Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to analyze whether the mode of embryo transfer (ZIFT vs IVF) affected the outcome in intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) cycles.
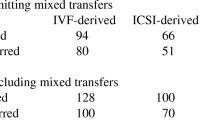
Methods and Results: Eighty-two ICSI cycles (42 ZIFT and 40 IVF) were analyzed. Several variables, including patient age and weight, numbers of mature eggs collected, injected, and fertilized, fertilization rate, number of fertilized eggs obtained per cycle, numbers of zygotes/embryos transferred, clinical pregnancy rate, and implantation rate, were compared. Mean patient age and weight were identical. The mean number of mature eggs collected and injected and fertilization rate were significantly higher in the ZIFT group, however, the mean numbers of zygotes/embryos transferred were identical. The clinical pregnancy and implantation rates in ZIFT cycles (52.3 and 23.2% respectively) were significantly higher than in IVF cycles (17.5 and 9.7%).
Conclusions: These data suggest that ZIFT is the more appropriate method for transfer of ICSI-derived embryos.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palermo G, Joris H, Devroey P, Van Steirteghem AC: Pregnancies after intracytoplasmic injection of single spermatozoon into an oocyte. Lancet 1993;340:17–18
Van Steirteghem AC, Nagy Z, Joris H, Liu J, Staessen C, Smitz J, Wisanto A, Devroey P: High fertilization and implantation rates after intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod 1993;8:1061–1066
Palermo GD, Cohen J, Alikani M, Adler A, Rosenwaks Z: Intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a novel treatment for all forms of male factor infertility. Fertil Steril 1995;63:1231–1240
Tucker MJ, Wright G, Morton PC, Mayer MP, Ingargiola PE, Jones AE: Practical evolution and application of direct intracytoplasmic sperm injection for male factor and idiopathic fertilization failure infertilities. Fertil Steril 1995;63:820–827
Svalander P, Forsberg A-S, Jakobsson A-H, Wikland M: Factors of importance for the establishment of a successful program of intracytoplasmic sperm injection treatment for male infertility. Fertil Steril 1995;63:828–837
Harari O, Bourne H, McDonald M, Richings N, Speirs AL, Johnston WIH, Baker HWG: Intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a major advance in the management of severe male subfertility. Fertil Steril 1995;64:360–368
Sherins RJ, Thorsall LP, Dorfmann A, Dennison-Lagos L, Calvo LP, Krysa L, Coulam CB, Schulman JD: Intracytoplasmic sperm injection facilitates fertilization even in the most severe forms of male infertility: pregnancy outcome correlates with maternal age and number of eggs available Fertil Steril 1995;64:369–375
Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology, American Society for Reproductive Medicine: Assisted reproductive technology in the United States and Canada: 1993 results generated from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine/Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology Registry. Fertil Steril 1995;64:13–21
American Fertility Society, Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology: Assisted reproductive technology in the United States and Canada: 1992 results generated from the American Fertility Society/Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology Registry. Fertil Steril 1994;62:1121–1128
Hammitt DG, Syrop CH, Hahn SJ, Walker DI, Butkowski CR, Donovan JF: Comparison of concurrent pregnancy rates for in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer, pronuclear stage embryo transfer and gamete intra-Fallopian transfer. Human Reprod 1990;5:947–954
Van Voorhis BJ, Syrop CH, Vincent Jr RD, Chestnut DH, Sparks AET, Chapler FK: Tubal versus uterine transfer of cryopreserved embryos: A prospective randomized trial. Fertil Steril 1994;63:578–583
Tournaye H, Devroey P, Camus M, Vanvalkenburg M, Bollen N, Van Steirteghem AC: Zygote intrafallopian transfer or in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer for the treatment of male-factor infertility: A prospective randomized trial. Fertil Steril 1992;58:344–350
Fluker MR, Zouves CG, Bebbington MW: A prospective randomized comparison of zygote intrafallopian transfer and in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer for nontubal factor infertility. Fertil Steril 1993;60:515–519
Kruger TF, Acosta AA, Simmons KF, Swanson RJ, Matta JF, Oeninger S: Predictive value of abnormal sperm morphology in in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril 1988;49:112–117
Atiee SH, Pool TB, Martin JE: A simplified approach to intracytoplasmic sperm injection Fertil Steril 1995;63:652–655
Abdelmassih R, Sollia S, Moretto M, Acosta AA: Female age is an important parameter to predict treatment outcome in intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil Steril 1995;65:573–577
Alikani M, Palermo G, Adler A, Bertoli M, Blake M, Cohen J: Intracytoplasmic sperm injection in dysmorphic human oocytes. Zygote 1995;3:283–288
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boldt, J., Schnarr, P., Ajamie, A. et al. Success rates following intracytoplasmic sperm injection are improved by using ZIFT vs IVF for embryo transfer. J Assist Reprod Genet 13, 782–785 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02066498
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02066498