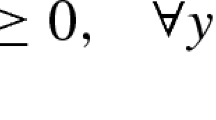Abstract
Nonlinear bilevel programming problems, of which the equilibrium network design problem is one, are extremely difficult to solve. Even if an optimum solution is obtained, there is no sure way of knowing whether the solution is the global optimum or not, due to the nonconvexity of the bilevel programming problem. This paper reviews and discusses recent developments in solution methodologies for nonlinear programming models of the equilibrium network design problem. In particular, it provides a primer for descent-type algorithms reported in the technical literature and proposes certain enhancements thereof.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Abdulaal and L. LeBlanc, Continuous equilibrium network design models, Transport. Res. 13B(1979)19–32.
R.E. Allsop, Some possibility for using traffic control to influence trip distribution and route choice, in:Transportation and Traffic Theory, Proc. 6th Int. Symp. on Transportation and Traffic Theory, ed. D.J. Buckley (Elsevier, New York, 1974), pp. 345–375.
O. Ben-Ayed, D.E. Boyce and C.E. Blair, The network design problem formulated as a bilevel linear programming problem, Transport. Res. 22B(1988)311–318.
D.P. Bertsckas,Constrained Optimization and Lagrange Multiplier Methods (Academic Press, New York, 1982).
R.M. Chamberlain, C. Lemarechal, H.C. Pedersen and M.J.D. Powell, The watchdog technique for forcing convergence in algorithms for constrained optimization, Math. Progr. Study 16(1982)1–17.
A.H. de Silva, Sensitivity formulas for nonlinear factorable programming and their application to the solution of an implicitly defined optimization model of US crude oil production, D.Sc. Dissertation, George Washington University, Washington, DC (1978).
A.V. Fiacco, Sensitivity analysis for nonlinear programming using penalty methods, Math. Progr. 10(1976)287–311.
A.V. Fiacco,Introduction to Sensitivity and Stability Analysis in Nonlinear Programming (Academic Press, New York, 1983).
R. Fletcher, An efficient, globally convergent algorithm for unconstrained and linearly constrained optimization problems, AERE TP.431, Harwell (1971)
T.L. Friesz and P.T. Harker, Properties of the iterative optimization-equilibrium algorithm, Civil Engin. Syst. 2(1985)142–154.
T.L. Friesz, T. Miller and R.L. Tobin, Algorithms for spatially competitive network facility-location, Environ. Planning B15(1988)191–203.
T.L. Friesz, R.L. Tobin, H.-L. Cho and N.J. Mchta, Sensitivity analysis based heuristic algorithms for mathematical programs with variational inequality constraints, Math. Progr. B (1990), to appear.
P.T. Harker and S.-C. Choi, A penalty function approach for mathematical programs with variational inequality constraints, Decision Science Working Paper 87-09-08, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia (1987).
P.T. Harker and J.-S. Pang, Finite-dimensional variational inequality and nonlinear complementarity problems: A survey of theory, algorithms and applications, Department of Decision Science, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia (1987).
T.J. Kim,Advanced Transport and Spatial Systems Models: Applications to Korea (Springer, New York, 1990).
T.J. Kim and S. Suh, Toward developing a national transportation planning model: A bilevel programming approach for Korea, Ann. Regional Sci. XXSPED(1988)65–80.
C.D. Kolstad, A review of the literature on bilevel mathematical programming, Los Alamos National Laboratory Report LA-10284-MS, Los Alamos, NM (1985).
C.D. Kolstad and L.S. Lasdon, Derivative evaluation and computational experience with large bilevel mathematical programs, Working Paper, Department of economics, University of Illinois, Urbana (1988).
L.J. LeBlanc and D.E. Boyce, A bilevel programming algorithm for exact solution of the network design problem with user-optimal flows, Transport. Res. 20B(1986)259–265.
L.J. LeBlanc, E.K. Morlok and W.P. Pierskalla, An efficient approach to solving the road network equilibrium traffic assignment problem, Transport. Res. 9(1975)309–318.
P. Marcotte, Network optimization with continuous control parameters, Transport. Sci. 17(1983)181–197.
P. Marcotte, Network design problem with congestion effects: A case of bilevel programming, Math. Progr. 34(1986)142–162.
M.J.D. Powell, Extensions to subroutine VF02AD, in:System Modeling and Optimization, Lecture Notes in Control and Information Science 38, ed. R.F. Drenick and F. Kozin (Springer, Berlin, 1982), pp. 529–539.
Y. Sheffi,Urban Transportation Networks: Equilibrium Analysis with Mathematical Programming Methods (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1985).
P.A. Steenbrink.Optimization of Transport Networks (Wiley, New York, 1974).
C. Suwansirikul, T.L. Friesz and R.L. Tobin, Equilibrium Decomposed Optimization: A heuristic for the continuous equilibrium network design problem, Transport. Sci. 21(1987)254–263.
H.-N. Tan, S.B. Gershwin and M. Athans, Hybrid optimization in urban traffic networks, Report No. DOT-TSC-RSPA-79-7, Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA (1979).
R.L. Tobin. Sensitivity analysis for variational inequalities. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 48(1986)191–204.
R.L. Tobin and T.L. Friesz, Sensitivity analysis for equilibrium network flow, Transport. Sci. 22(1988)242–250.
U.P. Wen, Mathematical methods for multilevel linear programing, Ph.D. Dissertation, State University of New York at Buffalo, NY (1981).
J.G. Wardrop, Some theoretical aspects of road traffic research, Proc., Institute of Civil Engineers 1(1952)325–378.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suh, S., Kim, T.J. Solving nonlinear bilevel programming models of the equilibrium network design problem: A comparative review. Ann Oper Res 34, 203–218 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02098180
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02098180