Abstract
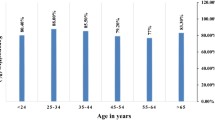
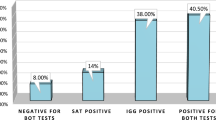
A prospective survey to investigate the seroprevalence of IgG againstHelicobacter pylori among endoscopists in Taiwan was conducted by analyzing blood samples of 70 study subjects and 64 nonendoscopist physicians with quantitative ELISA. Personal information and the practices of infection control related to gastroscopy examination were obtained by a self-administered questionnaire. Significant differences were detected in the IgG prevalence between study and control subjects (80.0% vs 51.6%;P<0.05). The serum level of antibody in endoscopists (385.2±36.1 unit/ml) was significantly higher than that of nonendoscopists (211.8±33.0 unit/ml;P=0.018). Endoscopists performing 30 or more sessions of gastroscopy per week had higher seroprevalence than those performing less than 30 sessions (90.9% vs 70.3%;P=0.0126). In conclusion, endoscopists in Taiwan had a high prevalence ofH. pylori infection. The cause might be related to the frequency of gastroscopies performed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parsonnet J, Blaser MJ, Perez-Perez GI, Hargrett-Bean N, Tauxe RV: Symptoms and risk factors ofHelicobacter pylori infection in a cohort of epidemiologists. Gastroenterology 102:41–46, 1992
Malaty HM, Evans DG, Evans DJ Jr, Graham DY:Helicobacter pylori in Hispanics: Comparison with blacks and whites of similar age and socioeconomic class. Gastroenterology 103:813–816, 1992
Sipponen P:Helicobacter pylori: A cohort phenomenon. Am J Surg Pathol 19(suppl 1):S30-S36, 1995
Cullen DJE, Collins BJ, Christiansen KJ, Epis J, Warren JR, Surveyor I, Cullen KJ: When isHelicobacter pylori infection acquired? Gut 34:1681–1682, 1993
Kuipers EJ, Peña AS, Kamp Gv, Uyterlinde AM, Pals G, Pels NFM, Kurz-Pohlmann E, Meuwissen SGM: Seroconversion forHelicobacter pylori. Lancet 342:328–331, 1993
Bell GD, Powell KU, Burridge SM, Harrison G, Rameh B, Weil J, Gant PW, Jones PH, Trowell JE: Reinfection or recrudescence after apparently successful eradication ofHelicobacter pylori infection: Implications for treatment of patients with duodenal ulcer disease. Q J Med 86:375–382, 1993
Borody TJ, Andrews P, Mancuso N, McCauley D, Jankiewicz E, Ferch N, Shortis NP, Brandl S:Helicobacter pylori reinfection rate, in patients with cured duodenal ulcer. Am J Gastroenterol 89:529–532, 1994
Louw JA, Lucke W, Jaskiewicz K, Lastovica AJ, Winter TA, Marks IN:Helicobacter pylori eradication in the African setting, with special reference to reinfection and duodenal recurrence. Gut 36:544–547, 1995
Mendall MA, Goggin PM, Molineaux N, Levy J, Toosy T, Strachan D, Northfield TC: Childhood living conditions andHelicobacter pylori seropositivity in adult life. Lancet 339:896–897, 1992
Malaty HM, Graham DY: Importance of childhood socioeconomic status on the current prevalence ofHelicobacter pylori infection. Gut 35:742–745, 1994
Drumm B, Perz-perz GI, Blaser MJ, Sherman PM: Intrafamilial clustering ofHelicobacter pylori infection. N Engl J Med 322:359–363, 1990
Malaty HM, Graham DY, Klein PD, Evans DG, Adam E: Transmission ofHelicobacter pylori infection. Studies in family of healthy individuals. Scand J Gastroenterol 26:927–932, 1991
Perez-Perez GI, Witkin SS, Decker MD, Blaser MJ: Seroprevalence ofHelicobacter pylori infection in couples. J Clin Microbiol 29:642–644, 1991
Polish LB, Douglas JM Jr, Davidson AJ, Perez-Perez GI, Blaser MJ: Characterization of risk factors forHelicobacter pylori infection among men attending a sexually transmitted disease clinic: Lack of evidence for sexual transmission. J Clin Microbiol 29:2139–2143, 1991
Basso L, Beattie S, Lawlor S, Clune J, O'Morain C: A descriptive follow-up study ofHelicobacter pylori infection before and after exposition to a war area. Eur J Epidemiol 10:109–111, 1994
Schütze K, Hentschel E, Dragosics B, Hirschl AM:Helicobacter pylori reinfection with identical organisms: Transmission by the patients' spouses. Gut 36:831–833, 1995
Reiff A, Jacobs E, Kist M: Seroepidemiological study of the immune response toCampylobactor pylori in potential risk groups. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 8:592–596, 1989
Morris A, Lloyd G, Nicholson G:Campylobacter pyloridis serology among gastroendoscopy clinic staff. NZ Med J 99:819–820, 1986
Rawles JW, Harris ML, Paull G, Dick J, Yardley JH, Kafonek DR, Hendrix TR, Ravich WJ: Antibody toCampylobacter pyloridis in endoscopy personnel, patients, and controls. Gastroenterology 92:1589, 1987
