of the amino acid sequence of troponin C from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem 252:6356–6362
Collins JH, Jakes R, Kendrick-Jones J, Leszyk J, Barouch W, Theibert JL, Spiegel J, Szent-Györgyi AG (1986) Amino acid sequence of myosin essential light chain from the scallopAquipecten irradians. Biochemistry 25:7651–7656
Collins JH, Cox JA, Theibert JL (1988) Amino acid sequence of a sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein from the sandwormNereis diversicolor. J Biol Chem 263:15378–15381
Cormier MJ (1978) Applications ofRenilla bioluminescence. Methods Enzymol 57:237–244
Cox JA (1986) Isolation and characterization of a new Mr 18,000 protein with calcium vector properties in amphioxus muscle and identification of its endogenous target protein. J Biol Chem 261:13173–13178
Cox JA (1990) Calcium vector protein and sarcoplasmic calcium binding proteins from invertebrate muscle. In: Dedman JR, Smith VL (eds) Stimulus-response coupling: the role of intracellular calcium. Telford Press, West Caldwell NJ (in press)
Cox JA, Bairoch A (1988) Sequence similarities in calcium-binding proteins. Nature 331:491–492
Davis TN, Urdea MS, Masiarz FR, Thorner J (1986) Isolation of the yeast calmodulin gene: calmodulin is an essential protein. Cell 47:423–431
Dedman JR, Jackson RL, Schreiber WE, Means AR (1978) Sequence homology of the Ca2+-dependent regulator of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase from rat testis with other Ca2+-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 253:343–346
Desplan C, Heidmann O, Lillie JW, Auffray C, Thomasset M (1983a) Sequence of rat intestinal vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein derived from a cDNA clone: evolutionary implications. J Biol Chem 258:13502–13505
Desplan C, Thomasset M, Moukhtar M (1983b) Synthesis, molecular cloning, and restriction analysis of DNA complementary to vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein mRNA from rat duodenum. J Biol Chem 258:2762–2765
Donato R (1986) S-100 proteins. Cell Calcium 7:123–145
Donato R (1988) Calcium-independent, pH-regulated effects of S-100 proteins on assembly-disassembly of brain microtubule protein in vitro. J Biol Chem 263:106–110
Dorin JR, Novak M, Hill RE, Brock DJH, Secher DS, van Heyningen V (1987) A clue to the basic defect in cystic fibrosis from cloning the CF antigen gene. Nature 326:614–617
Elsayed S, Bennich H (1975) The primary structure of allergen M from cod. Scan J Immunol 4:203–208
Emori Y, Kawasaki H, Imajoh S, Kawashima S, Suzuki K (1986a) Isolation and sequence analysis of cDNA clones for the small subunit of rabbit calcium-dependent protease. J Biol Chem 261:9472–9476
Emori Y, Kawasaki H, Sugihara H, Imajoh S, Kawashima S, Suzuki K (1986b) Isolation and sequence analyses of cDNA clones for the large subunits of two isozymes of rabbit calcium-dependent protease. J Biol Chem 261:9465–9471
Enfield DL, Ericsson LH, Blum HE, Fischer EH, Neurath H (1975) Amino-acid sequence of parvalbumin from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:1309–1313
Epstein P, Means AR, Berchtold MW (1986) Isolation of the rat parvalbumin gene and full length cDNA. J Biol Chem 261:5886–5891
Falkenthal S, Parker VP, Mattox WW, Davidson N (1984)Drosophila melanogaster has only one myosin alkali light-chain gene which encodes a protein with considerable amino acid sequence homology to chicken myosin alkali light chains. Mol Cell Biol 4:956–965
Falkenthal S, Parker VP, Davidson N (1985) Developmental variations in the splicing patterns of transcripts from theDrosophila gene encoding myosin alkali light chain result in different carboxyl-terminal amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:449–453
Fano G, Angelella P, Mariggio D, Aisa MC, Giambanco I, Donato R (1989) S-100α0 protein stimulates the basal (Mg2+-activated) adenylate cyclase activity associated with skeletal muscle membranes. FEBS Lett (in press)
Farris JS (1972) Estimating phylogenetic trees from distance matrices. Am Nat 106:645–668
Feher JJ, Fullmer CS, Fritzsch GK (1989) Comparison of the enhanced steady-state diffusion of calcium by calbindin-D 9k and calmodulin: possible importance in intestinal calcium absorption. Cell Calcium 10:189–203
Felsenstein J (1988) Phylogenies from molecular sequences: inference and reliability. Annu Rev Genet 22:521–565
Ferrari S, Calabretta B, de Riel JK, Battini R, Ghezzo F, Lauret E, Griffin C, Emanuel BS, Gurrieri F, Baserga R (1987) Structural and functional analysis of a growth-related gene, the human calcyclin. J Biol Chem 262:8325–8332
Fischer R, Koller M, Flura M, Mathews S, Strehler-Page M-A, Krebs J, Penniston JT, Carafoli E, Strehler EE (1988) Multiple divergent mRNAs code for a single human calmodulin. J Biol Chem 263:17055–17062
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20: 406–416
Fitch WM, Margoliash E (1967) The construction of phylogenetic trees—a generally applicable method utilizing estimates of the mutation distance obtained from cytochrome C sequences. Science 155:279–284
Floyd EE, Gong Z, Brandhorst BP, Klein WH (1986) Calmodulin gene expression during sea urchin development: persistence of a prevalent maternal protein. Dev Biol 113:501–511
