Abstract
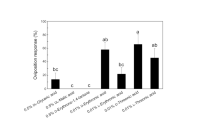
Oviposition responses ofPieris rapae andP. napi oleracea to 18 cardenolides were compared under the same conditions. Effects of different concentrations of selected cardenolides were also tested. Most of the compounds were deterrent to oviposition by both insects, but to significantly different degrees.P. rapae were strongly deterred by K-strophanthoside, K-strophanthin-β, cymarin, convallatoxin, oleandrin, erysimoside, erychroside, and gitoxigenin. The most deterrent compounds forP. napi oleracea were erychroside, cymarin, erysimoside, convallatoxin, and K-strophanthoside. Strophanthidin-based glycosides were more deterrent than digitoxigenin-based ones, and the number and type of sugar substitutions can have profound effects on activity. Both similarities and contrasts were found in responses ofP. rapae andP. napi oleracea to these cardenolides. Cymarin was equally deterrent to bothPieris species at all concentrations tested. However, when compared withP. rapae, P. napi oleracea was less sensitive to most of the cardenolides.P. napi oleracea was insensitive to K-strophanthin-β and oleandrin at 0.5 × 10−4 M, which were highly deterrent toP. rapae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brower, L.P. 1970. Plant poisons in a terrestrial food chain and implications for mimicry theory, pp. 69–82,in K.L. Chambers (ed.). Proceedings of the 29th Annual Biological Colloquium, 1968, Biochemical Coevolution. Oregon State University Press, Corvallis.
Dethier, V.G. 1982. Mechanisms of host-plant recognition.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 31:49–56.
Dimock, M.B., andRenwick, J.A.A. 1991. Oviposition by field populations ofPieris rapae (Lepidoptera: Pieridae) deterred by an extract of a wild crucifer.Environ. Entomol. 20:802–806.
Duffey, S.S., Blum, M.S., Isman, M.B., andScudder, G.G.E. 1978. Cardiac glycosides: A physical system for their sequestration by the milkweed bug.J. Insect Physiol. 24:639–645.
Huang, X.P., andRenwick, J.A.A. 1994. Relative activities of glucosinolates as oviposition stimulants forPieris rapae andP. napi oleracea.J. Chem. Ecol. 20:1025–1037.
Huang, X.P., Renwick, J.A.A., andSachdev-Gupta, K. 1993a. A chemical basis for differential acceptance ofErysimum cheiranthoides by twoPieris species.J. Chem. Ecol. 19:195–210.
Huang, X.P., Renwick, J.A.A., andSachdev-Gupta, K. 1993b. Oviposition stimulants and deterrents regulating differential acceptance ofIberis amara byPieris rapae andP. napi oleracea.J. Chem. Ecol. 19:1645–1663.
Huang, X.P., Renwick, J.A.A., andSachdev-Gupta, K. 1994. Oviposition stimulants inBarbarea vulgaris forPieris rapae andP. napi oleracea: Isolation, identification and differential activity.J. Chem. Ecol. 20:423–438.
Jermy, T. 1983. Multiplicity of insect antifeedants in plants, pp. 223–236,in D.L. Whitehead and W.S. Bowers (eds.). Natural Products for Innovative Pest Control. Pergamon Press, New York.
Jermy, T., andSzentesi, A. 1978. The role of inhibitory stimuli in the choice of oviposition site be phytophagous insects.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 24:458–471.
Malcolm, S.B. 1992. Cardenolide-mediated interactions between plants and herbivores, pp. 215–296,in M.R. Berenbaum and G.A. Rosenthal (eds.). Herbivores: Their Interaction with Secondary Plant Metabolites, 2nd ed., Vol. 2. Academic Press, New York.
Nelson, C.J., Seiber, J.N., andBrower, L.P. 1981. Seasonal and intraplant variation of cardenolide content in the California milkweed,Asclepias eriocarpa, and implications for plant defense.J. Chem. Ecol. 7:981–1010.
Oyeyele, S.O., andZalucki, M.P. 1990. Cardiac glycosides and oviposition byDanaus plexippus onAsclepias fructicosa in southeast Queensland (Australia), with notes on the effect of plant nitrogen content.Ecol. Entomol. 15:177–185.
Renwick, J.A.A., 1983. Nonpreference mechanisms: Plant characteristics influencing insect behavior. pp. 199–213,in P.A. Hedin (ed.). Plant Resistance to Insects, ACS Symposium Series No. 208. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C.
Renwick, J.A.A., andHuang, X.P. 1994. Interacting chemical stimuli mediating oviposition by Lepidoptera,in T.N. Ananthakrishnan (ed.). Functional Dynamics of Phytophagous Insects. Oxford & IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi. In press.
Renwick, J.A.A., andRadke, C.D. 1987. Chemical stimulants and deterrents regulating acceptance or rejection of crucifers by cabbage butterflies.J. Chem. Ecol. 13:1771–1776.
Renwick, J.A.A., andRadke, C.D. 1990. Plant constituents mediating oviposition by the diamondback moth,Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae).Phytophaga 3:37–46.
Renwick, J.A.A., Radke, C.D., andSachdev-Gupta, K. 1989. Chemical constituents ofErysimum cheiranthoides deterring oviposition by the cabbage butterfly,Pieris rapae.J. Chem. Ecol. 15:2161–2169.
Roeske, C.N., Seiber, J.N., Brower, L.P., andMoffitt, C.M. 1976. Milkweed cardenolides and their comparative processing by monarch butterflies (Danaus plexippus).Recent Adv. Phytochem. 10:93–167.
Rothschild, M. 1972. Secondary plant substances and warning colouration in insects, pp. 59–83,in H.F. van Emden (ed.). Insect/Plant Relationships. Symposium of the Royal Entomology Society, London, No. 6.
Sachdev-Gupta, K., Renwick, J.A.A., andRadke, C.D. 1990. Isolation and identification of oviposition deterrents to cabbage butterfly,Pieris rapae, fromErysimum cheiranthoides.J. Chem. Ecol. 16:1059–1067.
Sachdev-Gupta, K., Radke, C.D., Renwick, J.A.A., andDimock, M.B. 1993. Cardenolides fromErysimum cheiranthoides: Feeding deterrents toPieris rapae larvae.J. Chem. Ecol. 19:1355–1369.
Schultz, J.C. 1988. Many factors influence the evolution of herbivore diets, but plant chemistry is central.Ecology 69:896–897.
Seiber, J.N., Tuskes, P.M., Brower, L.P., andNelson, C.J. 1980. Pharmacodynamics of some individual milkweed cardenolides fed to larvae of the monarch butterfly.J. Chem. Ecol. 6:321–399.
Zalucki, M.P., Brower, L.P., andMalcolm, S.B. 1990. Oviposition byDanaus plexippus in relation to cardenolide content of threeAsclepias species in the southeastern U.S.A.Ecol. Entomol. 15:231–240.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Renwick, J.A.A. Cardenolides as oviposition deterrents to twoPieris species: Structure-activity relationships. J Chem Ecol 20, 1039–1051 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02059740
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02059740