Abstract
The chemical composition of a completely defined culture medium for the growth of strains ofCardiobacterium hominis is described.
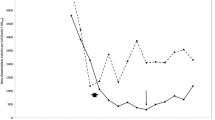
Riboflavin and flavin mononucleotide at low concentrations completely inhibit the growth response ofC. hominis. Only leucine, among a wide variety of substrates tested, prevents this toxicity over a range of riboflavin or flavin mononucleotide levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monod, J., Changeux, J.-P. andJacob, F. 1963. Allosteric proteins and cellular control systems. J. Mol. Biol.6: 306–329.
Slotnick, I. J. andDougherty, M. 1964. Further characterization of an unclassified group of bacteria causing endocarditis in man:Cardiobacterium hominis gen. et sp. n. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek30: 261–272.
Tucker, D. N., Slotnick, I. J., King, E. O., Tynes, B., Nicholson, J. andCrevasse, L. 1962. Endocarditis caused by aPasteurella-like organism. Report of four cases. New England J. Med.267: 913–916.
Woolley, D. W. 1952. A study of antimetabolites. John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slotnick, I.J., Dougherty, M. Unusual toxicity of riboflavin and flavin mononucleotide forCardiobacterium hominis . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 31, 355–360 (1965). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02045915
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02045915