Frank G, Weeds AG (1974) The amino-acid sequence of the alkali light chains of rabbit skeletal-muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem 44:317–334
Frankenne F, Joassin L, Gerday C (1973) The amino acid sequence of the pike (Esox lucius) parvalbumin III. FEBS Lett 35:145–147
Fullmer CS, Wasserman RH (1981) The amino acid sequence of bovine intestinal calcium-binding protein. J Biol Chem 256:5669–5674
Fullmer CS, Wasserman RH (1987) Chicken intestinal 28-kilodalton calbindin-D: complete amino acid sequence and structural considerations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4772–4776
Gahlmann R, Wade R, Gunning P, Kedes L (1988) Differential expression of slow and fast skeletal muscle troponin C. Slow skeletal muscle troponin C is expressed in human fibroblasts. J Mol Biol 201:379–391
Garfinkel LI, Periasamy M, Nadal-Ginard B (1982) Cloning and characterization of cDNA sequences corresponding to myosin light chains 1, 2, and 3, troponin-C, troponin-T, α-tropomyosin, and α-actin. J Biol Chem 257:11078–11086
Gerday C (1976) The primary structure of the parvalbumin II of pike (Esox lucius). Eur J Biochem 70:305–318
Gerday C (1988) Soluble calcium binding proteins in vertebrate and invertebrate muscles. In: Gerday C, Bolis L, Gilles R (eds) Calcium and calcium binding proteins: molecular and functional aspects. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 23–39
Gerday C, Collin S, Piront A (1978) Phylogenetic relationships between Cyprinidae parvalbumins. II. The amino acid sequence of the parvalbumin V of chub (Leuciscus cephalus L.). Comp Biochem Physiol 61B:451–457
Gerke V, Weber K (1985) The regulatory chain in the p36-kd substrate complex of viral tyrosine-specific protein kinases is related in sequence to the S-100 protein of glial cells. EMBO J 4:2917–2920
Gillen MF, Banville D, Rutledge RG, Narang S, Seligy VL, Whitfield JF, MacManus JP (1987) A complete complementary DNA for the oncodevelopmental calcium-binding protein, oncomodulin. J Biol Chem 262:5308–5312
Gillis J-M, Thomason DB, Le Fevre J, Kretsinger RH (1982) Parvalbumin and muscle relaxation: a computer simulation study. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 3:377–398
Glenney JR Jr, Tack BF (1985) Amino-terminal sequence of p36 and associated p10: identification of the site of tyrosine phosphorylation and homology with S-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7884–7888
Glenney JR Jr, Kindy MS, Zokas L (1989) Isolation of a new member of the S100 protien family: amino acid sequence, tissue, and subcellular distribution. J Cell Biol 108:569–578
Goodman M (1980) Molecular evolution of the calmodulin family. In: Siegel FL, Carafoli E, Kretsinger RH, MacLennan DH, Wasserman RH (eds) Calcium-binding proteins: structure and function. Elsevier North-Holland, New York, pp 347–354
Goodman M, Pechére J-F (1977) The evolution of muscular parvalbumins investigated by the maximum parsimony method. J Mol Evol 9:131–158
Goodman M, Pechére J-F, Haiech J, DeMaille JG (1979) Evolutionary diversification of structure and function in the family of intracellular calcium-binding proteins. J Mol Evol 13: 331–352
Goodwin EB, Szent-Györgyi AG, Leinwand LA (1987) Cloning and characterization of the scallop essential and regulatory myosin light chain cDNAs. J Biol Chem 262:11052–11056
Grand RJA, Perry SV (1978) Amino acid sequence of the troponin C-like protein (modulator protein) from bovine uterus. FEBS Lett 92:137–142
Grand RJA, Shenolikar S, Cohen P (1981) The amino acid sequence of the δ subunit (calmodulin) of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. Eur J Biochem 113:359–367
Hagiwara M, Achiai M, Owada K, Tanaka T, Hidaka H (1988) Modulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of p36 and other substrates by the S-100 protein. J Biol Chem 263:6438–6441
Hardin PE, Klein WH (1987) Unusual sequence conservation in the 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions of the sea urchin Spec mRNAs. J Mol Evol 25:126–133
Hardin PE, Angerer LM, Hardin SH, Angerer RC, Klein WH (1988) Spec 2 genes inStrongylocentrotus purpuratus. Structure and differential expression in embryonic aboral ectoderm cells. J Mol Biol 202:417–431
Hardin SH, Carpenter CD, Hardin PE, Bruskin AM, Klein WH (1985) Structure of the Spec1 gene encodinga major calciumbinding protein in the embryonic ectoderm of the sea urchin,Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. J Mol Biol 186:243–255
Hardin SH, Keast MJ, Hardin PE, Klein WH (1987) Use of consensus oligonucleotides for detecting and isolating nucleic acids encoding calicum binding domains of the troponin C superfamily. Biochemistry 26:3518–3523
Hardy DO, Bender PK, Kretsinger RH (1987) Two calmodulin genes are expressed inArbacia punctulata. An ancient gene duplication is indicated. J Mol Biol 198:223–227
Hartigan JA (1973) Minimum mutation fits to a given tree. Biometrics 29:53–65
Head JF (1989) Amino acid sequence of a low molecular weight, high affinity calcium-binding protein from the optic lobe of the squidLoligo pealei. J Biol Chem 264:7202–7209
Henderson SA, Xu Y-C, Chien KR (1988) Nucleotide sequence of full length cDNAs encoding rat cardiac myosin light chain-2. Nucleic Acids Res 16:4722
Henrotte JG (1952) A crystalline constitutent from myogen of carp muscle. Nature 169:968–969
