Abstract
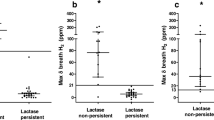
Ninety-eight adults ranging from 20 to 89 years in age (52 blacks, 46 whites; 48 males, 50 females) were tested for lactose maldigestion by breath hydrogen analysis after consuming milk containing 16.5 g lactose (360 ml milk). Older adults (≥50 years) displayed a significantly higher incidence (46%) of lactose maldigestion than younger adults (<50 years, 26%). In younger adults there were 2.4 times more maldigesters in blacks than in whites, while in older groups this ratio was 3.6. Level of breath hydrogen significantly increased with age up to the age group of 60–69 years. The interaction between age groups and race was highly significant. Of the maldigesters, 63% reported symptoms and 3% of the total sample reported severe symptoms. Results of this study indicate that the prevalance of lactose maldigestion significantly increases with age in blacks compared to whites and that the magnitude of the problem may be greater in black maldigesters than in white maldigesters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scrimshaw NS, Murray EB: The acceptability of milk and milk products in populations with a high prevalence of lactose intolerance. Am J Clin Nutr 48:1083–1159, 1988
Saavedra M, Perman JA: Current concepts in lactose malabsorption and intolerance. Annu Rev Nutr 9:475–502, 1989
Rao DR: Lactose maldigestion: Prevalence, significance, diagnosis, dietary management and dairy technology.In KW Young, LY Cha, LK Yull, JS Soon, KS He (eds). Proceedings of 14th International Congress of Nutrition, Vol II: Workshop No. 25. Seoul, Korea, Ewa Womans University
Rao DR, Pulusani SR, Chawan CB: Role of fermented milk products in milk intolerance and other clinical conditions. Adv Nutr Res 7:203–219, 1985
Ravich WJ, Bayless TM: Carbohydrate absorption and malabsorption. Clin Gastroenterol 12:335–356, 1983
Bayless TM: Lactose malabsorption, milk intolerance, and symptom awareness in adults.In Lactose Digestion: Clinical and Nutritional Implications. DM Paige, TM Bayless (eds). Baltimore, Maryland, Johns Hopkins University Press, 1981, pp 117–123
Caskey DA, Payne-Bose D, Welsh JD, et al: Effects of age on lactose malabsorption in Oklahoma native Americans as determined by breath H2 analysis. Am J Dig Dis 22:113–116, 1977
Welsh JD, Poley JR, Bhatia M, Stevenson DE: Intestinal disaccharidase activities in relation to age, race and mucosal damage. Gastroenterology 75:847–855, 1978
Feibusch JM, Holt PR: Impaired absorptive capacity for carbohydrate in the aging human. Dig Dis Sci 27:1095–1100, 1982
Cuatrecasas P, Lockwood DH, Caldwell JR: Lactase deficiency in the adult. A common occurrence. Lancet 1:14–18, 1965
Bayless TM, Rosenweig NS: A racial difference in the incidence of lactose deficiency. JAMA 197:968–972, 1966
Welsh JD, Zschiesche OM, Willits VL, Russell L: Studies of lactose intolerance in families. Arch Intern Med 122:315–317, 1968
Sasaki Y, Lio M, Kameda H, et al: Measurement of14C-lactose absorption in the diagnosis of lactase deficiency. J Lab Clin Med 76:824–835, 1970
Paige DM, Bayless TM, Huang S, Wexier R: Lactose hydrolyzed milk. Am J Clin Nutr 28:818–822, 1975
Bell RR, Draper HH, Bergan JD: Sucrose, lactose and glucose tolerance in northern Alaskan Eskimos. Am J Clin Nutr 26:1185–1190, 1973
Paige DM, Bayless TM, Dellinger WS: Relationship of milk consumption to blood glucose rise in lactose intolerant individuals. Am J Clin Nutr 20:677–680, 1975
Lisker R, Lopez-Habib G, Daltabuit M, Rotenberg I, Arroyo P: Lactase deficiency in a rural area of Mexico. Am J Clin Nutr 27:756–759, 1974
Kasir Z, Kellow AH: Lactose intolerance in Iraq. J Fac Med Baghdad 20:245–249, 1978
Rozen P, Shafrir E: Behavior of serum free fatty acids and glucose during lactose tolerance tests. Isr J Med Sci 4:100–109, 1968
Woteki CE, Weser E, Young EA: Lactose malabsorption in Mexican-American adults. Am J Clin Nutr 30:470–475, 1977
Rumessen JJ, Gudmand-Hoyer E: Functional bowel disease: Malabsorption and abdominal distress after ingestion of fructose, sorbitol, and fructose-sorbitol mixtures. Gastroenterology 95:694–700, 1988
Onwulata CI, Rao DR, Vankineni P: Relative efficiency of yogurt, sweet acidophilus milk, hydrolyzed-lactose milk and a commercial lactase tablet in alleviating lactose maldigestion. Am J Clin Nutr 49:1233–1237, 1989
Rao DR, Dehkordi N, Chawan CB: Effect of fruited yogurts, chocolate milk and skim milk with sucrose on lactose maldigestion. Paper presented at the XIV International Congress of Nutrition, Seoul, Korea, August 1989
Newcomer AD: Immediate symptomatic and long-term nutritional consequences of hypolactasia.In Lactose Digestion: Clinical and Nutritional Implications. DM Paige, TM Bayless (eds). Baltimore, Maryland, Johns Hopkins University Press, 1981, pp 124–133
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, D.R., Bello, H., Warren, A.P. et al. Prevalence of lactose maldigestion. Digest Dis Sci 39, 1519–1524 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02088058
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02088058