Abstract
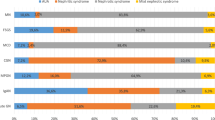
Autopsies of all uraemic patients in Leningrad for three years, and materials of the City Nephrological Service have demonstrated that the structures of nephrological diseases in their early and terminal stages were different. Chronic glomerulonephritis has been noted in patients with normal renal function just as often as chronic pyelonephritis but the former prevails considerably among the causes of uraemia. The proportion of polycystic kidney disease, amyloidosis, and diabetic nephropathy increases in patients with chronic renal failure. Due to these changes and the difference in the death age of patients with various diseases the majority of patients suitable for treatment with long-term dialysis suffer from chronic glomerulonephritis and only 14.89–20.5% from chronic pyelonephritis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlmen, J., Gustafson, A., Storm, B.: Morbidity in azotemia and mortality in uremia.Acta Med. Scand., 192, 113 (1972).
Barnes, B. A., Bergan, J. J., Braun, W. E., Hampers, C. L., Kayhoe, D. L., Kountz, S. L. Mickey, M. R., Rubon, A. L., Simmons, R. L., Stevens, L. E.: The Ninth Report of the Human Renal Transplant Registry.JAMA, 220, 253 (1972).
Bondarenko, B. B., Polyakov, I. V.: On the study of mortality due to diseases of the kidneys and the urinary system.Klin. Med. USSR, 10, 42 (1981).
Burton, B. T., Hirschman, G. H.: Demographic analysis: End-stage renal disease and its treatment in the United States.Clin. Nephrol., 11, 47 (1979).
Dombey, S. L., Sagar, D., Knapp, M. S.: Chronic renal failure and requirements for dialysis and transplant facilities.Br. Med. J., 2, 484 (1975).
Dubach, U. C.: Mortalitätsentwicklung für Nierenleiden in der Schweiz 1947–1966.Schweiz. Med. Wochenschr., 98, 1542 (1968).
Dutz, H., Precht, K.: Zur Organisation der nephrologischen Betreuung in der DDR.Z. Urol. Nephrol., 67, 737 (1974).
Ermolenko, V. M., Lalin, S. N., Troshina, I. M.: Incidence of chronic renal insufficiency.Sov. Med., 7, 24 (1981).
Ermolenko, V. M.: Chronic Hemodialysis. Meditsina, Moscow, 1982.
Gloor, F.: Die doppelseitige chronische, nicht obstruktive interstitielle Nephritis.Ergebn. Allg. Path. Path. Anat., 41, 63 (1961).
Gurland, H. J., Brunner, F. P., Chantier, C., Jacobs, C., Scharer, K., Selwood, N. H., Spies, G., Wing, A. J.: Combined report on regular dialysis and transplantation in Europe, 6, 1975.Proc. Eur. Dial. Transpl. Ass., 13, 3 (1976).
Heale, W. F., Laver, M. C., Mathew, T. H., Kincaid-Smith P.: The pathogenesis of chronic renal failure.Aust. N. Z. Med. J., 3, 330 (1973).
Kirsnis, V. A.: Morbidity in Glomerulonephritis. 2nd Congress on Nephrology, Moscow-Leningrad, USSR 1980, p. 21.
Lozovsky, I. R., Grinberga, R. I., Ermuisha, A. A.: Results of an epidemiological study of diseases of the kidney.Urol. Nefrol. (Mosk.),3, 3 (1977).
McGeown, M.: Chronic renal failure in Northern Ireland 1968–1970. A prospective survey.Lancet, 1, 307 (1972).
Nesson, H. R., Robbins, S. L.: Glomerulonephritis in older age groups.Arch. Intern. Med., 105, 23 (1960).
Pendreight, D. M., Howitt, L. E., Macdougal, A. Y. Robson, J. S., Hessman, M. A., Kennedy, A. C., MacLeod, M., Stewart, W. K.: Survey of chronic renal failure in Scotland.Lancet, 1, 304 (1972).
Precht, K., Buder, H. W., Schimmelpfennig, R., Briedigkeit, H.: Die klinische Pyelonephritis.Dtsch. Gesundheitswesen, 34, 111 (1979).
Sarre, H.: Chronische Glomerulonephritis. In: Nierenkrankheiten. Thieme, Stuttgart 1976, p. 295.
Tredt, H. J., Müller, K. H., Thiele, H. J., Lestin, H., Brasch, C., Seifert, A., Stotko, M.: Ergebnisse eines Nierenscreenings bei 16,000 Personen eines Landkreises.Dtsch. Gesundheitswesen, 25, 1323 (1970).
Tredt, H. J., Stolze, G., Prümers, K., Schwertz, G.: Territoriales Modell zur Früherkennung und Dispensairebetreuung chronischer Nierenkranker im Erwachsenen- und Kindesalter.Dtsch. Gesundheitswesen, 31, 1325 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryabov, S.I., Stavskaya, V.V. Epidemiology of chronic renal diseases. International Urology and Nephrology 15, 367–375 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02082557
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02082557