Herzberg O, James MNG (1985) Structure of the calcium regulatory protein troponin-C at 2.8 Å resolution. Nature 313: 653–659
Herzberg O, James MNG (1988) Refined crystal structure of troponin C from turkey skeletal muscle at 2.0 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 203:761–779
Hidaka H, Endo T, Kawamoto S, Yamada E, Umekawa H, Tanabe K, Hara K (1983) Purification and characterization of adipose tissue S-100b protein. J Biol Chem 258:2705–2709
Hoffmann E, Shi QW, Floroff M, Mickle DAG, Wu T-W, Olley PM, Jackowski G (1988) Molecular cloning and complete nucleotide sequence of a human ventricular myosin light chain 1. Nucleic Acids Res 16:2353
Hofmann T, Kawakami M, Hitchman AJW, Harrison JE, Dorrington KJ (1979) The amino acid sequence of porcine intestinal calcium-binding protein. Can J Biochem 57:737–748
Hosoya H, Takagi T, Mabuchi I, Iwaasa H, Sakai H, Hiramoto Y, Konishi K (1988) The amino acid sequence, immunofluorescence and microinjection studies on the 15 kDa calcium-binding protein from sea urchin egg. Cell Struct Funct 13:525–532
Huang B, Mengersen A, Lee VD (1988a) Molecular cloning of cDNA for caltractin, a basal body-associated Ca2+-binding protein: homology in its protein sequence with calmodulin and the yeast CDC31 gene product. J Cell Biol 107:133–140
Huang B, Watterson DM, Lee VD, Schibler MJ (1988b) Purification and characterization of a basal body-associated Ca2+-binding protein. J Cell Biol 107:121–131
Huang W-Y, Cohn DV, Hamilton JW (1975) Calcium-binding protein of bovine intestine. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem 250:7647–7655
Hunziker W (1986) The 28-kDa vitamin D-dependent calciumbinding protein has a six-domain structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7578–7582
Iida Y (1982) Molecular evolution of protein: internal homology in the amino acid sequence of calmodulin. J Mol Biol 159:167–177
Inouye S, Noguchi M, Sakaki Y, Takagi Y, Miyata T, Iwanaga S, Miyata T, Tsuji FI (1985) Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for the luminescent protein aequorin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3154–3158
Isobe T, Okuyama T (1978) The amino-acid sequence of S-100 protein (PAP I-b protein) and its relation to the calcium-binding proteins. Eur J Biochem 89:379–388
Isobe T, Okuyama T (1981) The amino-acid sequence of the α subunit in bovine brain S-100a protein. Eur J Biochem 116: 79–86
Jackson-Grusby LL, Swiergiel J, Linzer DIH (1987) A growthrelated mRNA in cultured mouse cells encodes a placental calcium-binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res 15:6677–6690
Jamieson GA Jr, Bronson DD, Schachat FH, Vanaman TC (1980) Structure and function relationships among calmodulins and troponin C-like proteins from divergent eukaryotic organisms. Ann NY Acad Sci 356:1–13
Jauregui-Adell J, Pechére J-F (1978) Parvalbumins from coelacanth muscle. III. Amino acid sequence of the major component. Biochim Biophys Acta 536:275–282
Jauregui-Adell J, Pechére J-F, Briand G, Richet C, DeMaille JG (1982) Amino-acid sequence of an α-parvalbumin, pI=4.88, from frog skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem 123:337–345
Jauregui-Adell J, Wnuk W, Cox JA (1989) Complete amino acid sequence of the sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein (SCP-I) from crayfish (Astacus leptodactilus [sic]). FEBS Lett 243:209–212
Jensen R, Marshak DR, Anderson C, Lukas TJ, Watterson DM (1985) Characterization of human brain S100 protein fraction: amino acid sequence of S100β. J Neurochem 45:700–705
Joassin L, Gerday C (1977) The amino acid sequence of the major parvalbumin of the whiting (Gadus merlangus). Comp Biochem Physiol 57B:159–161
Jukes TH (1963) Some recent advances in studies of the transcription of the genetic message. Adv Biol Med Phys 9:1–41
Kasai H, Kato Y, Isobe T, Kawasaki H, Okuyama T (1980) Determination of the complete amino acid sequence of calmodulin (phenylalanine-rich acidic protein II) from bovine brain. Biomed Res 1:248–264
Kato K, Kimura S (1985) S100ao (αα) protein is mainly located in the heart and striated muscles. Biochim Biophys Acta 842: 146–150
Kawashima M, Nabeshima Y, Obinata T, Fujii-Kuriyama Y (1987) A common myosin light chain is expressed in chicken embryonic, skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscles and in brain continuously from embryo to adult. J Biol Chem 262:14408–14414
Kay BK, Shah AJ, Halstead WE (1987) Expression of the Ca2+-binding protein, paravlbumin, during embryonic development of the frog,Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol 104:841–847
Kendrick-Jones J, Jakes R (1977) Myosin-linked regulation: a chemical approach. In: Riecker G, Weber A, Goodwin J (eds) Myocardial failure. International Boehringer Mannheim Symposium. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 28–40
Klee CB (1988) Ca2+-dependent phospholipid- (and membrane-) binding proteins. Biochemistry 27:6645–6653
Kligman D, Marshak DR (1985) Purification and characterization of a neurite extension factor from bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7136–7139
Kobayashi T, Takasaki Y, Takagi T, Konishi K (1984) The amino acid sequence of sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein obtained from sandworm,Perinereis vancaurica tetradentata. Eur J Biochem 144:401–408