Mitchell HM, Lee A, Carrick J: Increased incidence ofCampylobacter pylori infection in gastroenterologists: Further evidence to support person-to-person transmission ofC. pylori. Scand J Gastroenterol 24:396–400, 1989
Kahlon DS, Barnes RE, Nahhas GT, Zervos MA, Duffy MC:Helicobacter pylori antibodies in endoscopy personnel. Am J Gastroenterol 88:1510, 1993
Lin SK, Lambert JR, Schembri MA, Nicholson L, Korman MG:Helicobacter pylori prevalence in endoscopy and medical staff. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 9:319–324, 1994
Pristautz H, Eherer A, Brezinschek R, Truschnig-Wilders M, Petritsch W, Schreiber F, Hammer HF, Wenzl H, Hinterleitner T, Reicht G, Tilz GP, Krejs GJ: Prevalence ofHelicobacter pylori antibodies in the serum of gastroenterologists in Austria. Endoscopy 26:690–696, 1994
Chong J, Marshall BJ, Barkin JS, McCallum RW, Reiner DK, Hoffman SR, O'Phelan C: Occupational exposure toHelicobacter pylori for the endoscopy professional: A sera epidemiological study. Am J Gastroenterol 89:1987–1992, 1994
Wang WM, Chen CY, Jan CM, Chen LT, Perng DS, Lin SR, Liu CS: Long-term follow-up and serological study after triple therapy ofHelicobacter pylori associated duodenal ulcer. Am J Gastroenterol 89:1793–1796, 1994
Axon ATR: The role of acid inhibition in the treatment ofHelicobacter pylori infection. Scan J Gastroenterol 29(suppl 201):16–23, 1994
Kuipers EJ, Uyterlinde AM, Peña AS, Roosendaal R, Pals G, Nelis GF, Festen HPM, Meuwissen SGM: Long-term sequelae ofHelicobacter pylori infection. Lancet 345:1525–1528, 1995
Graham DY, Alpert LC, Smith JL, Yoshimura HH: IatrogenicCampylobacter pylori infection is a cause of epidemic achlorhydria. Am J Gastroenterol 88:974–980, 1988
Langenberg W, Rauws AJ, Oudbier JH, Tytgat GNJ: Patient-to-patient transmission ofCampylobacter pylori infection by fiberoptic gastroduodenoscopy and biopsy. J Infect Dis 161:507–511, 1990
Graham DY, Malaty HM, Go MF: Are there susceptible hosts toHelicobacter pylori infection? Scand J Gastroenterol 29(suppl 205):6–10, 1994
Mendall MA, Northfield TC: Transmission ofHelicobacter pylori infection. Gut 37:1–3, 1995
Gorse GJ, Messner RL: Infection control practices in gastrointestinal endoscopy in the United States: A national survey. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 12:289–296, 1991
Gossum AV, Loriers M, Serruys E, Cremer M: Methods of disinfecting endoscopic material: Results of an international survey. Endoscopy 21:247–250, 1989
Collignon P, Graham E: How well are endoscopes cleaned and disinfected between patients? Med J Aust 151:269–272, 1989
Nomura A, Stemmermann GN, Chyou PH, Perez-Perez GI, Blaser MJ:Helicobacter pylori infection and the risk for duodenal and gastric ulceration. Ann Intern Med 120:977–981, 1994
Martin DF, Montgomery E, Dobek AS, Patrissi GA, Peura DA: Noninvasive detection of histological gastritis. Gastroenterology 94:A285, 1988
Faulde M, Schröder JP, Sobe D: Serodiagnosis ofHelicobacter pylori infection by detection of immunoglobulin G antibodies using an immunoblot technique and enzyme immunoassay. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 11:589–594, 1992
Dubois A, Fiala N, Heman-Ackah LM, Drazek ES, Tranawski A, Fishbein WN, Perez-Perez GI, Blaser MJ: Natural gastric infection withHelicobacter pylori in monkey: A model for spiral bacterial infection in humans. Gastroenterology 106:1405–1417, 1994
Kreuning J, Lindeman J, Biemond I, Lamers CBHW: Relation between IgG and IgA antibody titres againstHelicobacter pylori in serum and severity of gastritis in asymptomatic subjects. J Clin Pathol 47:227–231, 1994
Kekki M, Maaroos H-I, Sipponen P, Uibo R, Tammur R, Tamm A, Villako K: Grade ofHelicobacter pylori colonisation in relation to gastritis: A six year population-based follow-up study. Scand J Gastroenterol 25(suppl 186):142–150, 1991
Niemelä S, Karttunen T, Kerola T:Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis. Evolution of histologic changes over 10 years. Scand J Gastroenterol 30:542–549, 1995
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, YC., Wang, WM., Chen, LT. et al. High seroprevalence of IgG againstHelicobacter pylori among endoscopists in Taiwan. Digest Dis Sci 41, 1571–1576 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02087902
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02087902