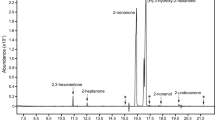
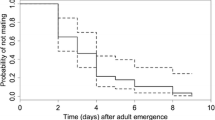
Abstract
AdultMaladera matrida Argaman (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Melolonthinae) males emerge from soil for an active period at dusk, a few minutes before the females. Adults are found during most of the active hours on the foliage in aggregations composed of an equal sex ratio. The mechanism of aggregation behavior ofM. matrida beetles was studied in a Y-shaped olfactometer. No evidence was found for the existence of an aggregation pheromone released either by males or by females, but behavior tests indicate that adultM. matrida beetles, males as well as females, are attracted to volatiles of an injured host plant. The following scenario is suggested: Males emerge daily from soil at dusk, a few minutes before the females, and immediately start feeding. Additional males are attracted to the injured host's volatiles and form aggregations. When females emerge from soil, the attractant volatiles are concentrated in spots, and the females join the aggregations, forming an equal sex ratio.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcock, J. 1982. Natural selection and communication among bark beetles.Fla. Entomol. 65:17–32.
Anonymous. 1991. Keep outdoor light off to discourage rust beetles.The Arabian Sun XLVII (37), September 25, 1991 p. 5, Saudi Aramco Public Affairs (Pub.), Dhahran, Saudi Arabia.
Argaman, Q. 1986.Maladera matrida—a new scarabaeid in Israel.Shapirit 4:41–46 (in Hebrew).
Argaman, Q. 1990. Redescription ofMaladera matrida (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Melolonthinae).Isr. J. Entomol. 24:21–27.
Bailey, W.J. 1991. Mate finding: selection on sensory cues, pp. 42–74,in W.J. Bailey and J. Ridsdill-Smith (eds.). Reproductive Behavior of Insects, Individuals and Populations, Chapman & Hall, London.
Bartelt, R.J., Dowd, P.F., Plattner, R.D., andWeisleder, D. 1990a. Aggregation pheromone of driedfruit beetle,Carpophilus hemipterus. Wind-tunnel bioassay and identification of two novel tetraene hydrocarbons.J. Chem. Ecol. 16:1015–1039.
Bartelt, R.J., Dowd, P.F., Shorey, H.H., andWeisleder, R. 1990b. Aggregation pheromone ofCarpophilus freemani (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae): A blend of conjugated triene and tetraene hydrocarbons.Chemoecology 1:105–113.
Dolinski, M.G., andLoschiavo, S.R. 1973. The effect of fungi and moisture on the locomotory behavior of the rusty grain beetle,Cryptolestes ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Cucujidae).Can. Entomol. 105:485–490.
Domek, J.M., andJohnson, D.T. 1988. Demonstration of semiochemically induced aggregation in the green June beetle,Cotinis nitida (L.) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae).Environ. Entomol. 17:147–149.
Domek, J.M., andJohnson, D.T. 1990. Inhibition of aggregation behavior in the green June beetle (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) by antibiotic treatment of food substrate.Environ. Entomol. 19:995–1000.
Dowd, P.F., andBartelt, R.J. 1991. Host-derived volatiles as attractants and pheromone synergists for driedfruit beetle,Carpophilus hemipterus.J. Chem. Ecol. 17:285–308.
Eisner, T., andMeinwald, J. 1987. Alkaloid-derived pheromones and sexual selection in Lepidoptera, pp. 251–269,in G.D. Prestwich and G.J. Blomquist (eds.). Pheromone Biochemistry. Academic Press, Orlando, Florida.
Gol'berg, A.M., Yathom, S., Almogi-Labin, A., andFridland-Wunder, G. 1989. Diurnal and seasonal occurrence, feeding habits and mating behavior ofMaladera matrida adults in Israel.Phytoparasitica 17:81–89.
Kard, B.M.R., andHaim, F.P. 1990. Flight patterns and white grub population densities of three beetle species (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) in the mountains of northwestern North Carolina.J. Entomol. Sci. 25:34–43.
Klein, Z.I., andChen, C. 1983. Interceptions and introductions of new pests in Israel.Phytoparasitica 11:124 (abstract).
Knope, J.A.E., andPitman, G.B. 1972. Aggregation pheromone for manipulation of the Douglasfir beetle.J. Econ. Entomol. 65:723–726.
Ladd, T.L. 1970. Sex attraction in the Japanese bettle.J. Econ. Entomol. 63:340–344.
Lin, H., Phelan, P.L., andBartelt, R.J. 1992. Synergism between synthetic food odors and the aggregation pheromone for attractingCarpophilus lugubris in the field (Coleoptera: Nitidulidae).Environ. Entomol. 21:156–159.
Peng, C., andWeiss, M.J. 1992. Evidence of an aggregation pheromone in the flea bettle,Phyllotreta cruciferae (Goeze) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae).J. Chem. Ecol. 18:875–884.
Phillips, J.K., andBurkholder, W.E. 1981. Evidence for a male-produced aggregation pheromone in the rice weevil.J. Econ. Entomol. 74:539–542.
Potter, D.A. 1980. Flight activity and sex attraction of northern and southern masked chafers in Kentucky.Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 73:414–417.
Shorey, H.H. 1973. Behavioral response to insect pheromones.Annu. Rev. Entomol. 18:349–380.
Sokal, R.R., andRohlf, F.J. 1969. Biometry. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco, 776 pp.
Trematerra, P., andGiragenti, P. 1989. Influence of pheromone and food attractants on trapping ofSitophilus oryzae (L.) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): A new trap.J. Appl. Entomol. 108:12–20.
Visser, J.H. 1986. Host odor perception in phytophagous insects.Annu. Rev. Entomol. 31:121–144.
Walgenbach, C.A., Burkholder, W.E., Curtis, M.J., andKhan, Z.A. 1987. Laboratory trapping studies withSitophilus zeamais (Coleoptera: Curculionidae).J. Econ. Entomol. 80:763–767.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harari, A.R., Ben-Yakir, D. & Rosen, D. Mechanism of aggregation behavior inMaladera matrida Argaman (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). J Chem Ecol 20, 361–371 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02064443
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02064443