Kobayashi T, Takagi T, Konishi K, Cox JA (1987) The primary structure of a new Mr 18,000 calcium vector protein from amphioxus. J Biol Chem 262:2613–2623
Kobayashi T, Takagi T, Konishi K, Hamada Y, Kawaguchi M, Kohama K (1988a) Amino acid sequence of the calcium-binding light chain of myosin from the lower eukaryote,Physarum polycephalum. J Biol Chem 263:305–313
Kobayashi T, Takagi T, Konishi K, Ohnishi K, Watanabe Y (1988b) Amino acid sequence of a calcium-binding protien (TCBP-10) fromTetrahymena. Eur J Biochem 174:579–584
Koller M, Strehler EE (1988) Characterization of an intronless human calmodulin-like pseudogene. FEBS Lett 239:121–129
Kretsinger RH (1972) Gene triplication deduced from the tertiary structure of a muscle calcium binding protein. Nature New Biol 240:85–88
Kretsinger RH (1975) Hypothesis: calcium modulated proteins contain EF-hands. In: Carafoli E (ed) Calcium transport in contraction and secretion. North-Holland Publishing, Amsterdam, p 469
Kretsinger RH (1987) Calcium coordination and the calmodulin fold: divergent versus convergent evolution. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 52:499–510
Kretsinger RH, Barry CD (1975) The predicted structure of the calcium binding component of troponin. Biochim Biophys Acta 405:40–52
Kretsinger RH, Hardy DO (1987) Duplication of calmodulin gene inferred to occur prior to echinoderm, chordate divergence. In: Yagi K, Miyazak T (eds) Calcium signal and cell response. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 157–163
Kretsinger RH, Nockolds CE, Coffee CJ, Bradshaw RA (1971) The structure of a calcium binding protein from carp muscle. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 36:217–220
Kretsinger RH, Mann JE, Simmonds JG (1982) Model of facilitated diffusion of calcium by the intestinal calcium binding protein. In: Normal AW, Schaefer K, Herrath DV, Grigoleit H-G (eds) Proceedings of the fifth workshop on vitamin D: chemical, biochemical and clinical endocrinology of calcium metabolism. de Gruyter, New York, pp 233–248
Kretsinger RH, Rudnick SE, Weissman LJ (1986) Crystal structure of calmodulin. J Inorg Biochem 28:289–302
Kretsinger RH, Moncrief ND, Goodman M, Czelusniak J (1988) Homology of calcium-modulated proteins: their evolutionary and functional relationships. In: Morad M, Nayler W, Kazda S, Schramm M (eds) The calcium channel: structure, function and implications. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 16–35
Kumar CC, Cribbs L, Delaney P, Chien KR, Siddiqui MAQ (1986) Heart myosinlight chain 2 gene. Nucleotide sequence of full length cDNA and expression in normal and hypertensive rat. J Biol Chem 261:2866–2872
Kumar R, Wieben E, Beecher SJ (1989) The molecular cloning of the complementary deoxyribonucleic acid for bovine vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein: structure of the full-length protein and evidence for homologies with other calcium-binding proteins of the troponin-C superfamily of proteins. Mol Endocrinol 3:427–432
Kuwano R, Usui H, Maeda T, Fukui T, Yamanari N, Ohtsuka E, Ikehara M, Takahashi Y (1984) Molecular cloning and the complete nucleotide sequence of cDNA to mRNA for S-100 protein of rat brain. Nucleic Acids Res 12:7455–7465
Lagace L, Chandra T, Woo SLC, Means AR (1983) Identification of multiple species of calmodulin messenger RNA using a full length complementary DNA. J Biol Chem 258:1684–1688
Lefort A, Lecocq R, Libert F, Lamy F, Swillens S, Vassart G, Dumont JE (1989) Cloning and sequencing of a calciumbinding protein regulated by cyclic AMP in the thyroid. EMBO J 8:111–116
Lenz S, Lohse P, Seidel U, Arnold H-H (1989) The alkali light chains of human smooth and nonmuscle myosins are encoded by a single gene. Tissue specific expression by alternative splicing pathways. J Biol Chem 264:9009–9015
Lipman DJ, Pearson WR (1985) Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science 227:1435–1441
Lorkin PA, Lehmann H (1983) Malignant hyperthermia in pigs: a search for abnormalities in Ca2+ binding proteins. FEBS Lett 153:81–87
Lukas TJ, Iverson DB, Schleicher M, Watterson DM (1984) Structural characterization of a higher plant calmodulinSpinacia oleracea. Plant Physiol 75:788–795
Lukas TJ, Wiggins ME, Watterson DM (1985) Amino acid sequence of a novel calmodulin from the unicellular algaChlamydomonas. Plant Physiol 78:477–483
MacManus JP, Watson DC, Yaguchi M (1983) The complete amino acid sequence of oncomodulin—a parvalbumin-like calcium-binding protein from Morris hepatoma 5123tc. Eur J Biochem 136:9–17
MacManus JP, Watson DC, Yaguchi M (1986) The purification and complete amino acid sequence of the 9000-Mr Ca2+-binding protein from rat placenta. Identity with the vitamin D-dependent intestinal Ca2+-binding protein. Biochem J 235: 585–595
Maeda N, Zhu D, Fitch WM (1984) Amino acid sequences of lower vertebrateparvalbumins and their evolution: parvalbumins of boa, turtle, and salamander. Mol Biol Evol 1:473–488
Maisonpierre PC, Hastings KEM, Emerson CP Jr (1987) The cloning and the codon and amino acid sequence of the quail slow/cardiac troponin C cDNA. Methods Enzymol 139:326–337
Maita T, Umegane T, Kato Y, Matsuda G (1980) Amino-acid sequence of the L-1 light chain of chicken cardiac-muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem 107:565–575
