Abstract
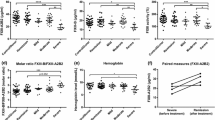
Serum concentrations of immunoreactive von Willebrand factor (vWF) and soluble thrombomodulin (TM), and vWF multimer patterns were measured to assess endothelial function in patients with inflammatory intestinal diseases. In Crohn's disease and acute infective diarrhea, vWF concentrations were significantly higher than in normal controls. In all patient groups, multimeric analysis of vWF and the concentration of serum TM were not different from normal controls. The results indicate alteration of endothelial function in inflammatory intestinal disorders. They may be compatible with the presence of localized vasculitis, but indicate that systemic endothelial destruction does not occur in inflammatory bowel disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lockhart-Mummery HE, Morson BC: Crohn's disease (regional enteritis) of the large intestine and its distinction from ulcerative colitis. Gut 1:87–105, 1960
McGovern VJ, Goulston SJM: Crohn's disease of the colon. Gut 9:164–176, 1968
Van Patter WN, Bargen JA, Dockerty MB, Feldman WH, Wayo CW, Waugh JM: Regional enteritis. Gastroenterology 26:347–450, 1954
Knutson H, Lunderquist A, Lunderquist A: Vascular changes in Crohn's disease. Am J Roentgenol 103:380–385, 1968
Geller SA, Cohen A: Arterial inflammatory infiltration in Crohn's disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med 107:473–475, 1983
Wakefield AJ, Sawyerr AM, Dhillon AP, Pittilo RM, Rowles PM, Lewis AAM, Pounder RE: Pathogenesis of Crohn's disease; multifocal gastrointestinal infarction. Lancet 2:1057–1062, 1989
Wakefield AJ, Dhillon AP, Sankey EA, Sawyerr AM, More L, Sim R, Pittilo RM, Rowles PM, Hudson M, Lewis AAM, Pounder RE: Granulomatous vasculitis in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 100:1279–1287, 1991
Ginsburg D: The von Willebrand factor gene and genetics of von Willebrand's disease. Mayo Clin Proc 66:506–515, 1991
Woolf AD, Wakerly G, Wallington TB, Scott DGI, Dieppe PA: Factor VIII related antigen in the assessment of vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 46:441–447, 1987
Federici AB, Fox RI, Espinoza LR, Zimmerman TS: Elevation of von Willebrand factor is independent of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and persists after glucocorticoid treatment in giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 27:1046–1049, 1984
Bern MM, Cassani MP, Horton J, Rand L, Davis G: Changes of fibrinolysis and factor VIII coagulant, antigen and ristocetin cofactor in diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. Thromb Res 19:831–839, 1980
Maruyama I, Bell CE, Majerus PW: Thrombomodulin found on endothelium of arteries veins, capillaries and lymphatics, and on syncytiotrophoblas of human placenta. J Cell Biol 101:363–371, 1985
Ishii H, Majerus PW: Thrombomodulin is present in human plasma and urine. J Clin Invest 76:2178–2181, 1985
Iwashima Y, Sato T, Watanabe K, Ooshima E, Hiraishi S, Ishii H, Kazama M, Makino I: Elevation of plasma thrombomodulin level in diabetic patients with early diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 39:983–988, 1990
Wada H, Ohiwa M, Kaneko T, Tamaki S, Tanigawa M, Shirakawa S, Koyama M, Hayashi T, Suzuki K: Plasma thrombomodulin as a marker of vascular disorders in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Am J Hematol 39:20–24, 1992
Hay CRM, Hay EM, Holt PJL, Kamiguti-Yamaga A, Patterson DA, Tomura H: Soluble thrombomodulin reflects vascular injury in vasculitis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Haematol Supplement:8, 1992
Short PE, Williams CE, Picken AM, Hill FGH: Factor VIII related antigen: An improved enzyme immunoassay. Med Lab Sci 39:351–355, 1982
Kodama S, Uchijima E, Nagai M, Mikawatani K, Hayashi T, Suzuki K: One-step sandwich enzyme immunoassay for soluble thrombomodulin using monoclonal antibodies. Clin Chem Acta 192:191–199, 1990
Ruggeri ZM, Zimmerman TS: Variant von Willebrand's disease. Characterization of two subtypes by analysis of multimeric composition of factor VIII/von Willebrand factor in plasma and platelets. J Clin Invest 65:1318–1325, 1980
Harvey RF, Bradshaw JM: A simple index of Crohn's disease activity. Lancet 1:514, 1980
Zielen S, Bender SW, Kreuz W, Posselt HG, Solem E, Scharrer I: Crohn's disease activity: assessment by factor VIII coagulation proteins. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 4:730–734, 1985
Stevens TRJ, James JP, McCarthy DA, Simmonds NJ, Maddison PJ, Rampton DS: Von Willebrand protein in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 33:502–506, 1992
Pottinger BE, Read RC, Paleolog EM, Higgins PG, Pearson JD: Von Willebrand factor is an acute phase reactant in man. Thromb Res 53:387–394, 1989
