Summary
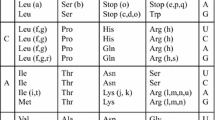
The amino acid code is usually presented as a table of 64 codons. Actually the code results from the action of tRNA molecules that carry amino acids to codons in mRNA by means of codon-anticodon pairing. The tRNA molecules are transcribed from genes that undergo evolution and the number of anticodons can therefore increase during evolution, but the number of codons is fixed at 64. Mammalian mitochondrial codes contain only 22 anticodons for 20 amino acids as compared with 54 anticodons for 20 amino acids in the universal code. It is proposed that an archetypal code containing 16 anticodons for 15 amino acids evolved into the universal code by gene duplication, followed by mutations that modified the anticodons and amino acid acceptor sites. In substantiation of this proposal, it is noted that the mammalian mitochondrial code, is simplified by comparison with the universal code. For example, single anticodons are used for each of eight amino acids in the mammalian mitochondrial code. This simplification may represent an evolutionary retrogression towards the proposed archetypal code.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson S, Bankier AT, Barrell BG, de Bruijn MHL, Coulson AR, Drouin J, Eperon IC, Nierlich DP, Roe BA, Sanger F, Schreier PH, Smith AJH, Staden R, Young IG (1981) Sequence and organization of the human mitochondrial genome. Nature 290:457–470
Anderson S, de Brujin MHL, Coulson AR, Eperon, IC, Sanger E, Young IG (1982) The complete sequence of bovine mitochondrial DNA: Conserved features of the mammalian mitochondrial genome. J Mol Biol 156:683–717
Balasubramanian R (1982) Origin of life: A hypothesis for the origin of adaptor-mediated ordered synthesis of proteins and explanation for the choice of terminating codons in the genetic code. Biosystems 15:99–104
Barrell BG, Anderson S, Bankier AT, de Bruijn MHL, Chen E, Coulson AR, Drouin, J, Eperon IC, Nierlich DP, Roe BA, Sanger F, Schreier PH, Smith AJH, Staden R, Young IG (1980) Different pattern of codon recognition by mammalian mitochondrial tRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:3164–3166
Bibb MJ, Van Etten RA, Wright CT, Walberg MW, Clayton DA (1981) Sequence and gene organization of mouse mitochondrial DNA. Cell 26:167–180
Bonitz SG, Berlani R, Coruzzi G, Li M, Macino G, Nobrega FB, Nobrega MP, Thalenfeld BE, Tzagoloff A (1980) Codon recognition rules in yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:3167–3170
Bonitz SG, Coruzzi G, Thalenfeld BE, Tzagoloff A, Macino G (1980a) Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. J Biol Chem 255:11927–11941
Coruzzi G, Bonitz SG, Thalenfeld BE, Tzagoloff A (1981) Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system: Analysis of the nucleotide sequence and transcripts in theoxil regions of yeast mitochondrial DNA. J Biol Chem 256:12780–12787
Crick FHC (1966) Codon-anticodon pairing: The wobble hypothesis. J Mol Biol 19:548–555
Crick FHC (1968) The origin of the genetic code. J Mol Biol 38:367–379
Eck RV (1963) Genetic code: Emergence of a symmetrical pattern. Science 140:477–482
Fox TD, Leaver CJ (1981) The Zea mays mitochondrial gene coding cytochrome oxidase subunit II has an intervening sequence and does not contain TGA codons. Cell 26:315–323
Fukada K, Abelson J (1980) DNA sequence of a T4 transfer RNA gene cluster. J Mol Biol 139:377–391
Groshean HJ, De Henan S, Crothers DM (1978) On the physical basis for ambiguity in genetic coding interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 75:610–614
Heckman JE, XX, XXX (1980) Novel features in the genetic code and codon reading patterns inNeurospora crasa mitochondria based on sequences of six mitochondrial tRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:3159–3163
Jukes TH (1966) Molecules and Evolution. Columbia, New York
Jukes TH (1973) Arginine as a evolutionary intruder into protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 53:704–714
Jukes TH (1977) The amino acid code. In: Neuberger A (ed) Comprehensive biochemistry. Vol 24, Biological information transfer. Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, p 235
Jukes TH (1981) Amino acid codes in mitochondria as possible clues to primitive codes. J Mol Evol 18:15–16
Jukes TH, Holmquist R, Moise H (1975) Amino acid composition of proteins: Selection against the genetic code. Science 189:50–51
Kammen HO, Spengler SJ (1970) The biosynthesis of inosinic acid in transfer RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 213:352
Köchel HG, Küntzel H (1982) Mitochondrial L-rRNA fromAspergillus nidulans: Potential secondary structure and evolution. Nucl Acids Res 10:4795–4801
Köchel HG, Lazarus CM, Basak N, Küntzel H (1981) Mitochondrial tRNA gene clusters in Aspergillus nidulans: Organization and nucleotide sequence. Cell 23:625–633
Kuchino Y, Watanabe S, Harada F, Nishimura S (1980) Primary structure of AUA-specific isoleucine transfer ribonucleic acid fromEschericia coli. Biochemistry 19:2985–2098
Lagerkvist U (1981) Unorthodox codon reading and the evolution of the genetic code. Cell 23:305–306
Li W-H (1982) Ch. 3 in Evolution of Genes and Proteins (in press)
Nishimura S (1972) Minor components in transfer RNA: Their characterization, location and function. Prog Nucl Acid Res Mol Biol 12:49–85
Woese CR (1981) Archaebacteria. Sci Am 244:98–122
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jukes, T.H. Evolution of the amino acid code: Inferences from mitochondrial codes. J Mol Evol 19, 219–225 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02099969
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02099969