Maita T, Chen J-I, Matsuda G (1981a) Amino-acid sequence of the 20000-molecular-weight light chain of chicken gizzardmuscle myosin. Eur J Biochem 117:417–424
Maita T, Umegane T, Matsuda G (1981b) Amino-acid sequence of the L-4 light chain of chicken skeletal-muscle myosin. Eur J Biochem 114:45–49
Maita T, Konno K, Ojima T, Matsuda G (1984) Amino acid sequences of the regulatory light chains of striated adductor muscle myosins from Ezo giant scallop and Akazara scallop. J Biochem 95:167–177
Maita T, Konno K, Maruta S, Norisue H, Matsuda G (1987a) Amino acid sequence of the essential light chain of adductor muscle myosin from Ezo giant scallop,Patinopecten yessoensis. J Biochem 102:1141–1149
Maita T, Tanaka H, Konno K, Matsuda G (1987b) Amino acid sequence of the regulatory light chain of squid mantle muscle myosin. J Biochem 102:1151–1157
Mangelsdorf DJ, Komm BS, McDonnell DP, Pike JW, Haussler MR (1987) Immunoselection of cDNAs to avian intestinal calcium binding protein 28K and a novel calmodulin-like protein: assessment of mRNA regulation by the vitamin D hormone. Biochemistry 26:8332–8338
Marshak DR, Clarke M, Roberts DM, Watterson DM (1984) Structural and functional properties of calmodulin from the eukaryotic microorganismDictyostelium discoideum. Biochemistry 23:2891–2899
Masiakowski P, Shooter EM (1988) Nerve growth factor induces the genes for two proteins related to a family of calcium-binding proteins in PC12 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 1277–1281
Matsuda G, Maita T, Suzuyama Y, Setoguchi M, Umegane T (1977a) Amino acid sequence of the L-2 light chain of rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. J Biochem 81:809–811
Matsuda G, Suzuyama Y, Maita T, Umegane T (1977b) The L-2 light chain of chicken skeletal muscle myosin. FEBS Lett 84:53–56
Matsuda G, Maita T, Suzuyama Y, Setoguchi M, Umegane T (1978) The amino acid sequences of the tryptic, chymotryptic, and peptic peptides from the L-2 light chain of rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Hoppe-Seyler's Z Physiol Chem 359: 629–640
Matsuda G, Maita T, Kato Y, Chen J-I, Umegane T (1981a) Amino acid sequences of the cardiac L-2A, L-2B, and gizzard 17000-M, light chains of chicken muscle myosin. FEBS Lett 135:232–236
Matsuda G, Maita T, Umegane T (1981b) The primary structure of L-1 light chain of chicken fast skeletal muscle myosin and its genetic implication. FEBS Lett 126:111–113
Miyake S, Emori Y, Suzuki K (1986) Gene organization of human calcium-activated neutral protease. Nucleic Acids Res 14:8805–8817
Miyanishi T, Maita T, Morita F, Kondo S, Matsuda G (1985) Amino acid sequences of the two kinds of regulatory light chains of adductor smooth muscle myosin fromPatinopecten yessoensis. J Biochem 97:541–551
Moews PG, Kretsinger RH (1975) Refinement of the structure of carp muscle calcium-binding parvalbumin by model building and difference Fourier analysis. J Mol Biol 91:201–228
Moore GW (1976) Proof for the maximum parsimony (“Red King”) algorithm. In: Goodman M, Tashian RE (eds) Molecular anthropology. Plenum Press, New York, p 117
Moore GW, Barnabas J, Goodman M (1973) A method for constructing maximum parsimony ancestral amino acid sequences on a given network. J Theor Biol 38:459–485
Murphy LC, Murphy LJ Tsuyuki D, Duckworth ML, Shiu RPC (1988) Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding a highly conserved, putative calcium binding protein, identified by an anti-prolactin receptor antiserum. J Biol Chem 263: 2397–2401
Mutus B, Karuppiah N, Sharma RK, MacManus JP (1985) The differential stimulation of brain and heart cyclic-AMP phosphodiesterase by oncomodulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 131:500–506
Nabeshima Y, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Muramatsu M, Ogata K (1982) Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequences of the complementary DNAs to chicken skeletal muscle myosin alkali light chain mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 10:6099–6110
Nabeshima Y, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Muramatsu M, Ogata K (1984) Alternative transcription and two modes of splicing result in two myosin light chains from one gene. Nature 308: 333–338
Nabeshima Y, Nabeshima Y-I, Nonomura Y, Fujii-Kuriyama Y (1987) Nonmuscle and smooth muscle myosin light chain mRNAs are generated from a single gene by the tissue-specific alternative RNA splicing. J Biol Chem 262:10608–10612
Nakamura S, Nabeshima Y-I, Kobayashi H, Nabeshima Y, Nonomura Y, Fujii-Kuriyama Y (1988) Single chicken cardiac myosin alkali light-chain gene generates two different mRNAs by alternative splicing of a complex exon. J Mol Biol 203: 895–904
Noegel A, Witke W, Schleicher M (1987) Calcium-sensitive non-muscle α-actinin contains EF-hand structures and highly-conserved regions. FEBS Lett 221:391–396
Nojima H (1989) Structural organization of multiple rat calmodulin genes. J Mol Biol 208:269–282
Nojima H, Sokabe H (1986) Structure of rat calmodulin processed genes with implications for a mRNA-mediated process of insertion. J Mol Biol 190:391–400
Nojima H, Kishi K, Sokabe H (1987) Multiple calmodulin mRNA species are derived from two distinct genes. Mol Cell Biol 7:1873–1880
Nudel U, Calvo JM, Shani M, Levy Z (1984) The nucleotide sequence of a rat myosin light chain 2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res 12:7175–7186
