Abstract
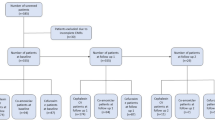
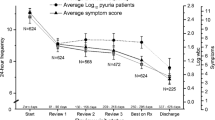
Bacteriologic examinations of urine were performed daily in 85 patients admitted for chronic recurrent urinary tract infections and treated with antibacterial drugs. The results have shown that the effect of therapy, can be evaluated fairly accurately on the basis of bacteriological findings in urine within the first four days of treatment. When sterility was achieved as early as after one or two days of therapy, the urine remained sterile in more than 90% of the patients throughout the first post-treatment week; in more than 80% therapy had a long-term effect. A slowly subsiding urinary tract infection or reduced urinary bacterial count indicates that therapy will be ineffective.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar, J. F.: Dynamique de la bactériurie dans les infections urinaires á bacilles Gram négatif traitée par les antibiotiques.Path. Biol., 17, 859 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prát, V., Bohuslav, V. & Hatala, M. Daily bacteriological examination of urine during antimicrobial treatment of urinary tract infections. International Urology and Nephrology 11, 3–10 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02082805
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02082805