Abstract
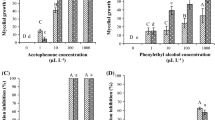
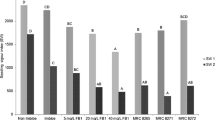
Aflatoxin B1, crude aflatoxins and palmotoxins B0 and G0 were tested for seed germination and chlorophyll formation using the cowpea. It was found that aflatoxin B and crude aflatoxins inhibited both chlorophyll formation and seed germination and palmotoxins inhibited these processes to a lesser extent. 3 — Indolylacetic acid reduced the inhibitory effects of the aflatoxins in seed germination and chlorophyll formation in the cowpea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koehler, B. &Woodworth, C. M. (1938). Corn-seedling virescence caused byAspergillus flavus andAspergillus tamarii.Phytopathol. 28:811–823.
Schoental, R. (1965) Aflatoxins and “albinism” in plants.Nature 205:57–58.
Ryan, G. F., Greenblatt, G. &Al-Delaimy, K. A. (1961) Seedling albinism induced by an extract ofAlternaria tenuis.Science 134:833–834.
Bassir, O. &Adekunle, A. A. (1968) Two new metabolites ofAspergillus flavus (Link).Febs Letters 2:23–25.
Leonard, L. T. (1968) To be or not to be. United States Department of Agriculture.Circular 703:14 pp.
Arnon, D. I. (1938) Microelements in culture solution experiments with higher plants.Amer. J. Botany 24:322–325.
Staff of the Cunningham Laboratory C. S. I.R.O., Australia, (1958) Some concepts and methods in sub-tropical pasture research. Reprint, 242 pp.
Osborne, D. J. &McCalla, D. R. (1961) Rapid bioassay for kinetin and alkins using senescing leaf tissue.Plant physiol. 36:219–221.
Bennet, E. L. &Bonner, J. (1953) Isolation of plant growth inhibitors fromThamnosama montana.Amer. J. Botany 40:29–33.
Reinhold, L. &Powell, R. G. (1956) A stimulatory action of Indoyl-3-acetic acid on the uptake of amino acids by plant cells.Nature 177:658–659.
Keyl, A. C., Booth, A. N., Mastri, M. S., Gumbmann, M. R. &Gagne, W. E. (1968) Chronic effects of aflatoxin in farm animal feeding studies. Proceedings of the First United States — Japan Conference on toxic micro-organisms.
Semeniuk, G., Harshifield, G. S., Carlson, C. W., Hesseltine, C. W. &Kwolek, W. F. (1968) Occurrence of mycotoxins inAspergillus. Proceedings of the First United States — Japan Conference on toxic micro-organims.
Clifford, J. &Rees, K. R. (1967) The interaction of aflatoxins with purine and purine nucleosides.Biochem. J. 103:467–471.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adekunle, A.A., Bassir, O. The effects of aflatoxin B1 and palmotoxins B0 and G0 on the germination and leaf colour of the cowpea (vigna sinensis). Mycopathologia et Mycologia Applicata 51, 299–305 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02057800
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02057800