Odink K, Cerletti N, Bruggen J, Clerc RG, Tarcsay L, Zwadlo G, Gerhards G, Schlegel R, Sorg C (1987) Two calcium-binding proteins in infiltrate macrophages of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 330:80–82
Ohno S, Emori Y, Imajoh S, Kawasaki H, Kisaragi M, Suzuki K (1984) Evolutionary origin of a calcium-dependent protease by fusion of genes for a thiol protease and a calcium-binding protein? Nature 312:566–570
Ohno S, Emori Y, Suzuki K (1986) Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA coding for the small subunit of human calcium-dependent protease. Nucleic Acids Res 14:5559
Parker VP, Falkenthal S, Davidson N (1985) Characterization of the myosin light-chain-2 gene ofDrosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol 5:3058–3068
Parmacek MS, Leiden JM (1989) Structure and expression of the murine slow/cardiac troponin C gene. J Biol Chem 264: 13217–13225
Parmentier M, Lawson DEM, Vassart G (1987) Human 27-kDa calbindin complementary DNA sequence. Evolutionary and functional implications. Eur J Biochem 170:207–215
Pearson RB, Jakes R, John M, Kendrick-Jones J, Kemp BE (1986) Phosphorylation site sequence of smooth muscle myosin light chain (Mr=20000). FEBS Lett 168:108–112
Pechére J-F, Capony JP, Ryden L, DeMaille J (1971) The amino acid sequence of the major parvalbumin from hake muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 43:1106–1111
Pechére J-F, Capony J-P, DeMaille J (1973) Evolutionary aspects of the structure of muscular parvalbumins. Syst Zool 22:533–548
Pechére J-F, Rochat H, Ferraz C (1978) Parvalbumins from coelacanth muscle. II. Amino acid sequence of the two less acidic components. Biochim Biophys Acta 536:269–274
Periasamy M, Strehler EE, Garfinkel LI, Gubits RM, Ruiz-Opazo N, Nadal-Ginard B (1984) Fast skeletal muscle myosin light chains 1 and 3 are produced from a single gene by a combined process of differential RNA transcription and splicing. J Biol Chem 259:13595–13604
Perret C, Lomri N, Gouhier N, Auffray C, Thomasset M (1988a) The rat vitamin-D-dependent calcium-binding protein (9-kDa CaBP) gene. Complete nucleotide sequence and structural organization. Eur J Biochem 172:43–51
Perret C, Lomri N, Thomasset M (1988b) Evolution of the EF-hand calcium-binding protein family: evidence for exon shuffling and intron insertion. J Mol Evol 27:351–364
Persechini A, Kretsinger RH (1988) The central helix of calmodulin functions as a flexible tether. J Biol Chem 263:12175–12178
Persechini A, Blumenthal DK, Jarrett HW, Klee CB, Hardy DO, Kretsinger RH (1989) The effects of deletions in the central helix of calmodulin on enzyme activation and peptide binding. J Biol Chem 264:8052–8058
Prasher DC, McCann RO, Longiaru M, Cormier MJ (1987) Sequence comparisons of complementary DNAs encoding aequorin isotypes. Biochemistry 26:1326–1332
Putkey JA, Ts'ui KF, Tanaka T, Lagace L, Stein JP, Lai EC, Means AR (1983) Chicken calmodulin genes. A species comparison of cDNA sequences and isolation of a genomic clone. J Biol Chem 258:11864–11870
Putkey JA, Carroll SL, Means AR (1987) The nontranscribed chicken calmodulin pseudogene cross-hybridizes with mRNA from the slow-muscle troponin C gene. Mol Cell Biol 7:1549–1553
Reid RE, Gariépy J, Saund AK, Hodges RS (1981) Calcium-induced protein folding. Structure-affinity relationships in synthetic analogs of the helix-loop-helix calcium binding unit. J Biol Chem 256:2742–2751
Reinach FC, Karlsson R (1988) Cloning, expression, and sitedirected mutagenesis of chicken skeletal muscle troponin C. J Biol Chem 263:2371–2376
Robert B, Daubas P, Akimenko M-A, Cohen A, Garner I, Guenet J-L, Buckingham M (1984) A single locus in the mouse encodes both myosin light chains 1 and 3, a second locus corresponds to a related pseudogene. Cell 39:129–140
Rogers JH (1987) Calretinin: a gene for a novel calcium-binding protein expressed principally in neurons. J Cell Biol 105: 1343–1353
Roher A, Lieska N, Spitz W (1986) The amino acid sequence of human cardiac troponin-C. Muscle Nerve 9:73–77
Romero-Herrera AE, Castillo O, Lehmann H (1976) Human skeletal muscle proteins. The primary structure of troponin C. J Mol Evol 8:251–270
Sakihama T, Kakidani H, Zenita K, Yymoto N, Kikuchi T, Sasaki T, Kannagi R, Nakanishi S, Ohmori M, Takio K, Titani K, Murachi T (1985) A putative Ca2+-binding protein: structure of the light subunit of porcine calpain elucidated by molecular cloning and protein sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:6075–6079
Salvato M, Sulston J, Albertson D, Brenner S (1986) A novel calmodulin-like gene from the nematodeCaenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol 190:281–290
Saris CJ, Kristensen T, D'Eustachio P, Hicks LJ, Noonan DJ, Hunter T, Tack BF (1987) cDNA sequence and tissue distribution of the mRNA for bovine and murine p11, the S100-related light chain of the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I). J Biol Chem 262:10663–10671
Sasagawa T, Ericsson LH, Walsh KA, Schreiber WE, Fischer EH, Titani K (1982) Complete amino acid sequence of human brain calmodulin. Biochemistry 21:2565–2569
Satyshur KA, Rao ST, Pyzalska D, Drendel W, Greaser M, Sundaralingam M (1988) Refined structure of chicken skeletal muscle troponin C in the two-calcium state at 2-Å resolution. J Biol Chem 263:1628–1647
