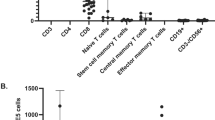
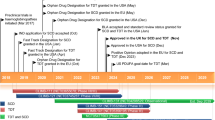
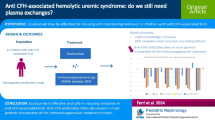
Summary
The management of pure red cell aplasia (PRCA) continues to challenge clinical investigators because the pathophysiology is heterogeneous and poorly understood. There are five treatment regimens that have established efficacy for patients with chronic PRCA. In patients with congenital hypoplastic anemia the best results have been reported using corticosteroids. Cyclosporine A is recommended as the treatment of choice in acquired PRCA. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy is highly effective in PRCA associated with parvovirus B19 infections and impaired IgG-antibody response. Treatment failures may be successfully managed with horse anti-human thymocyte globulin or cyclophosphamide plus corticosteroids. The potential of hematopoietic growth factors in the treatment of PRCA awaits further studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abkowitz J, Powell JS, Nakamura JM, Kadin M, Adamson JW (1986) Pure red cell aplasia: Response to therapy with antithymocyte globulin. Am J Hematol 23: 363–371
Belloy M, Morinet F, Blondin G, Courouce AM, Peyrol Y, Vilmer E (1990) Erythroid hypoplasia due to chronic infection with parvovirus B19. N Engl J Med 322: 633–642
Berkman SA, Lee ML, Gale RP (1988) Clinical use of intravenous immunoglobulins. Semin Hematol 25: 140–158
Berlin G, Liedén G (1986) Long-term remission of pure red cell aplasia after plasma exchange and lymphocytopheresis. Scand J Haematol 36: 121–122
Bierloy L, Wright R, Nienhuis AW, Young NS, Kaliner MA (1988) Antithymocyte globulin hypersensitivity in bone marrow failure patients. JAMA 260: 3164–3167
Chikkappa G, Pasquale D, Phillips PG, Mangan KF, Tsau MF (1987) Cyclosporine A for the treatment of pure red cell aplasia in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Am J Hematol 26: 179–189
Chikkappa G, Zarrabi MH, Tran MF (1986) Pure red cell aplasia in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Medicine 65: 339–351
Christen R, Morant R, Fehr J (1989) Cyclosporin A therapy of pure red cell aplasia in a patient with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Eur J Haematol 42: 303–307
Clark DA, Dessypris EN, Krantz SB (1984) Studies on pure red cell aplasia. XI. Results of immunosuppressive treatment of 37 patients. Blood 63: 277–280
Clauvel JP, Vainchenker W, Herrera A, Dellagik, Vinci G, Tabilio A, Lacombe C (1983) Treatment of pure red cell aplasia by high dose intravenous immunoglobulins. Br J Haematol 55: 380–382
Debusscher L, Paridaens R, Stryckmans P (1985) Cyclosporine for pure red cell aplasia. Blood 65: 249
Dessypris EN (1988) Pure red cell aplasia. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Diamond LK, Wang WC, Alter BP (1976) Congenital hypoplastic anemia. In: Schulman I (ed) Advances in pediatrics, vol 22. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, pp 349–378
Finlay JL, Toretsky J, Hoffman R, Bruno E, Shakidi NT (1984) Cyclosporine A in refractory aplastic anemia. Blood 64 [Suppl 1]: 104a (abstr)
Firkin TC, Maker D (1988) Cytotoxic immunosuppressive drug treatment strategy in pure red cell aplasia. Eur J Haematol 41: 212–217
Frickhofen N, Abkowitz J, King L, Astrow A, Halperin I, Young N (1989) Red cell aplasia due to persistent B19 parvovirus infection in HIV-infected patients and its treatment with immunoglobulin. Blood 74 [Suppl 1]: 44a (abstr)
Gratwohl A, Speck B, Osterwalder M, Corneo M, Nissen C (1983) Behandlung der Erythroaplasie (pure red cell aplasia) mit Antilymphozytenglobulin und kurzfristig hochdosiertem Prednison. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 113: 1480 (abstr)
Hagberg H, Nilsson P, Nisell J (1980) Treatment of pure red cell anemia with antilymphocyte globulin. Report of two cases. Scand J Haematol 24: 360–364
Halperin DS, Estrov Z, Freedman MH (1989) Diamond-Blackfan anemia: promotion of marrow erythropoiesis in vitro by recombinant interleukin-3. Blood 73: 1168–1174
Harris K, Kitamura T, Jacobs H, Winkelmann JC (1989) Pure red cell aplasia associated with an autoantibody specific for a membrane protein on red cell precursors. Blood 74 [Suppl 1]: 102a (abstr)
Hinterberger-Fischer M, Höcker P, Lechner K, Seewann H, Hinterberger W (1989) Oral cyclosporin A is effective treatment for untreated and also for previously immunosuppressed patients with severe bone marrow failure. Eur J Haematol 43: 136–142
Jacobs P, Wood L (1988) Pure red cell aplasia. Stable complete remission following antilymphocyte globulin administration. Eur J Haematol 40: 371–374
Kahan BD (1989) Drug therapy: cyclosporine. N Engl J Med 321: 1725–1738