Lombardi R, Mannucci PM, Seghatchian MJ, Vincente-Garcia V, Coppola R: Alterations of factor VII von Willebrand factor in clinical conditions associated with an increase in its plasma concentration. Br J Haematol 49:61–68, 1981
Sawyerr AM, Smith MS, Chitolie A, Wakefield AJ, Pounder RE: Von Willebrand factor antigen and vasculitis in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 33:S24, 1992
Giddings JC, Shall L: Enhanced release of von Willebrand factor by human endothelial cells in culture in the presence of phorbol myristate acetate and interleukin 1. Thromb Res 47:259–267, 1987
Zavoico GB, Ewenstein BM, Schafter AI, Pober JS. IL-1 and related cytokines enhance thrombin stimulated PGI2 production in cultured endothelial cells without affecting thrombin-stimulated von Willebrand factor secretion or platelet-activating factor biosynthesis. J Immunol 142:3993–3999, 1989
De Groot PG, Verweij CL, Nawroth PP, De Boer HC, Stern DM, Sixma JJ: Interleukin 1 inhibits the release of von Willebrand factor in endothelial cells which results in a decreased reactivity of their matrix towards platelets. Atherosclerosis 7:605–611, 1987
Paleolog EM, Crossman DC, McVey JH, Pearson JD: Differential regulation by cytokines of constitutive and stimulated secretion of von Willebrand factor from endothelial cells. Blood 75:688–695, 1990
Gralnick HR, McKeown LP, Wilson OM, Williams SB, Elin RJ: Von Willebrand factor release induced by endotoxin. J Lab Clin Med 113:118–122, 1989
Sporn LA, Marder VJ, Wagner DD: Inducible secretion of large biologically potent von Willebrand factor multimers. Cell 46:185–190, 1986
Ewenstein BM, Warhol MH, Handin RI, Pober JS: Composition of the von Willebrand factor storage organelle (Weibel-Palade body) isolated from cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 104:1423–1433, 1987
Hattori R, Hamilton KK, Fugates RD, McEver RP, Sims PJ: Stimulated secretion of endothelial von Willebrand factor is accompanied by rapid redistribution to the cell surface of the intracellular granule membrane protein GMP-140. J Biol Chem 264:7768–7771, 1989
Takano S, Kimura S, Ohdama S, Aoki N: Plasma thrombomodulin in health and disease. Blood 76:2024–2029, 1990
Nawroth PP, Stern DM: Modulation of endothelial haemostatic properties by tumour necrosis factor. J Exp Med 163:740–745, 1986
Nawroth PP, Handley DA, Esmon CT, Stern DM. Interleukin-1 induces endothelial procoagulant activity while suppressing cell surface anticoagulant activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:3460–3464, 1986
Hamilton KK, Hattori R, Esmon CT, Sims PJ: Complement proteins C5b-9 induce vesiculation of the endothelial plasma membrane and expose catalytic surface for assembly of the prothrombinase enzyme complex. J Biol Chem 265:3809–3814, 1990
Ishii H, Uchiyama H, Kazama M: Soluble thrombomodulin antigen in conditioned medium is increased by damage of endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost 65:618–623, 1991
Kamiguti AS, Rugman FP, Theakston RDG, Franca FOS, Ishii H, Hay CRM, BIASG: The role of venom haemorrhagin in spontaneous bleeding inBothrops jararaca envenoming. Thromb Haemost 67:484–488, 1992
Wellmann W, Fink PC, Benner F, Schmidt FW: Endotoxaemia in active Crohn's disease. Treatment with whole gut irrigation and 5-aminosalicylic acid. Gut 27:814–820, 1986
Moore KL, Andreoli SP, Esmon NL, Bang NU: Endotoxin enhances tissue factor and suppresses thrombomodulin expression of human vascular endotheliumin vitro. J Clin Invest 79:124–130, 1987
Halstensen TS, Mollnes TE, Fausa O, Brandtzaeg P: Deposits of terminal complement complex (TCC) in the muscularis mucosae and submucosal vessels in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease of the colon. Gut 30:361–366, 1989
Hattori R, Hamilton KK, McEver RP, Sims PJ: Complement proteins C5b-9 induce secretion of high molecular weight multimers of endothelial von Willebrand factor and translocation of granule membrane protein GMP-140 to the cell surface. J Biol Chem 264:9053–9060, 1989
Ribes JA, Francis CW, Wagner DD: Fibrin induces release of von Willebrand factor from endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 79:117–123, 1987
Edwards RL, Levine JB, Green R, Duffy M, Matthews E, Brande W, Rickles FR: Activation of blood coagulation in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology 92:329–337, 1987
Hudson M, Hutton RA, Wakefield AJ, Sawyerr AM, Pounder RE. Evidence for activation of coagulation in Crohn's disease. Blood Coag Fibrinol 3:773–778, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawyerr, A.M., Smith, M.S., Hall, A. et al. Serum concentrations of von Willebrand factor and soluble thrombomodulin indicate alteration of endothelial function in inflammatory bowel diseases. Digest Dis Sci 40, 793–799 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02064981
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02064981