Schaefer WH, Hinrichsen RD, Burgess-Cassler A, Kung C, Blair IA, Watterson DM (1987a) A mutantParamecium with a defective calcium-dependent potassium conductance has an altered calmodulin: a nonlethal selective alteration in calmodulin regulation Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3931–3935
Schaefer WH, Lukas TJ, Blair IA, Schultz JE, Watterson DM (1987b) Amino acid sequence of a novel calmodulin fromParamecium tetraurelia that contains dimethyllysine in the first domain. J Biol Chem 262:1025–1029
Seidel U, Bober E, Winter B, Lenz S, Lohse P, Arnold HH (1987) The complete nucleotide sequences of cDNA clones coding for human myosin light chains 1 and 3. Nucleic Acids Res 15:4989
SenGupta B, Friedberg F, Detera-Wadleigh SD (1987) Molecular analysis of human and rat calmodulin complementary DNA clones. J Biol Chem 262:16663–16670
Sherbany AA, Parent AS, Brosius J (1987) Rat calmodulin cDNA. DNA 6:267–272
Simmen RCM, Tanaka T, Ts'ui KF, Putkey JA, Scott MJ, Lai EC, Means AR (1985) The structural organization of the chicken calmodulin gene. J Biol Chem 260:907–912
Smith VL, Doyle KE, Maune JF, Munjaal RP, Beckingham K (1987) Structure and sequence of theDrosophila melanogaster calmodulin gene. J Mol Biol 196:471–485
Sokal RR, Michener CD (1958) A statistical method for evaluating systematic relationships. Univ Kansas Sci Bull 38:1409–1438
Stein JP, Munjaal RP, Lagace L, Lai EC, O'Malley BW, Means AR (1983) Tissue-specific expression of a chicken calmodulin pseudogene lacking intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:6485–6489
Strehler EE, Periasamy M, Strehler-Page M-A, Nadal-Ginard B (1985) Myosin light chain 1 and 3 gene has two structurally distinct and differentially regulated promotors evolving at different rates. Mol Cell Biol 5:3168–3182
Strynadka NCJ, James MNG (1989) Crystal structures of the helix-loop-helix calcium-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 58:951–998
Suzuyama Y, Umegane T, Maita T, Matsuda G (1980) The amino acid sequence of the L-2 light chain of chicken skeletal muscle myosin. Hoppe-Seyler's Z Physiol Chem 361:119–127
Swan DG, Hale RS, Dhillon N, Leadlay PF (1987) A bacterial calcium-binding protein homologous to calmodulin. Nature 329:84–85
Szebenyi DME, Moffat K (1986) The refined structure of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine intestine. Molecular details, ion binding, and implications for the structure of other calcium-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 261:8761–8777
Szebenyi DME, Obendorf SK, Moffat K (1981) Structure of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine intestine. Nature 294:327–332
Takagi T, Konishi K (1983) Amino acid sequence of troponin C obtained from ascidian (Halocynthia roretzi) body wall muscle. J Biochem 94:1753–1760
Takagi T, Konishi K (1984a) Amino acid sequence of the β chain of sarcoplasmic calcium binding protein (SCP) obtained from shrimp tail muscle. J Biochem 96:59–67
Takagi T, Konishi K (1984b) Amino acid sequence of α chain of sarcoplasmic calcium binding protein obtained from shrimp tail muscle. J Biochem 95:1603–1615
Takagi T, Nemoto T, Konishi K, Yazawa M, Yagi K (1980) The amino acid sequence of the calmodulin obtained from sea anemone (Metridium senile) muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 96:377–381
Takagi T, Kobayashi T, Konishi K (1984) Amino-acid sequence of sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein from scallop (Patinopecten yessoensis) adductor striated muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta 787:252–257
Takagi T, Konishi K, Cox JA (1986a) Amino acid sequence of two sarcoplasmic calcium-binding proteins from the protochordate amphioxus. Biochemistry 25:3585–3592
Takagi T, Kudoh S, Konishi K (1986b) The amino acid sequence of ascidian (Halocynthia roretzi) myosin light chains. Biochim Biophys Acta 874:318–325
Takagi T, Nojiri M, Konishi K, Maruyama K, Nonomura Y (1986c) Amino acid sequence of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein from bovine cerebellum. FEBS Lett 201: 41–45
Takeda T, Yamamoto M (1987) Analysis andin vivo disruption of the gene coding for calmodulin inSchizosaccharomyces pombe. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3580–3584
Tanaka H, Maita T, Ojima T, Nishita K, Matsuda G (1988) Amino acid sequence of the regulatory light chain of clam foot muscle myosin. J Biochem 103:572–580
Thatcher DR, Pechére J-F (1977) The amino-acid sequence of the major parvalbumin from thornback-ray muscle. Eur J Biochem 75:121–132
Thomasset M, Desplan C, Warembourg M, Perret C (1986) Vitamin-D dependent 9 kDa calcium-binding protein gene: cDNA cloning, mRNA distribution and regulation. Biochimie 68:935–940
Toda H, Yazawa M, Kondo K, Honma T, Narita K, Yagi K (1981) Amino acid sequence of calmodulin from scallop (Patinopecten) adductor muscle. J Biochem 90:1493–1505
Toda H, Yazawa M, Sakiyama F, Yagi K (1985) Amino acid sequence of calmodulin from wheat germ. J Biochem 98:833–842
Tomlinson CR, Klein WH (1989) Temporal and spatial transcriptional regulation of the aboral ectoderm-specific Spec genes during sea urchin embryogenesis. Mol Rep Dev (in press)