Khelif A, Vau HV, Tremisi JP, Alfons F, Perrot D, Motin J, Viala JJ (1985) Remission of pure red cell aplasia following plasma exchange. Scand J Haematol 34: 13–15
Krantz SB (1972) Studies on pure red cell aplasia. III. Treatment with horse antihuman thymocyte gammaglobulin. Blood 39: 347–360
Kurtzman G, Frickhofen N, Kimball J, Jenkins DW, Nienhuis AW, Young NS (1989) Pure red cell aplasia of 10 years' duration due to persistent parvovirus B19 infection and its cure with immunoglobulin therapy. N Engl J Med 321: 519–523
Lacombe C, Casadevall N, Muller O, Varet B (1984) Erythroid progenitors in adult chronic pure red cell aplasia: Relationship of in vitro erythroid colonies to therapeutic response. Blood 64: 71–77
Leonard EM, Raefsky E, Griffith P, Kimball J, Nienhuis AW, Young NS (1989) Cyclosporine therapy of aplastic anemia, congenital and acquired red cell aplasia. Br J Haematol 72: 278–284
Mangan K, Shadduck RK (1984) Successful treatment of chronic refractory pure red cell aplasia with antithymocyte globulin: Correlation with in vitro erythroid culture studies. Am J Hematol 17: 417–426
Marimone G, Mombelloni P, Marini G, Ghio R, Roucoli B, Rossi G, Verzura P, Protto C (1981) Bone marrow erythroblastic recovery after plasmapheresis in acquired pure red cell aplasia. Haematologica 66: 796–802
Marmont A (1984) Is antilymphocytic globulin a better immunosuppressant than cyclophosphamide for pure red cell aplasia? Br J Haematol 56: 680–681
Marmont A, Peschle C, Sanguineti M, Condorelli M (1975) Pure red cell aplasia: response of three patients to cyclophosphamide and/or antilymphocyte globulin and demonstration of two types of serum IgG inhibitors to erythropoiesis. Blood 45: 247–261
McGuirre WA, Yank HH, Bruno E, Brandt J, Briddell R, Coates TD, Hoffman R (1987) Treatment of antibody-mediated pure red cell aplasia with high-dose intravenous gammaglobulin. N Engl J Med 317: 1004–1008
Means RT, Olsen NJ, Krantz SB, Graber SE, Dessypris EN, Stone WJ, Pincus TP, O'Neil V (1987) Treatment of the anemia of rheumatoid arthritis with recombinant human erythropoietin: clinical and in vitro results. Blood 70 [Suppl 1): 139 (abstr)
Messner HA, Fauser AA, Curtis JE, Ootten D (1981) Control of antibody-mediated pure red cell aplasia by plasmapheresis. N Engl J Med 304: 1334–1338
Mintzer D, Reilly R (1987) Pure red cell aplasia associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection: response to intravenous gammaglobulin. Blood 70 [Suppl 1]: 124a (abstr)
Needleman SW (1989) Durable remission of pure red cell aplasia after treatment with high-dose intravenous gammaglobulin and prednisone. Am J Hematol 32: 150–152
Peschle C, Marmont AM, Marone G, Genovese A, Sasso GF, Condorelli M (1975) Pure red cell aplasia: studies on an IgG serum inhibitor neutralizing erythropoietin. Br J Haematol 30: 411–417
Raghavachar A, Buck C, Heimpel H (1988) Cyclosporin A in B-CLL: Remission of pure red cell aplasia and reduction of the leukemic cell mass (abstr). XXII Congress ISH, abstract book, p 302
Raghavachar A, Heimpel H (1989) Cyclosporine A treatment in seven cases of pure red cell aplasia. Blut 59: 349 (abstr)
Seip M, Vidues J (1985) Cyclosporine A in a case of refractory severe aplastic anemia. Scand J Haematol 34: 228–230
Sieff C (1983) Pure red cell aplasia. Br J Haematol 54: 331–336
Tischler HJ, Leblanc S, Brune H, Welte K, Poliwoda H, Link H (1989) Recombinant human erythropoietin in treatment of pure red cell anemia. Blut 59: 340 (abstr)
Tötterman TH, Höglund M, Bengtsson M, Simonsson B, Almqvist D, Killander A (1989) Treatment of pure red cell aplasia and aplastic anemia with cyclosporin: long-term clinical effects. Eur J Haematol 42: 126–133
Tötterman TH, Nisell J, Killander A, Gahrton G, Lönqvist B (1984) Successful treatment of pure red cell aplasia with cyclosporin. Lancet II: 693
Tsai HP, Arkin S, Lipton JM (1989) An intrinsic progenitor defect in Diamond-Blackfan anemia. Br J Haematol 73: 112–120
Varet B, Picard F, Casadevall N, Dreyfus F, Muller O, Lacombe C (1987) Cyclosporin induced remission in two patients with B-CLL associated PRCA who were resistant to other immunosuppressive drugs. Blood 70 [Suppl 1]: 144a (abstr)
Zaentz SD, Krantz SB, Brown EB (1976) Studies on pure red cell aplasia. VIII. Maintenance therapy with immunosuppressive drugs. Br J Haematol 32: 47–54
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raghavachar, A. Pure red cell aplasia: Review of treatment and proposal for a treatment strategy. Blut 61, 47–51 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02076698
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02076698