Tschudi C, Young AS, Ruben L, Patton CL, Richards FF (1985) Calmodulin genes in trypanosomes are tandemly repeated and produce multiple mRNAs with a common 5′ leader sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3998–4002
Tufty RM, Kretsinger RH (1975) Troponin and parvalbumin calcium binding regions predicted in myosin light chain and T7 lysozyme. Science 187:167–169
Umegane T, Maita T, Matsuda G (1982) Amino-acid sequence of the L-1 light chain of chicken fast skeletal-muscle myosin. Hoppe-Seyler's Z Physiol Chem 363:1321–1330
Vanaman TC, Sharief F (1979) Structural properties of calmodulin from divergent eucaryotic organisms. Fed Proc 38:788
Van der Bliek AM, Meyers MB, Biedler JL, Hes E, Borst P (1986) A 22-kd protein (sorcin/V19) encoded by an amplified gene in multidrug-resistant cells, is homologous to the calcium-binding light chain of calpain. EMBO J 5:3201–3208
van Eerd J-P, Takahashi K (1976) Determination of the complete amino acid sequence of bovine cardiac troponin C. Biochemistry 15:1171–1180
van Eerd J-P, Capony J-P, Ferraz C, Pechére J-F (1978) The amino-acid sequence of troponin C from frog skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem 91:231–242
Varghese S, Lee S, Huang Y-C, Christakos S (1988) Analysis of rat vitamin D-dependent calbindin-D28K gene expression. J Biol Chem 263:9776–9784
Wasserman RH, Taylor AN (1966) Vitamin D3-induced calcium-binding protein in chick intestinal mucosa. Science 152: 791–793
Watanabe B, Maita T, Konno K, Matsuda G (1986) Aminoacid sequence of LC-1 light chain of squid mantle muscle myosin. Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler 367:1025–1032
Watterson DM, Sharief F, Vanaman TC (1980) The complete amino acid sequence of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein (calmodulin) of bovine brain. J Biol Chem 255:962–975
Weeds AG, McLachlan AD (1974) Structural homology of myosin alkali light chains, troponin C and carp calcium binding protein. Nature 252:646–649
Wilkinson JM (1976) The amino acid sequence of troponin C from chicken skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett 70:254–256
Wilkinson JM (1980) Troponin C from rabbit slow skeletal and cardiac muscle is the product of a single gene. Eur J Biochem 103:179–188
Wilson PW, Harding M, Lawson DEM (1985) Putative amino acid sequences of chick calcium-binding protein deduced from a complementary DNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 13:8867–8881
Wilson PW, Rogers J, Harding M, Pohl V, Pattyn G, Lawson DEM (1988) Structure of chick chromosomal genes for calbindin and calretinin. J Mol Biol 200:615–625
Wnuk W (1988) Calcium binding to troponin C and the regulation of muscle contraction. In: Gerday C, Bolis L, Gilles R (eds) Calcium and calcium binding proteins: molecular and functional aspects. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 44–68
Wnuk W, Schoechlin M, Kobayashi T, Takagi T, Konishi K, Hoar PE, Kerrick WGL (1986) Two isoforms of troponin C from crayfish. Their characterization and a comparison of their primary structure with the tertiary structure of skeletal troponin C. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 7:67–68
Wood TL, Kobayashi Y, Frantz G, Varghese S, Christakos S, Tobin AJ (1988) Molecular cloning of mammalian 28,000 Mr vitamin D-dependent calcium binding protein (calbindin-D 28K): expression of calbindin-D28K RNAs in rodent brain and kidney. DNA 7:585–593
Xiang M, Bedard P-A, Wessel G, Filion M, Brandhorst B, Klein WH (1988) Tandem duplication and divergence of a sea urchin protein belonging to the troponin C superfamily. J Biol Chem 263:17173–17180
Yamakuni T, Kuwano R, Odani S, Miki N, Yamaguchi Y, Takahashi Y (1986) Nucleotide sequence of cDNA to mRNA for a cerebellar Ca-binding protein, spot 35 protein. Nucleic Acids Res 14:6768
Yamanaka MK, Saugstad JA, Hanson-Painton O, McCarthy BJ, Tobin SL (1987) Structure and expression of theDrosophila calmodulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res 15:3335–3348
Yazawa M, Yagi K, Toda H, Kondo K, Narita K, Yamazaki R, Sobue K, Kakiuchi S, Nagao S, Nozawa Y (1981) The amino acid sequence of theTetrahymena calmodulin which specifically interacts with guanylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 99:1051–1057
Zhu D-X, Maeda N, Fitch WM (1985) Amino acid sequences of two parvalbumins from electric eel (Electrophorus electricus). Sci Sin 28B:926–941
Zimmer DB, Van Eldik LJ (1989) Analysis of the calciummodulated proteins, calmodulin, and their target proteins during C6 glioma cell differentiation. J Cell Biol 108:141–151
Zolese G, Tangorra A, Curatola G, Giambanco I (1988) Interaction of S100-b protein with cardiolipin vesicles as monitored by electron spin resonance, pyrene fluorescence and circular dichroism. Cell Calcium 9:149–157
Zot AS, Potter JD, Straus WL (1987) Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone for rabbit fast skeletal muscle troponin C. Homology with calmodulin and parvalbumin. J Biol Chem 262:15418–15421
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moncrief, N.D., Kretsinger, R.H. & Goodman, M. Evolution of EF-hand calcium-modulated proteins. I. Relationships based on amino acid sequences. J Mol Evol 30, 522–562 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02101108
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02101108